Main Content

-

- ABOUT
- REFERENCES
-
APPENDICES
- A: Abbreviations
- B: International Organizations and Groups
- C: Selected International Environmental Agreements
- D: Cross-Reference List of Country Data Codes
- E: Cross-Reference List of Hydrographic Data Codes
- F: Cross-Reference List of Geographic Names
- G: Weights and Measures
- H: Strategic Materials
- T: Terrorist Organizations
- FAQs
- CONTACT
- THE WORLD FACTBOOK ARCHIVE

note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia
-
Jump to topic
- Introduction
-
Geography
- Area
- Area - comparative
- Climate
- Coastline
- Elevation
- Environment - current issues
- Environment - international agreements
- Geographic coordinates
- Geography - note
- Irrigated land
- Land boundaries
- Land use
- Location
- Map references
- Maritime claims
- Natural hazards
- Natural resources
- Population distribution
- Terrain
-
People and Society
- Age structure
- Birth rate
- Children under the age of 5 years underweight
- Contraceptive prevalence rate
- Current Health Expenditure
- Death rate
- Demographic profile
- Dependency ratios
- Drinking water source
- Education expenditures
- Ethnic groups
- HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
- HIV/AIDS - deaths
- HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
- Hospital bed density
- Infant mortality rate
- Languages
- Life expectancy at birth
- Literacy
- Major infectious diseases
- Major urban areas - population
- Maternal mortality rate
- Median age
- Mother's mean age at first birth
- Nationality
- Net migration rate
- Obesity - adult prevalence rate
- Physicians density
- Population
- Population distribution
- Population growth rate
- Religions
- Sanitation facility access
- School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- Sex ratio
- Total fertility rate
- Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
- Urbanization
-
Government
- Administrative divisions
- Capital
- Citizenship
- Constitution
- Country name
- Diplomatic representation from the US
- Diplomatic representation in the US
- Executive branch
- Flag description
- Government type
- Independence
- International law organization participation
- International organization participation
- Judicial branch
- Legal system
- Legislative branch
- National anthem
- National holiday
- National symbol(s)
- Political parties and leaders
- Suffrage
-
Economy
- Agriculture - products
- Budget
- Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)
- Current account balance
- Debt - external
- Ease of Doing Business Index scores
- Economic overview
- Exchange rates
- Exports
- Exports - commodities
- Exports - partners
- Fiscal year
- GDP - composition, by end use
- GDP - composition, by sector of origin
- GDP - per capita (PPP)
- GDP (official exchange rate)
- GDP (purchasing power parity) - real
- GDP real growth rate
- Gross national saving
- Household income or consumption by percentage share
- Imports
- Imports - commodities
- Imports - partners
- Industrial production growth rate
- Industries
- Inflation rate (consumer prices)
- Labor force
- Labor force - by occupation
- Population below poverty line
- Public debt
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
- Taxes and other revenues
- Unemployment rate
-
Energy
- Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy
- Crude oil - exports
- Crude oil - imports
- Crude oil - production
- Crude oil - proved reserves
- Electricity - consumption
- Electricity - exports
- Electricity - from fossil fuels
- Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
- Electricity - from nuclear fuels
- Electricity - from other renewable sources
- Electricity - imports
- Electricity - installed generating capacity
- Electricity - production
- Electricity access
- Natural gas - consumption
- Natural gas - exports
- Natural gas - imports
- Natural gas - production
- Natural gas - proved reserves
- Refined petroleum products - consumption
- Refined petroleum products - exports
- Refined petroleum products - imports
- Refined petroleum products - production
- Communications
- Transportation
- Military and Security
- Transnational Issues
-
Introduction :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
Background: This entry usually highlights major historic events and current issues and may include a statement about one or two key future trends.

Portugal discovered and colonized the uninhabited islands in the late 15th century, setting up a sugar-based economy that gave way to coffee and cocoa in the 19th century - all grown with African plantation slave labor, a form of which lingered into the 20th century. While independence was achieved in 1975, democratic reforms were not instituted until the late 1980s. The country held its first free elections in 1991, but frequent internal wrangling between the various political parties precipitated repeated changes in leadership and four failed, non-violent coup attempts in 1995, 1998, 2003, and 2009. In 2012, three opposition parties combined in a no confidence vote to bring down the majority government of former Prime Minister Patrice TROVOADA, but in 2014, legislative elections returned him to the office. President Evaristo CARVALHO, of the same political party as Prime Minister TROVOADA, was elected in September 2016, marking a rare instance in which the positions of president and prime minister are held by the same party. Prime Minister TROVOADA resigned at the end of 2018 and was replaced by Jorge BOM JESUS. New oil discoveries in the Gulf of Guinea may attract increased attention to the small island nation.
-
Geography :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
Location: This entry identifies the country's regional location, neighboring countries, and adjacent bodies of water.
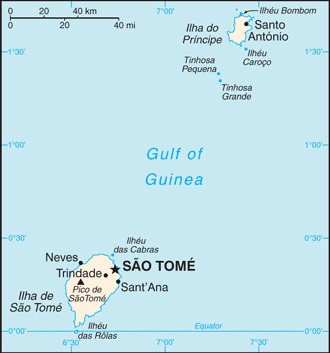
 Central Africa, islands in the Gulf of Guinea, just north of the Equator, west of GabonGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names.
Central Africa, islands in the Gulf of Guinea, just north of the Equator, west of GabonGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names. 1 00 N, 7 00 EMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries.
1 00 N, 7 00 EMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries. AfricaArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines.
AfricaArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres).
Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres). more than five times the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ.
more than five times the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ. 0 kmCoastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea.
0 kmCoastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea. 209 kmMaritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more
209 kmMaritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmmeasured from claimed archipelagic baselinesClimate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more
territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmmeasured from claimed archipelagic baselinesClimate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more tropical; hot, humid; one rainy season (October to May)Terrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography.
tropical; hot, humid; one rainy season (October to May)Terrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography. volcanic, mountainousElevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point.
volcanic, mountainousElevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point. lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Pico de Sao Tome 2,024 mNatural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future.
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Pico de Sao Tome 2,024 mNatural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future. fish, hydropowerLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more
fish, hydropowerLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more agricultural land: 50.7% (2011 est.)arable land: 9.1% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 40.6% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 1% (2011 est.)forest: 28.1% (2011 est.)other: 21.2% (2011 est.)Irrigated land: This entry gives the number of square kilometers of land area that is artificially supplied with water.
agricultural land: 50.7% (2011 est.)arable land: 9.1% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 40.6% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 1% (2011 est.)forest: 28.1% (2011 est.)other: 21.2% (2011 est.)Irrigated land: This entry gives the number of square kilometers of land area that is artificially supplied with water. 100 sq km (2012)Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures.
100 sq km (2012)Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures. Sao Tome, the capital city, has roughly a quarter of the nation's population; Santo Antonio is the largest town on Principe; the northern areas of both islands have the highest population densities as shown in this population distribution mapNatural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes.
Sao Tome, the capital city, has roughly a quarter of the nation's population; Santo Antonio is the largest town on Principe; the northern areas of both islands have the highest population densities as shown in this population distribution mapNatural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes. floodingEnvironment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more
floodingEnvironment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more deforestation and illegal logging; soil erosion and exhaustion; inadequate sewage treatment in cities; biodiversity preservationEnvironment - international agreements: This entry separates country participation in international environmental agreements into two levels - party to and signed, but not ratified. Agreements are listed in alphabetical order by the abbreviated form of the full name.
deforestation and illegal logging; soil erosion and exhaustion; inadequate sewage treatment in cities; biodiversity preservationEnvironment - international agreements: This entry separates country participation in international environmental agreements into two levels - party to and signed, but not ratified. Agreements are listed in alphabetical order by the abbreviated form of the full name. party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere.
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere. the second-smallest African country (after the Seychelles); the two main islands form part of a chain of extinct volcanoes and both are mountainous
the second-smallest African country (after the Seychelles); the two main islands form part of a chain of extinct volcanoes and both are mountainous -
People and Society :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
Population: This entry gives an estimate from the US Bureau of the Census based on statistics from population censuses, vital statistics registration systems, or sample surveys pertaining to the recent past and on assumptions about future trends. The total population presents one overall measure of the potential impact of the country on the world and within its region. Note: Starting with the 1993 Factbook, demographic estimates for some countries (mostly African) have explicitly taken into account t . . . more
 211,122 (July 2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Nationality: This entry provides the identifying terms for citizens - noun and adjective.
211,122 (July 2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Nationality: This entry provides the identifying terms for citizens - noun and adjective. noun: Sao Tomean(s)adjective: Sao TomeanEthnic groups: This entry provides an ordered listing of ethnic groups starting with the largest and normally includes the percent of total population.
noun: Sao Tomean(s)adjective: Sao TomeanEthnic groups: This entry provides an ordered listing of ethnic groups starting with the largest and normally includes the percent of total population. mestico, angolares (descendants of Angolan slaves), forros (descendants of freed slaves), servicais (contract laborers from Angola, Mozambique, and Cabo Verde), tongas (children of servicais born on the islands), Europeans (primarily Portuguese), Asians (mostly Chinese)Languages: This entry provides a listing of languages spoken in each country and specifies any that are official national or regional languages. When data is available, the languages spoken in each country are broken down according to the percent of the total population speaking each language as a first language. For those countries without available data, languages are listed in rank order based on prevalence, starting with the most-spoken language.
mestico, angolares (descendants of Angolan slaves), forros (descendants of freed slaves), servicais (contract laborers from Angola, Mozambique, and Cabo Verde), tongas (children of servicais born on the islands), Europeans (primarily Portuguese), Asians (mostly Chinese)Languages: This entry provides a listing of languages spoken in each country and specifies any that are official national or regional languages. When data is available, the languages spoken in each country are broken down according to the percent of the total population speaking each language as a first language. For those countries without available data, languages are listed in rank order based on prevalence, starting with the most-spoken language. Portuguese 98.4% (official), Forro 36.2%, Cabo Verdian 8.5%, French 6.8%, Angolar 6.6%, English 4.9%, Lunguie 1%, other (including sign language) 2.4% (2012 est.)
Portuguese 98.4% (official), Forro 36.2%, Cabo Verdian 8.5%, French 6.8%, Angolar 6.6%, English 4.9%, Lunguie 1%, other (including sign language) 2.4% (2012 est.)note: shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
Religions: This entry is an ordered listing of religions by adherents starting with the largest group and sometimes includes the percent of total population. The core characteristics and beliefs of the world's major religions are described below. Baha'i - Founded by Mirza Husayn-Ali (known as Baha'u'llah) in Iran in 1852, Baha'i faith emphasizes monotheism and believes in one eternal transcendent God. Its guiding focus is to encourage the unity of all peoples on the earth so that justice and peace m . . . more Catholic 55.7%, Adventist 4.1%, Assembly of God 3.4%, New Apostolic 2.9%, Mana 2.3%, Universal Kingdom of God 2%, Jehovah's Witness 1.2%, other 6.2%, none 21.2%, unspecified 1% (2012 est.)Demographic profile: This entry describes a country’s key demographic features and trends and how they vary among regional, ethnic, and socioeconomic sub-populations. Some of the topics addressed are population age structure, fertility, health, mortality, poverty, education, and migration.
Catholic 55.7%, Adventist 4.1%, Assembly of God 3.4%, New Apostolic 2.9%, Mana 2.3%, Universal Kingdom of God 2%, Jehovah's Witness 1.2%, other 6.2%, none 21.2%, unspecified 1% (2012 est.)Demographic profile: This entry describes a country’s key demographic features and trends and how they vary among regional, ethnic, and socioeconomic sub-populations. Some of the topics addressed are population age structure, fertility, health, mortality, poverty, education, and migration.
Sao Tome and Principe’s youthful age structure – more than 60% of the population is under the age of 25 – and high fertility rate ensure future population growth. Although Sao Tome has a net negative international migration rate, emigration is not a sufficient safety valve to reduce already high levels of unemployment and poverty. While literacy and primary school attendance have improved in recent years, Sao Tome still struggles to improve its educational quality and to increase its secondary school completion rate. Despite some improvements in education and access to healthcare, Sao Tome and Principe has much to do to decrease its high poverty rate, create jobs, and increase its economic growth.
The population of Sao Tome and Principe descends primarily from the islands’ colonial Portuguese settlers, who first arrived in the late 15th century, and the much larger number of African slaves brought in for sugar production and the slave trade. For about 100 years after the abolition of slavery in 1876, the population was further shaped by the widespread use of imported unskilled contract laborers from Portugal’s other African colonies, who worked on coffee and cocoa plantations. In the first decades after abolition, most workers were brought from Angola under a system similar to slavery. While Angolan laborers were technically free, they were forced or coerced into long contracts that were automatically renewed and extended to their children. Other contract workers from Mozambique and famine-stricken Cape Verde first arrived in the early 20th century under short-term contracts and had the option of repatriation, although some chose to remain in Sao Tome and Principe.
Today’s Sao Tomean population consists of mesticos (creole descendants of the European immigrants and African slaves that first inhabited the islands), forros (descendants of freed African slaves), angolares (descendants of runaway African slaves that formed a community in the south of Sao Tome Island and today are fishermen), servicais (contract laborers from Angola, Mozambique, and Cape Verde), tongas (locally born children of contract laborers), and lesser numbers of Europeans and Asians.
Age structure: This entry provides the distribution of the population according to age. Information is included by sex and age group as follows: 0-14 years (children), 15-24 years (early working age), 25-54 years (prime working age), 55-64 years (mature working age), 65 years and over (elderly). The age structure of a population affects a nation's key socioeconomic issues. Countries with young populations (high percentage under age 15) need to invest more in schools, while countries with older population . . . more 0-14 years: 39.77% (male 42,690/female 41,277)15-24 years: 21.59% (male 23,088/female 22,487)25-54 years: 31.61% (male 32,900/female 33,834)55-64 years: 4.17% (male 4,095/female 4,700)65 years and over: 2.87% (male 2,631/female 3,420) (2020 est.)population pyramid:The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Sao Tome and Principe PrintImage DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Sao Tome and Principe. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
0-14 years: 39.77% (male 42,690/female 41,277)15-24 years: 21.59% (male 23,088/female 22,487)25-54 years: 31.61% (male 32,900/female 33,834)55-64 years: 4.17% (male 4,095/female 4,700)65 years and over: 2.87% (male 2,631/female 3,420) (2020 est.)population pyramid:The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Sao Tome and Principe PrintImage DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Sao Tome and Principe. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios: Dependency ratios are a measure of the age structure of a population. They relate the number of individuals that are likely to be economically "dependent" on the support of others. Dependency ratios contrast the ratio of youths (ages 0-14) and the elderly (ages 65+) to the number of those in the working-age group (ages 15-64). Changes in the dependency ratio provide an indication of potential social support requirements resulting from changes in population age structures. As fertility leve . . . more total dependency ratio: 81youth dependency ratio: 75.6elderly dependency ratio: 5.4potential support ratio: 18.4 (2020 est.)Median age: This entry is the age that divides a population into two numerically equal groups; that is, half the people are younger than this age and half are older. It is a single index that summarizes the age distribution of a population. Currently, the median age ranges from a low of about 15 in Niger and Uganda to 40 or more in several European countries and Japan. See the entry for "Age structure" for the importance of a young versus an older age structure and, by implication, a low versus a high . . . more
total dependency ratio: 81youth dependency ratio: 75.6elderly dependency ratio: 5.4potential support ratio: 18.4 (2020 est.)Median age: This entry is the age that divides a population into two numerically equal groups; that is, half the people are younger than this age and half are older. It is a single index that summarizes the age distribution of a population. Currently, the median age ranges from a low of about 15 in Niger and Uganda to 40 or more in several European countries and Japan. See the entry for "Age structure" for the importance of a young versus an older age structure and, by implication, a low versus a high . . . more total: 19.3 yearsmale: 18.9 yearsfemale: 19.7 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Population growth rate: The average annual percent change in the population, resulting from a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths and the balance of migrants entering and leaving a country. The rate may be positive or negative. The growth rate is a factor in determining how great a burden would be imposed on a country by the changing needs of its people for infrastructure (e.g., schools, hospitals, housing, roads), resources (e.g., food, water, electricity), and jobs. Rapid population growth can be seen as . . . more
total: 19.3 yearsmale: 18.9 yearsfemale: 19.7 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Population growth rate: The average annual percent change in the population, resulting from a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths and the balance of migrants entering and leaving a country. The rate may be positive or negative. The growth rate is a factor in determining how great a burden would be imposed on a country by the changing needs of its people for infrastructure (e.g., schools, hospitals, housing, roads), resources (e.g., food, water, electricity), and jobs. Rapid population growth can be seen as . . . more 1.58% (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Birth rate: This entry gives the average annual number of births during a year per 1,000 persons in the population at midyear; also known as crude birth rate. The birth rate is usually the dominant factor in determining the rate of population growth. It depends on both the level of fertility and the age structure of the population.
1.58% (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Birth rate: This entry gives the average annual number of births during a year per 1,000 persons in the population at midyear; also known as crude birth rate. The birth rate is usually the dominant factor in determining the rate of population growth. It depends on both the level of fertility and the age structure of the population. 29.7 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Death rate: This entry gives the average annual number of deaths during a year per 1,000 population at midyear; also known as crude death rate. The death rate, while only a rough indicator of the mortality situation in a country, accurately indicates the current mortality impact on population growth. This indicator is significantly affected by age distribution, and most countries will eventually show a rise in the overall death rate, in spite of continued decline in mortality at all ages, as declining . . . more
29.7 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Death rate: This entry gives the average annual number of deaths during a year per 1,000 population at midyear; also known as crude death rate. The death rate, while only a rough indicator of the mortality situation in a country, accurately indicates the current mortality impact on population growth. This indicator is significantly affected by age distribution, and most countries will eventually show a rise in the overall death rate, in spite of continued decline in mortality at all ages, as declining . . . more 6.3 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 152Net migration rate: This entry includes the figure for the difference between the number of persons entering and leaving a country during the year per 1,000 persons (based on midyear population). An excess of persons entering the country is referred to as net immigration (e.g., 3.56 migrants/1,000 population); an excess of persons leaving the country as net emigration (e.g., -9.26 migrants/1,000 population). The net migration rate indicates the contribution of migration to the overall level of population chan . . . more
6.3 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 152Net migration rate: This entry includes the figure for the difference between the number of persons entering and leaving a country during the year per 1,000 persons (based on midyear population). An excess of persons entering the country is referred to as net immigration (e.g., 3.56 migrants/1,000 population); an excess of persons leaving the country as net emigration (e.g., -9.26 migrants/1,000 population). The net migration rate indicates the contribution of migration to the overall level of population chan . . . more -7.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures.
-7.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures. Sao Tome, the capital city, has roughly a quarter of the nation's population; Santo Antonio is the largest town on Principe; the northern areas of both islands have the highest population densities as shown in this population distribution mapUrbanization: This entry provides two measures of the degree of urbanization of a population. The first, urban population, describes the percentage of the total population living in urban areas, as defined by the country. The second, rate of urbanization, describes the projected average rate of change of the size of the urban population over the given period of time. It is possible for a country with a 100% urban population to still display a change in the rate of urbanization (up or down). For example . . . more
Sao Tome, the capital city, has roughly a quarter of the nation's population; Santo Antonio is the largest town on Principe; the northern areas of both islands have the highest population densities as shown in this population distribution mapUrbanization: This entry provides two measures of the degree of urbanization of a population. The first, urban population, describes the percentage of the total population living in urban areas, as defined by the country. The second, rate of urbanization, describes the projected average rate of change of the size of the urban population over the given period of time. It is possible for a country with a 100% urban population to still display a change in the rate of urbanization (up or down). For example . . . more urban population: 74.4% of total population (2020)rate of urbanization: 3.33% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population: This entry provides the population of the capital and up to six major cities defined as urban agglomerations with populations of at least 750,000 people. An urban agglomeration is defined as comprising the city or town proper and also the suburban fringe or thickly settled territory lying outside of, but adjacent to, the boundaries of the city. For smaller countries, lacking urban centers of 750,000 or more, only the population of the capital is presented.
urban population: 74.4% of total population (2020)rate of urbanization: 3.33% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population: This entry provides the population of the capital and up to six major cities defined as urban agglomerations with populations of at least 750,000 people. An urban agglomeration is defined as comprising the city or town proper and also the suburban fringe or thickly settled territory lying outside of, but adjacent to, the boundaries of the city. For smaller countries, lacking urban centers of 750,000 or more, only the population of the capital is presented. 80,000 SAO TOME (capital) (2018)Sex ratio: This entry includes the number of males for each female in five age groups - at birth, under 15 years, 15-64 years, 65 years and over, and for the total population. Sex ratio at birth has recently emerged as an indicator of certain kinds of sex discrimination in some countries. For instance, high sex ratios at birth in some Asian countries are now attributed to sex-selective abortion and infanticide due to a strong preference for sons. This will affect future marriage patterns and fertilit . . . more
80,000 SAO TOME (capital) (2018)Sex ratio: This entry includes the number of males for each female in five age groups - at birth, under 15 years, 15-64 years, 65 years and over, and for the total population. Sex ratio at birth has recently emerged as an indicator of certain kinds of sex discrimination in some countries. For instance, high sex ratios at birth in some Asian countries are now attributed to sex-selective abortion and infanticide due to a strong preference for sons. This will affect future marriage patterns and fertilit . . . more at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.97 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.87 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth: This entry provides the mean (average) age of mothers at the birth of their first child. It is a useful indicator for gauging the success of family planning programs aiming to reduce maternal mortality, increase contraceptive use – particularly among married and unmarried adolescents – delay age at first marriage, and improve the health of newborns.
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.97 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.87 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth: This entry provides the mean (average) age of mothers at the birth of their first child. It is a useful indicator for gauging the success of family planning programs aiming to reduce maternal mortality, increase contraceptive use – particularly among married and unmarried adolescents – delay age at first marriage, and improve the health of newborns. 19.4 years (2008/09 est.)
19.4 years (2008/09 est.)note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality rate: The maternal mortality rate (MMR) is the annual number of female deaths per 100,000 live births from any cause related to or aggravated by pregnancy or its management (excluding accidental or incidental causes). The MMR includes deaths during pregnancy, childbirth, or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, for a specified year. 130 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Infant mortality rate: This entry gives the number of deaths of infants under one year old in a given year per 1,000 live births in the same year. This rate is often used as an indicator of the level of health in a country.
130 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Infant mortality rate: This entry gives the number of deaths of infants under one year old in a given year per 1,000 live births in the same year. This rate is often used as an indicator of the level of health in a country. total: 41.7 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 43.6 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 39.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Life expectancy at birth: This entry contains the average number of years to be lived by a group of people born in the same year, if mortality at each age remains constant in the future. Life expectancy at birth is also a measure of overall quality of life in a country and summarizes the mortality at all ages. It can also be thought of as indicating the potential return on investment in human capital and is necessary for the calculation of various actuarial measures.
total: 41.7 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 43.6 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 39.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Life expectancy at birth: This entry contains the average number of years to be lived by a group of people born in the same year, if mortality at each age remains constant in the future. Life expectancy at birth is also a measure of overall quality of life in a country and summarizes the mortality at all ages. It can also be thought of as indicating the potential return on investment in human capital and is necessary for the calculation of various actuarial measures. total population: 66.3 yearsmale: 64.9 yearsfemale: 67.8 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 187Total fertility rate: This entry gives a figure for the average number of children that would be born per woman if all women lived to the end of their childbearing years and bore children according to a given fertility rate at each age. The total fertility rate (TFR) is a more direct measure of the level of fertility than the crude birth rate, since it refers to births per woman. This indicator shows the potential for population change in the country. A rate of two children per woman is considered the replaceme . . . more
total population: 66.3 yearsmale: 64.9 yearsfemale: 67.8 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 187Total fertility rate: This entry gives a figure for the average number of children that would be born per woman if all women lived to the end of their childbearing years and bore children according to a given fertility rate at each age. The total fertility rate (TFR) is a more direct measure of the level of fertility than the crude birth rate, since it refers to births per woman. This indicator shows the potential for population change in the country. A rate of two children per woman is considered the replaceme . . . more 3.82 children born/woman (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Contraceptive prevalence rate: This field gives the percent of women of reproductive age (15-49) who are married or in union and are using, or whose sexual partner is using, a method of contraception according to the date of the most recent available data. The contraceptive prevalence rate is an indicator of health services, development, and women’s empowerment. It is also useful in understanding, past, present, and future fertility trends, especially in developing countries.
3.82 children born/woman (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 33Contraceptive prevalence rate: This field gives the percent of women of reproductive age (15-49) who are married or in union and are using, or whose sexual partner is using, a method of contraception according to the date of the most recent available data. The contraceptive prevalence rate is an indicator of health services, development, and women’s empowerment. It is also useful in understanding, past, present, and future fertility trends, especially in developing countries. 40.6% (2014)Drinking water source: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved drinking water sources available to segments of the population of a country. Improved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: piped water into dwelling, yard, or plot; public tap or standpipe; tubewell or borehole; protected dug well; protected spring; or rainwater collection. Unimproved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: unprotected dug well; unprotected spring; cart with small tank or . . . more
40.6% (2014)Drinking water source: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved drinking water sources available to segments of the population of a country. Improved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: piped water into dwelling, yard, or plot; public tap or standpipe; tubewell or borehole; protected dug well; protected spring; or rainwater collection. Unimproved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: unprotected dug well; unprotected spring; cart with small tank or . . . more improved: urban: 100% of populationrural: 88.4% of populationtotal: 96.8% of populationunimproved: urban: 0% of populationrural: 11.6% of populationtotal: 3.2% of population (2017 est.)Current Health Expenditure: Current Health Expenditure (CHE) describes the share of spending on health in each country relative to the size of its economy. It includes expenditures corresponding to the final consumption of health care goods and services and excludes investment, exports, and intermediate consumption. CHE shows the importance of the health sector in the economy and indicates the priority given to health in monetary terms. Note: Current Health Expenditure replaces the former Health Expenditures field . . . more
improved: urban: 100% of populationrural: 88.4% of populationtotal: 96.8% of populationunimproved: urban: 0% of populationrural: 11.6% of populationtotal: 3.2% of population (2017 est.)Current Health Expenditure: Current Health Expenditure (CHE) describes the share of spending on health in each country relative to the size of its economy. It includes expenditures corresponding to the final consumption of health care goods and services and excludes investment, exports, and intermediate consumption. CHE shows the importance of the health sector in the economy and indicates the priority given to health in monetary terms. Note: Current Health Expenditure replaces the former Health Expenditures field . . . more 6.2% (2017)Physicians density: This entry gives the number of medical doctors (physicians), including generalist and specialist medical practitioners, per 1,000 of the population. Medical doctors are defined as doctors that study, diagnose, treat, and prevent illness, disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in humans through the application of modern medicine. They also plan, supervise, and evaluate care and treatment plans by other health care providers. The World Health Organization estimates that f . . . more
6.2% (2017)Physicians density: This entry gives the number of medical doctors (physicians), including generalist and specialist medical practitioners, per 1,000 of the population. Medical doctors are defined as doctors that study, diagnose, treat, and prevent illness, disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in humans through the application of modern medicine. They also plan, supervise, and evaluate care and treatment plans by other health care providers. The World Health Organization estimates that f . . . more 0.05 physicians/1,000 population (2017)Hospital bed density: This entry provides the number of hospital beds per 1,000 people; it serves as a general measure of inpatient service availability. Hospital beds include inpatient beds available in public, private, general, and specialized hospitals and rehabilitation centers. In most cases, beds for both acute and chronic care are included. Because the level of inpatient services required for individual countries depends on several factors - such as demographic issues and the burden of disease - there is . . . more
0.05 physicians/1,000 population (2017)Hospital bed density: This entry provides the number of hospital beds per 1,000 people; it serves as a general measure of inpatient service availability. Hospital beds include inpatient beds available in public, private, general, and specialized hospitals and rehabilitation centers. In most cases, beds for both acute and chronic care are included. Because the level of inpatient services required for individual countries depends on several factors - such as demographic issues and the burden of disease - there is . . . more 2.9 beds/1,000 population (2011)Sanitation facility access: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved sanitation facilities available to segments of the population of a country. Improved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush to a piped sewer system, septic tank or pit latrine; ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrine; pit latrine with slab; or a composting toilet. Unimproved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush not piped to a sewer system, septic tank . . . more
2.9 beds/1,000 population (2011)Sanitation facility access: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved sanitation facilities available to segments of the population of a country. Improved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush to a piped sewer system, septic tank or pit latrine; ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrine; pit latrine with slab; or a composting toilet. Unimproved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush not piped to a sewer system, septic tank . . . more improved: urban: 54.4% of populationrural: 35.3% of populationtotal: 49.1% of populationunimproved: urban: 45.6% of populationrural: 64.7% of populationtotal: 50.9% of population (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives an estimate of the percentage of adults (aged 15-49) living with HIV/AIDS. The adult prevalence rate is calculated by dividing the estimated number of adults living with HIV/AIDS at yearend by the total adult population at yearend.
improved: urban: 54.4% of populationrural: 35.3% of populationtotal: 49.1% of populationunimproved: urban: 45.6% of populationrural: 64.7% of populationtotal: 50.9% of population (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives an estimate of the percentage of adults (aged 15-49) living with HIV/AIDS. The adult prevalence rate is calculated by dividing the estimated number of adults living with HIV/AIDS at yearend by the total adult population at yearend. 0.7% (2018)country comparison to the world: 56HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: This entry gives an estimate of all people (adults and children) alive at yearend with HIV infection, whether or not they have developed symptoms of AIDS.
0.7% (2018)country comparison to the world: 56HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: This entry gives an estimate of all people (adults and children) alive at yearend with HIV infection, whether or not they have developed symptoms of AIDS. 1,100 (2018)country comparison to the world: 144HIV/AIDS - deaths: This entry gives an estimate of the number of adults and children who died of AIDS during a given calendar year.
1,100 (2018)country comparison to the world: 144HIV/AIDS - deaths: This entry gives an estimate of the number of adults and children who died of AIDS during a given calendar year. <100 (2018)Major infectious diseases: This entry lists major infectious diseases likely to be encountered in countries where the risk of such diseases is assessed to be very high as compared to the United States. These infectious diseases represent risks to US government personnel traveling to the specified country for a period of less than three years. The degree of risk is assessed by considering the foreign nature of these infectious diseases, their severity, and the probability of being affected by the diseases present. Th . . . more
<100 (2018)Major infectious diseases: This entry lists major infectious diseases likely to be encountered in countries where the risk of such diseases is assessed to be very high as compared to the United States. These infectious diseases represent risks to US government personnel traveling to the specified country for a period of less than three years. The degree of risk is assessed by considering the foreign nature of these infectious diseases, their severity, and the probability of being affected by the diseases present. Th . . . more degree of risk: high (2020)food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue feverwater contact diseases: schistosomiasisObesity - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives the percent of a country's population considered to be obese. Obesity is defined as an adult having a Body Mass Index (BMI) greater to or equal to 30.0. BMI is calculated by taking a person's weight in kg and dividing it by the person's squared height in meters.
degree of risk: high (2020)food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue feverwater contact diseases: schistosomiasisObesity - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives the percent of a country's population considered to be obese. Obesity is defined as an adult having a Body Mass Index (BMI) greater to or equal to 30.0. BMI is calculated by taking a person's weight in kg and dividing it by the person's squared height in meters. 12.4% (2016)country comparison to the world: 133Children under the age of 5 years underweight: This entry gives the percent of children under five considered to be underweight. Underweight means weight-for-age is approximately 2 kg below for standard at age one, 3 kg below standard for ages two and three, and 4 kg below standard for ages four and five. This statistic is an indicator of the nutritional status of a community. Children who suffer from growth retardation as a result of poor diets and/or recurrent infections tend to have a greater risk of suffering illness and death.
12.4% (2016)country comparison to the world: 133Children under the age of 5 years underweight: This entry gives the percent of children under five considered to be underweight. Underweight means weight-for-age is approximately 2 kg below for standard at age one, 3 kg below standard for ages two and three, and 4 kg below standard for ages four and five. This statistic is an indicator of the nutritional status of a community. Children who suffer from growth retardation as a result of poor diets and/or recurrent infections tend to have a greater risk of suffering illness and death. 8.8% (2014)country comparison to the world: 69Education expenditures: This entry provides the public expenditure on education as a percent of GDP.
8.8% (2014)country comparison to the world: 69Education expenditures: This entry provides the public expenditure on education as a percent of GDP. 5.1% of GDP (2018)country comparison to the world: 56Literacy: This entry includes a definition of literacy and UNESCO's percentage estimates for populations aged 15 years and over, including total population, males, and females. There are no universal definitions and standards of literacy. Unless otherwise specified, all rates are based on the most common definition - the ability to read and write at a specified age. Detailing the standards that individual countries use to assess the ability to read and write is beyond the scope of the Factbook. Info . . . more
5.1% of GDP (2018)country comparison to the world: 56Literacy: This entry includes a definition of literacy and UNESCO's percentage estimates for populations aged 15 years and over, including total population, males, and females. There are no universal definitions and standards of literacy. Unless otherwise specified, all rates are based on the most common definition - the ability to read and write at a specified age. Detailing the standards that individual countries use to assess the ability to read and write is beyond the scope of the Factbook. Info . . . more definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 92.8%male: 96.2%female: 89.5% (2018)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education): School life expectancy (SLE) is the total number of years of schooling (primary to tertiary) that a child can expect to receive, assuming that the probability of his or her being enrolled in school at any particular future age is equal to the current enrollment ratio at that age. Caution must be maintained when utilizing this indicator in international comparisons. For example, a year or grade completed in one country is not necessarily the same in terms of educational content or qualit . . . more
definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 92.8%male: 96.2%female: 89.5% (2018)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education): School life expectancy (SLE) is the total number of years of schooling (primary to tertiary) that a child can expect to receive, assuming that the probability of his or her being enrolled in school at any particular future age is equal to the current enrollment ratio at that age. Caution must be maintained when utilizing this indicator in international comparisons. For example, a year or grade completed in one country is not necessarily the same in terms of educational content or qualit . . . more total: 12 yearsmale: 12 yearsfemale: 13 years (2015)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24: This entry gives the percent of the total labor force ages 15-24 unemployed during a specified year.
total: 12 yearsmale: 12 yearsfemale: 13 years (2015)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24: This entry gives the percent of the total labor force ages 15-24 unemployed during a specified year.
-
Government :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
Country name: This entry includes all forms of the country's name approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (Italy is used as an example): conventional long form (Italian Republic), conventional short form (Italy), local long form (Repubblica Italiana), local short form (Italia), former (Kingdom of Italy), as well as the abbreviation. Also see the Terminology note.
 conventional long form: Democratic Republic of Sao Tome and Principeconventional short form: Sao Tome and Principelocal long form: Republica Democratica de Sao Tome e Principelocal short form: Sao Tome e Principeetymology: Sao Tome was named after Saint THOMAS the Apostle by the Portuguese who discovered the island on 21 December 1470 (or 1471), the saint's feast day; Principe is a shortening of the original Portuguese name of "Ilha do Principe" (Isle of the Prince) referring to the Prince of Portugal to whom duties on the island's sugar crop were paidGovernment type: This entry gives the basic form of government. Definitions of the major governmental terms are as follows. (Note that for some countries more than one definition applies.): Absolute monarchy - a form of government where the monarch rules unhindered, i.e., without any laws, constitution, or legally organized opposition. Anarchy - a condition of lawlessness or political disorder brought about by the absence of governmental authority. Authoritarian - a form of government in whic . . . more
conventional long form: Democratic Republic of Sao Tome and Principeconventional short form: Sao Tome and Principelocal long form: Republica Democratica de Sao Tome e Principelocal short form: Sao Tome e Principeetymology: Sao Tome was named after Saint THOMAS the Apostle by the Portuguese who discovered the island on 21 December 1470 (or 1471), the saint's feast day; Principe is a shortening of the original Portuguese name of "Ilha do Principe" (Isle of the Prince) referring to the Prince of Portugal to whom duties on the island's sugar crop were paidGovernment type: This entry gives the basic form of government. Definitions of the major governmental terms are as follows. (Note that for some countries more than one definition applies.): Absolute monarchy - a form of government where the monarch rules unhindered, i.e., without any laws, constitution, or legally organized opposition. Anarchy - a condition of lawlessness or political disorder brought about by the absence of governmental authority. Authoritarian - a form of government in whic . . . more semi-presidential republicCapital: This entry gives the name of the seat of government, its geographic coordinates, the time difference relative to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and the time observed in Washington, DC, and, if applicable, information on daylight saving time (DST). Where appropriate, a special note has been added to highlight those countries that have multiple time zones.
semi-presidential republicCapital: This entry gives the name of the seat of government, its geographic coordinates, the time difference relative to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and the time observed in Washington, DC, and, if applicable, information on daylight saving time (DST). Where appropriate, a special note has been added to highlight those countries that have multiple time zones. name: Sao Tomegeographic coordinates: 0 20 N, 6 44 Etime difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: named after Saint Thomas the ApostleAdministrative divisions: This entry generally gives the numbers, designatory terms, and first-order administrative divisions as approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (BGN). Changes that have been reported but not yet acted on by the BGN are noted. Geographic names conform to spellings approved by the BGN with the exception of the omission of diacritical marks and special characters.
name: Sao Tomegeographic coordinates: 0 20 N, 6 44 Etime difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: named after Saint Thomas the ApostleAdministrative divisions: This entry generally gives the numbers, designatory terms, and first-order administrative divisions as approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (BGN). Changes that have been reported but not yet acted on by the BGN are noted. Geographic names conform to spellings approved by the BGN with the exception of the omission of diacritical marks and special characters. 6 districts (distritos, singular - distrito), 1 autonomous region* (regiao autonoma); Agua Grande, Cantagalo, Caue, Lemba, Lobata, Me-Zochi, Principe*Independence: For most countries, this entry gives the date that sovereignty was achieved and from which nation, empire, or trusteeship. For the other countries, the date given may not represent "independence" in the strict sense, but rather some significant nationhood event such as the traditional founding date or the date of unification, federation, confederation, establishment, fundamental change in the form of government, or state succession. For a number of countries, the establishment of statehood . . . more
6 districts (distritos, singular - distrito), 1 autonomous region* (regiao autonoma); Agua Grande, Cantagalo, Caue, Lemba, Lobata, Me-Zochi, Principe*Independence: For most countries, this entry gives the date that sovereignty was achieved and from which nation, empire, or trusteeship. For the other countries, the date given may not represent "independence" in the strict sense, but rather some significant nationhood event such as the traditional founding date or the date of unification, federation, confederation, establishment, fundamental change in the form of government, or state succession. For a number of countries, the establishment of statehood . . . more 12 July 1975 (from Portugal)National holiday: This entry gives the primary national day of celebration - usually independence day.
12 July 1975 (from Portugal)National holiday: This entry gives the primary national day of celebration - usually independence day. Independence Day, 12 July (1975)Constitution: This entry provides information on a country’s constitution and includes two subfields. The history subfield includes the dates of previous constitutions and the main steps and dates in formulating and implementing the latest constitution. For countries with 1-3 previous constitutions, the years are listed; for those with 4-9 previous, the entry is listed as “several previous,” and for those with 10 or more, the entry is “many previous.” The amendments subfield summarizes the process of am . . . more
Independence Day, 12 July (1975)Constitution: This entry provides information on a country’s constitution and includes two subfields. The history subfield includes the dates of previous constitutions and the main steps and dates in formulating and implementing the latest constitution. For countries with 1-3 previous constitutions, the years are listed; for those with 4-9 previous, the entry is listed as “several previous,” and for those with 10 or more, the entry is “many previous.” The amendments subfield summarizes the process of am . . . more history: approved 5 November 1975amendments: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly; the Assembly can propose to the president of the republic that an amendment be submitted to a referendum; revised several times, last in 2006Legal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more
history: approved 5 November 1975amendments: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly; the Assembly can propose to the president of the republic that an amendment be submitted to a referendum; revised several times, last in 2006Legal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more mixed legal system of civil law based on the Portuguese model and customary lawInternational law organization participation: This entry includes information on a country's acceptance of jurisdiction of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and of the International Criminal Court (ICCt); 59 countries have accepted ICJ jurisdiction with reservations and 11 have accepted ICJ jurisdiction without reservations; 122 countries have accepted ICCt jurisdiction. Appendix B: International Organizations and Groups explains the differing mandates of the ICJ and ICCt.
mixed legal system of civil law based on the Portuguese model and customary lawInternational law organization participation: This entry includes information on a country's acceptance of jurisdiction of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and of the International Criminal Court (ICCt); 59 countries have accepted ICJ jurisdiction with reservations and 11 have accepted ICJ jurisdiction without reservations; 122 countries have accepted ICCt jurisdiction. Appendix B: International Organizations and Groups explains the differing mandates of the ICJ and ICCt. has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtCitizenship: This entry provides information related to the acquisition and exercise of citizenship; it includes four subfields: citizenship by birth describes the acquisition of citizenship based on place of birth, known as Jus soli, regardless of the citizenship of parents. citizenship by descent only describes the acquisition of citizenship based on the principle of Jus sanguinis, or by descent, where at least one parent is a citizen of the state and being born within the territorial limits of the s . . . more
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtCitizenship: This entry provides information related to the acquisition and exercise of citizenship; it includes four subfields: citizenship by birth describes the acquisition of citizenship based on place of birth, known as Jus soli, regardless of the citizenship of parents. citizenship by descent only describes the acquisition of citizenship based on the principle of Jus sanguinis, or by descent, where at least one parent is a citizen of the state and being born within the territorial limits of the s . . . more citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Sao Tome and Principedual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 yearsSuffrage: This entry gives the age at enfranchisement and whether the right to vote is universal or restricted.
citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Sao Tome and Principedual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 yearsSuffrage: This entry gives the age at enfranchisement and whether the right to vote is universal or restricted. 18 years of age; universalExecutive branch: This entry includes five subentries: chief of state; head of government; cabinet; elections/appointments; election results. Chief of state includes the name, title, and beginning date in office of the titular leader of the country who represents the state at official and ceremonial functions but may not be involved with the day-to-day activities of the government. Head of government includes the name, title of the top executive designated to manage the executive branch of the government, a . . . more
18 years of age; universalExecutive branch: This entry includes five subentries: chief of state; head of government; cabinet; elections/appointments; election results. Chief of state includes the name, title, and beginning date in office of the titular leader of the country who represents the state at official and ceremonial functions but may not be involved with the day-to-day activities of the government. Head of government includes the name, title of the top executive designated to manage the executive branch of the government, a . . . more chief of state: President Evaristo CARVALHO (since 3 September 2016)head of government: Prime Minister Jorge Bom JESUS (since 3 December 2018)cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the prime minister, appointed by the presidentelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 7 July 2016 and 7 August 2016 (next to be held in July 2021); prime minister chosen by the National Assembly and approved by the presidentelection results: Evaristo CARVALHO elected president; percent of vote - Evaristo CARVALHO (ADI) 49.8%, Manuel Pinto DA COSTA (independent) 24.8%, Maria DAS NEVES (MLSTP-PSD) 24.1%; note - first round results for CARVALHO were revised downward from just over 50%, prompting the 7 August runoff; however, on 1 August 2016 DA COSTA withdrew from the runoff, citing voting irregularities, and CARVALHO was declared the winnerLegislative branch: This entry has three subfields. The description subfield provides the legislative structure (unicameral – single house; bicameral – an upper and a lower house); formal name(s); number of member seats; types of constituencies or voting districts (single seat, multi-seat, nationwide); electoral voting system(s); and member term of office. The elections subfield includes the dates of the last election and next election. The election results subfield lists percent of vote by party/coalition an . . . more
chief of state: President Evaristo CARVALHO (since 3 September 2016)head of government: Prime Minister Jorge Bom JESUS (since 3 December 2018)cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the prime minister, appointed by the presidentelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 7 July 2016 and 7 August 2016 (next to be held in July 2021); prime minister chosen by the National Assembly and approved by the presidentelection results: Evaristo CARVALHO elected president; percent of vote - Evaristo CARVALHO (ADI) 49.8%, Manuel Pinto DA COSTA (independent) 24.8%, Maria DAS NEVES (MLSTP-PSD) 24.1%; note - first round results for CARVALHO were revised downward from just over 50%, prompting the 7 August runoff; however, on 1 August 2016 DA COSTA withdrew from the runoff, citing voting irregularities, and CARVALHO was declared the winnerLegislative branch: This entry has three subfields. The description subfield provides the legislative structure (unicameral – single house; bicameral – an upper and a lower house); formal name(s); number of member seats; types of constituencies or voting districts (single seat, multi-seat, nationwide); electoral voting system(s); and member term of office. The elections subfield includes the dates of the last election and next election. The election results subfield lists percent of vote by party/coalition an . . . more description: unicameral National Assembly or Assembleia Nacional (55 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by closed party-list proportional representation vote to serve 4-year terms)elections: last held on 7 October 2018 (next to be held in October 2022)election results: percent of vote by party - ADI 41.8%, MLSTP/PSD 40.3%, PCD-GR 9.5%, MCISTP 2.1%, other 6.3%; seats by party - ADI 25, MLSTP-PSD 23, PCD-MDFM-UDD 5, MCISTP 2; composition - men 45, women 10, percent of women 18.2%Judicial branch: This entry includes three subfields. The highest court(s) subfield includes the name(s) of a country's highest level court(s), the number and titles of the judges, and the types of cases heard by the court, which commonly are based on civil, criminal, administrative, and constitutional law. A number of countries have separate constitutional courts. The judge selection and term of office subfield includes the organizations and associated officials responsible for nominating and appointing j . . . more
description: unicameral National Assembly or Assembleia Nacional (55 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by closed party-list proportional representation vote to serve 4-year terms)elections: last held on 7 October 2018 (next to be held in October 2022)election results: percent of vote by party - ADI 41.8%, MLSTP/PSD 40.3%, PCD-GR 9.5%, MCISTP 2.1%, other 6.3%; seats by party - ADI 25, MLSTP-PSD 23, PCD-MDFM-UDD 5, MCISTP 2; composition - men 45, women 10, percent of women 18.2%Judicial branch: This entry includes three subfields. The highest court(s) subfield includes the name(s) of a country's highest level court(s), the number and titles of the judges, and the types of cases heard by the court, which commonly are based on civil, criminal, administrative, and constitutional law. A number of countries have separate constitutional courts. The judge selection and term of office subfield includes the organizations and associated officials responsible for nominating and appointing j . . . more highest courts: Supreme Court or Supremo Tribunal Justica (consists of 5 judges); Constitutional Court or Tribunal Constitucional (consists of 5 judges, 3 of whom are from the Supreme Court)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the National Assembly; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges nominated by the president and elected by the National Assembly for 5-year termssubordinate courts: Court of First Instance; Audit CourtPolitical parties and leaders: This entry includes a listing of significant political parties, coalitions, and electoral lists as of each country's last legislative election, unless otherwise noted.
highest courts: Supreme Court or Supremo Tribunal Justica (consists of 5 judges); Constitutional Court or Tribunal Constitucional (consists of 5 judges, 3 of whom are from the Supreme Court)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the National Assembly; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges nominated by the president and elected by the National Assembly for 5-year termssubordinate courts: Court of First Instance; Audit CourtPolitical parties and leaders: This entry includes a listing of significant political parties, coalitions, and electoral lists as of each country's last legislative election, unless otherwise noted. Force for Democratic Change Movement or MDFM [Fradique Bandeira Melo DE MENEZES]
Force for Democratic Change Movement or MDFM [Fradique Bandeira Melo DE MENEZES]
Independent Democratic Action or ADI [vacant]
Movement for the Liberation of Sao Tome and Principe-Social Democratic Party or MLSTP-PSD [Aurelio MARTINS]
Party for Democratic Convergence-Reflection Group or PCD-GR [Leonel Mario D'ALVA]
other small partiesInternational organization participation: This entry lists in alphabetical order by abbreviation those international organizations in which the subject country is a member or participates in some other way. ACP, AfDB, AOSIS, AU, CD, CEMAC, CPLP, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)Diplomatic representation in the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, chancery address, telephone, FAX, consulate general locations, and consulate locations. The use of the annotated title Appointed Ambassador refers to a new ambassador who has presented his/her credentials to the secretary of state but not the US president. Such ambassadors fulfill all diplomatic functions except meeting with or appearing at functions attended by the president until such time as they formally present their credentials at a White Hou . . . more
ACP, AfDB, AOSIS, AU, CD, CEMAC, CPLP, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)Diplomatic representation in the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, chancery address, telephone, FAX, consulate general locations, and consulate locations. The use of the annotated title Appointed Ambassador refers to a new ambassador who has presented his/her credentials to the secretary of state but not the US president. Such ambassadors fulfill all diplomatic functions except meeting with or appearing at functions attended by the president until such time as they formally present their credentials at a White Hou . . . more chief of mission: Ambassador Carlos Filomeno Azevedo Agostinho das NEVES (since 3 December 2013)chancery: 675 Third Avenue, Suite 1807, New York, NY 10017telephone: [1] (212) 651-8116FAX: [1] (212) 651-8117Diplomatic representation from the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, embassy address, mailing address, telephone number, FAX number, branch office locations, consulate general locations, and consulate locations.
chief of mission: Ambassador Carlos Filomeno Azevedo Agostinho das NEVES (since 3 December 2013)chancery: 675 Third Avenue, Suite 1807, New York, NY 10017telephone: [1] (212) 651-8116FAX: [1] (212) 651-8117Diplomatic representation from the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, embassy address, mailing address, telephone number, FAX number, branch office locations, consulate general locations, and consulate locations. the US does not have an embassy in Sao Tome and Principe; the US Ambassador to Gabon is accredited to Sao Tome and PrincipeFlag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags.
the US does not have an embassy in Sao Tome and Principe; the US Ambassador to Gabon is accredited to Sao Tome and PrincipeFlag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags. three horizontal bands of green (top), yellow (double width), and green with two black five-pointed stars placed side by side in the center of the yellow band and a red isosceles triangle based on the hoist side; green stands for the country's rich vegetation, red recalls the struggle for independence, and yellow represents cocoa, one of the country's main agricultural products; the two stars symbolize the two main islands
three horizontal bands of green (top), yellow (double width), and green with two black five-pointed stars placed side by side in the center of the yellow band and a red isosceles triangle based on the hoist side; green stands for the country's rich vegetation, red recalls the struggle for independence, and yellow represents cocoa, one of the country's main agricultural products; the two stars symbolize the two main islandsnote: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia
National symbol(s): A national symbol is a faunal, floral, or other abstract representation - or some distinctive object - that over time has come to be closely identified with a country or entity. Not all countries have national symbols; a few countries have more than one. palm tree; national colors: green, yellow, red, blackNational anthem: A generally patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
palm tree; national colors: green, yellow, red, blackNational anthem: A generally patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not. name: "Independencia total" (Total Independence)lyrics/music: Alda Neves DA GRACA do Espirito Santo/Manuel dos Santos Barreto de Sousa e ALMEIDA
name: "Independencia total" (Total Independence)lyrics/music: Alda Neves DA GRACA do Espirito Santo/Manuel dos Santos Barreto de Sousa e ALMEIDAnote: adopted 1975
-
Economy :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
Economic overview: This section briefly describes four key economic components for a given country:* National Economy, including economic histories, domestic labor and wage markets, and the economic sector portfolios that drive fiscal and monetary policymaking;* Financial Power & Public Finance, including brief discussions of lending/exchange rates, capital stocks/flows, and foreign direct investments arising from a country's financial and capital markets;* International Trade, including chief imports an . . . more

The economy of São Tomé and Príncipe is small, based mainly on agricultural production, and, since independence in 1975, increasingly dependent on the export of cocoa beans. Cocoa production has substantially declined in recent years because of drought and mismanagement. Sao Tome depends heavily on imports of food, fuels, most manufactured goods, and consumer goods, and changes in commodity prices affect the country’s inflation rate. Maintaining control of inflation, fiscal discipline, and increasing flows of foreign direct investment into the nascent oil sector are major economic problems facing the country. In recent years the government has attempted to reduce price controls and subsidies. In 2017, several business-related laws were enacted that aim to improve the business climate.
São Tomé and Príncipe has had difficulty servicing its external debt and has relied heavily on concessional aid and debt rescheduling. In April 2011, the country completed a Threshold Country Program with The Millennium Challenge Corporation to help increase tax revenues, reform customs, and improve the business environment. In 2016, Sao Tome and Portugal signed a five-year cooperation agreement worth approximately $64 million, some of which will be provided as loans. In 2017, China and São Tomé signed a mutual cooperation agreement in areas such as infrastructure, health, and agriculture worth approximately $146 million over five years.
Considerable potential exists for development of tourism, and the government has taken steps to expand tourist facilities in recent years. Potential also exists for the development of petroleum resources in São Tomé and Príncipe's territorial waters in the oil-rich Gulf of Guinea, some of which are being jointly developed in a 60-40 split with Nigeria, but production is at least several years off.
Volatile aid and investment inflows have limited growth, and poverty remains high. Restricteded capacity at the main port increases the periodic risk of shortages of consumer goods. Contract enforcement in the country’s judicial system is difficult. The IMF in late 2016 expressed concern about vulnerabilities in the country’s banking sector, although the country plans some austerity measures in line with IMF recommendations under their three year extended credit facility. Deforestation, coastal erosion, poor waste management, and misuse of natural resources also are challenging issues.
GDP real growth rate: This entry gives GDP growth on an annual basis adjusted for inflation and expressed as a percent. The growth rates are year-over-year, and not compounded. Inflation rate (consumer prices): This entry furnishes the annual percent change in consumer prices compared with the previous year's consumer prices.
Inflation rate (consumer prices): This entry furnishes the annual percent change in consumer prices compared with the previous year's consumer prices. GDP (purchasing power parity) - real: This entry gives the gross domestic product (GDP) or value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. A nation's GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP) exchange rates is the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States in the year noted. This is the measure most economists prefer when looking at per-capita welfare and when comparing living conditions or use of resources across countries. The measur . . . more
GDP (purchasing power parity) - real: This entry gives the gross domestic product (GDP) or value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. A nation's GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP) exchange rates is the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States in the year noted. This is the measure most economists prefer when looking at per-capita welfare and when comparing living conditions or use of resources across countries. The measur . . . more $737 million (2019 est.)$719 million (2018 est.)$701 million (2017 est.)
$737 million (2019 est.)$719 million (2018 est.)$701 million (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate): This entry gives the gross domestic product (GDP) or value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. A nation's GDP at official exchange rates (OER) is the home-currency-denominated annual GDP figure divided by the bilateral average US exchange rate with that country in that year. The measure is simple to compute and gives a precise measure of the value of output. Many economists prefer this measure when gauging the economic power an economy maintains vis- . . . more $0 (2018 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP): This entry shows GDP on a purchasing power parity basis divided by population as of 1 July for the same year.
$0 (2018 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP): This entry shows GDP on a purchasing power parity basis divided by population as of 1 July for the same year. $1 (2019 est.)$1 (2018 est.)$1 (2017 est.)
$1 (2019 est.)$1 (2018 est.)$1 (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
country comparison to the world: 227Gross national saving: Gross national saving is derived by deducting final consumption expenditure (household plus government) from Gross national disposable income, and consists of personal saving, plus business saving (the sum of the capital consumption allowance and retained business profits), plus government saving (the excess of tax revenues over expenditures), but excludes foreign saving (the excess of imports of goods and services over exports). The figures are presented as a percent of GDP. A negative . . . more 18.7% of GDP (2017 est.)21% of GDP (2016 est.)19.3% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 107GDP - composition, by sector of origin: This entry shows where production takes place in an economy. The distribution gives the percentage contribution of agriculture, industry, and services to total GDP, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. Agriculture includes farming, fishing, and forestry. Industry includes mining, manufacturing, energy production, and construction. Services cover government activities, communications, transportation, finance, and all other private economic activities that do not prod . . . more
18.7% of GDP (2017 est.)21% of GDP (2016 est.)19.3% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 107GDP - composition, by sector of origin: This entry shows where production takes place in an economy. The distribution gives the percentage contribution of agriculture, industry, and services to total GDP, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. Agriculture includes farming, fishing, and forestry. Industry includes mining, manufacturing, energy production, and construction. Services cover government activities, communications, transportation, finance, and all other private economic activities that do not prod . . . more agriculture: 11.8% (2017 est.)industry: 14.8% (2017 est.)services: 73.4% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by end use: This entry shows who does the spending in an economy: consumers, businesses, government, and foreigners. The distribution gives the percentage contribution to total GDP of household consumption, government consumption, investment in fixed capital, investment in inventories, exports of goods and services, and imports of goods and services, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. household consumption consists of expenditures by resident households, and by nonprofit insti . . . more
agriculture: 11.8% (2017 est.)industry: 14.8% (2017 est.)services: 73.4% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by end use: This entry shows who does the spending in an economy: consumers, businesses, government, and foreigners. The distribution gives the percentage contribution to total GDP of household consumption, government consumption, investment in fixed capital, investment in inventories, exports of goods and services, and imports of goods and services, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. household consumption consists of expenditures by resident households, and by nonprofit insti . . . more household consumption: 81.4% (2017 est.)government consumption: 17.6% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 33.4% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 0% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 7.9% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -40.4% (2017 est.)Ease of Doing Business Index scores: The World Bank Group Doing Business project measures business regulations and enforcement mechanisms across economies and selected cities. The project evaluates domestic small and medium-size companies and measures the regulations applying to them through their life cycle. The project encourages economies to compete towards more efficient regulation; offers measurable benchmarks for reform; and serves as a resource for academics, journalists, private sector researchers and others intereste . . . more
household consumption: 81.4% (2017 est.)government consumption: 17.6% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 33.4% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 0% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 7.9% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -40.4% (2017 est.)Ease of Doing Business Index scores: The World Bank Group Doing Business project measures business regulations and enforcement mechanisms across economies and selected cities. The project evaluates domestic small and medium-size companies and measures the regulations applying to them through their life cycle. The project encourages economies to compete towards more efficient regulation; offers measurable benchmarks for reform; and serves as a resource for academics, journalists, private sector researchers and others intereste . . . more 66.0 (2020)Agriculture - products: This entry is an ordered listing of major crops and products starting with the most important.
66.0 (2020)Agriculture - products: This entry is an ordered listing of major crops and products starting with the most important. cocoa, coconuts, palm kernels, copra, cinnamon, pepper, coffee, bananas, papayas, beans; poultry; fishIndustries: This entry provides a rank ordering of industries starting with the largest by value of annual output.
cocoa, coconuts, palm kernels, copra, cinnamon, pepper, coffee, bananas, papayas, beans; poultry; fishIndustries: This entry provides a rank ordering of industries starting with the largest by value of annual output. light construction, textiles, soap, beer, fish processing, timberIndustrial production growth rate: This entry gives the annual percentage increase in industrial production (includes manufacturing, mining, and construction).
light construction, textiles, soap, beer, fish processing, timberIndustrial production growth rate: This entry gives the annual percentage increase in industrial production (includes manufacturing, mining, and construction). 5% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Labor force: This entry contains the total labor force figure.
5% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Labor force: This entry contains the total labor force figure. 72,600 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Labor force - by occupation: This entry lists the percentage distribution of the labor force by sector of occupation. Agriculture includes farming, fishing, and forestry. Industry includes mining, manufacturing, energy production, and construction. Services cover government activities, communications, transportation, finance, and all other economic activities that do not produce material goods. The distribution will total less than 100 percent if the data are incomplete and may range from 99-101 percent due to rounding. more
72,600 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Labor force - by occupation: This entry lists the percentage distribution of the labor force by sector of occupation. Agriculture includes farming, fishing, and forestry. Industry includes mining, manufacturing, energy production, and construction. Services cover government activities, communications, transportation, finance, and all other economic activities that do not produce material goods. The distribution will total less than 100 percent if the data are incomplete and may range from 99-101 percent due to rounding. more agriculture: 26.1%industry: 21.4%services: 52.5% (2014 est.)Unemployment rate: This entry contains the percent of the labor force that is without jobs. Substantial underemployment might be noted.
agriculture: 26.1%industry: 21.4%services: 52.5% (2014 est.)Unemployment rate: This entry contains the percent of the labor force that is without jobs. Substantial underemployment might be noted. Population below poverty line: National estimates of the percentage of the population falling below the poverty line are based on surveys of sub-groups, with the results weighted by the number of people in each group. Definitions of poverty vary considerably among nations. For example, rich nations generally employ more generous standards of poverty than poor nations.
Population below poverty line: National estimates of the percentage of the population falling below the poverty line are based on surveys of sub-groups, with the results weighted by the number of people in each group. Definitions of poverty vary considerably among nations. For example, rich nations generally employ more generous standards of poverty than poor nations. 66.2% (2009 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share: Data on household income or consumption come from household surveys, the results adjusted for household size. Nations use different standards and procedures in collecting and adjusting the data. Surveys based on income will normally show a more unequal distribution than surveys based on consumption. The quality of surveys is improving with time, yet caution is still necessary in making inter-country comparisons.
66.2% (2009 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share: Data on household income or consumption come from household surveys, the results adjusted for household size. Nations use different standards and procedures in collecting and adjusting the data. Surveys based on income will normally show a more unequal distribution than surveys based on consumption. The quality of surveys is improving with time, yet caution is still necessary in making inter-country comparisons. lowest 10%: NAhighest 10%: NABudget: This entry includes revenues, expenditures, and capital expenditures. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
lowest 10%: NAhighest 10%: NABudget: This entry includes revenues, expenditures, and capital expenditures. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. revenues: 103 million (2017 est.)expenditures: 112.4 million (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues: This entry records total taxes and other revenues received by the national government during the time period indicated, expressed as a percent of GDP. Taxes include personal and corporate income taxes, value added taxes, excise taxes, and tariffs. Other revenues include social contributions - such as payments for social security and hospital insurance - grants, and net revenues from public enterprises. Normalizing the data, by dividing total revenues by GDP, enables easy comparisons acr . . . more
revenues: 103 million (2017 est.)expenditures: 112.4 million (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues: This entry records total taxes and other revenues received by the national government during the time period indicated, expressed as a percent of GDP. Taxes include personal and corporate income taxes, value added taxes, excise taxes, and tariffs. Other revenues include social contributions - such as payments for social security and hospital insurance - grants, and net revenues from public enterprises. Normalizing the data, by dividing total revenues by GDP, enables easy comparisons acr . . . more 26.2% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 114Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-): This entry records the difference between national government revenues and expenditures, expressed as a percent of GDP. A positive (+) number indicates that revenues exceeded expenditures (a budget surplus), while a negative (-) number indicates the reverse (a budget deficit). Normalizing the data, by dividing the budget balance by GDP, enables easy comparisons across countries and indicates whether a national government saves or borrows money. Countries with high budget deficits (relat . . . more
26.2% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 114Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-): This entry records the difference between national government revenues and expenditures, expressed as a percent of GDP. A positive (+) number indicates that revenues exceeded expenditures (a budget surplus), while a negative (-) number indicates the reverse (a budget deficit). Normalizing the data, by dividing the budget balance by GDP, enables easy comparisons across countries and indicates whether a national government saves or borrows money. Countries with high budget deficits (relat . . . more -2.4% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Public debt: This entry records the cumulative total of all government borrowings less repayments that are denominated in a country's home currency. Public debt should not be confused with external debt, which reflects the foreign currency liabilities of both the private and public sector and must be financed out of foreign exchange earnings.
-2.4% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Public debt: This entry records the cumulative total of all government borrowings less repayments that are denominated in a country's home currency. Public debt should not be confused with external debt, which reflects the foreign currency liabilities of both the private and public sector and must be financed out of foreign exchange earnings. Fiscal year: This entry identifies the beginning and ending months for a country's accounting period of 12 months, which often is the calendar year but which may begin in any month. All yearly references are for the calendar year (CY) unless indicated as a noncalendar fiscal year (FY).
Fiscal year: This entry identifies the beginning and ending months for a country's accounting period of 12 months, which often is the calendar year but which may begin in any month. All yearly references are for the calendar year (CY) unless indicated as a noncalendar fiscal year (FY). calendar yearCurrent account balance: This entry records a country's net trade in goods and services, plus net earnings from rents, interest, profits, and dividends, and net transfer payments (such as pension funds and worker remittances) to and from the rest of the world during the period specified. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
calendar yearCurrent account balance: This entry records a country's net trade in goods and services, plus net earnings from rents, interest, profits, and dividends, and net transfer payments (such as pension funds and worker remittances) to and from the rest of the world during the period specified. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. Exports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise exports on an f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
Exports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise exports on an f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. Exports - partners: This entry provides a rank ordering of trading partners starting with the most important; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value.
Exports - partners: This entry provides a rank ordering of trading partners starting with the most important; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value. Guyana 43.7%, Germany 23.6%, Portugal 6%, Netherlands 5.5%, Poland 4.4% (2017)Exports - commodities: This entry provides a listing of the highest-valued exported products; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value.
Guyana 43.7%, Germany 23.6%, Portugal 6%, Netherlands 5.5%, Poland 4.4% (2017)Exports - commodities: This entry provides a listing of the highest-valued exported products; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value. cocoa 68%, copra, coffee, palm oil (2010 est.)Imports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise imports on a c.i.f. (cost, insurance, and freight) or f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
cocoa 68%, copra, coffee, palm oil (2010 est.)Imports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise imports on a c.i.f. (cost, insurance, and freight) or f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. Imports - commodities: This entry provides a listing of the highest-valued imported products; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value.
Imports - commodities: This entry provides a listing of the highest-valued imported products; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value. machinery and electrical equipment, food products, petroleum productsImports - partners: This entry provides a rank ordering of trading partners starting with the most important; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value.
machinery and electrical equipment, food products, petroleum productsImports - partners: This entry provides a rank ordering of trading partners starting with the most important; it sometimes includes the percent of total dollar value. Portugal 54.7%, Angola 16.5%, China 5.6% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold: This entry gives the dollar value for the stock of all financial assets that are available to the central monetary authority for use in meeting a country's balance of payments needs as of the end-date of the period specified. This category includes not only foreign currency and gold, but also a country's holdings of Special Drawing Rights in the International Monetary Fund, and its reserve position in the Fund.
Portugal 54.7%, Angola 16.5%, China 5.6% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold: This entry gives the dollar value for the stock of all financial assets that are available to the central monetary authority for use in meeting a country's balance of payments needs as of the end-date of the period specified. This category includes not only foreign currency and gold, but also a country's holdings of Special Drawing Rights in the International Monetary Fund, and its reserve position in the Fund. $58.95 million (31 December 2017 est.)$61.5 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Debt - external: This entry gives the total public and private debt owed to nonresidents repayable in internationally accepted currencies, goods, or services. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
$58.95 million (31 December 2017 est.)$61.5 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Debt - external: This entry gives the total public and private debt owed to nonresidents repayable in internationally accepted currencies, goods, or services. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. $292.9 million (31 December 2017 est.)$308.5 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Exchange rates: This entry provides the average annual price of a country's monetary unit for the time period specified, expressed in units of local currency per US dollar, as determined by international market forces or by official fiat. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 4217 alphabetic currency code for the national medium of exchange is presented in parenthesis. Closing daily exchange rates are not presented in The World Factbook, but are used to convert stock values - e.g., the . . . more
$292.9 million (31 December 2017 est.)$308.5 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Exchange rates: This entry provides the average annual price of a country's monetary unit for the time period specified, expressed in units of local currency per US dollar, as determined by international market forces or by official fiat. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 4217 alphabetic currency code for the national medium of exchange is presented in parenthesis. Closing daily exchange rates are not presented in The World Factbook, but are used to convert stock values - e.g., the . . . more dobras (STD) per US dollar -22,689 (2017 est.)21,797 (2016 est.)22,149 (2015 est.)22,091 (2014 est.)18,466 (2013 est.)
dobras (STD) per US dollar -22,689 (2017 est.)21,797 (2016 est.)22,149 (2015 est.)22,091 (2014 est.)18,466 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
Electricity access: This entry provides information on access to electricity. Electrification data – collected from industry reports, national surveys, and international sources – consists of four subfields. Population without electricity provides an estimate of the number of citizens that do not have access to electricity. Electrification – total population is the percent of a country’s total population with access to electricity, electrification – urban areas is the percent of a country’s urban population w . . . more
 electrification - total population: 71% (2019)electrification - urban areas: 87% (2019)electrification - rural areas: 25% (2019)Electricity - production: This entry is the annual electricity generated expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution.
electrification - total population: 71% (2019)electrification - urban areas: 87% (2019)electrification - rural areas: 25% (2019)Electricity - production: This entry is the annual electricity generated expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution. 66 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Electricity - consumption: This entry consists of total electricity generated annually plus imports and minus exports, expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution.
66 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Electricity - consumption: This entry consists of total electricity generated annually plus imports and minus exports, expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution. 61.38 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Electricity - exports: This entry is the total exported electricity in kilowatt-hours.
61.38 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Electricity - exports: This entry is the total exported electricity in kilowatt-hours. 0 kWh (2016)country comparison to the world: 193Electricity - imports: This entry is the total imported electricity in kilowatt-hours.
0 kWh (2016)country comparison to the world: 193Electricity - imports: This entry is the total imported electricity in kilowatt-hours. 0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 195Electricity - installed generating capacity: This entry is the total capacity of currently installed generators, expressed in kilowatts (kW), to produce electricity. A 10-kilowatt (kW) generator will produce 10 kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity, if it runs continuously for one hour.
0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 195Electricity - installed generating capacity: This entry is the total capacity of currently installed generators, expressed in kilowatts (kW), to produce electricity. A 10-kilowatt (kW) generator will produce 10 kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity, if it runs continuously for one hour. 18,100 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Electricity - from fossil fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by burning fossil fuels (such as coal, petroleum products, and natural gas), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
18,100 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Electricity - from fossil fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by burning fossil fuels (such as coal, petroleum products, and natural gas), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 88% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Electricity - from nuclear fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity through radioactive decay of nuclear fuel, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
88% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Electricity - from nuclear fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity through radioactive decay of nuclear fuel, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 177Electricity - from hydroelectric plants: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by water-driven turbines, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 177Electricity - from hydroelectric plants: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by water-driven turbines, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 11% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 115Electricity - from other renewable sources: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by using renewable energy sources other than hydroelectric (including, for example, wind, waves, solar, and geothermal), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
11% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 115Electricity - from other renewable sources: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by using renewable energy sources other than hydroelectric (including, for example, wind, waves, solar, and geothermal), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 1% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 166Crude oil - production: This entry is the total amount of crude oil produced, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
1% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 166Crude oil - production: This entry is the total amount of crude oil produced, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 196Crude oil - exports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil exported, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
0 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 196Crude oil - exports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil exported, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 189Crude oil - imports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil imported, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 189Crude oil - imports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil imported, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 191Crude oil - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of crude oil, in barrels (bbl). Proved reserves are those quantities of petroleum which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions.
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 191Crude oil - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of crude oil, in barrels (bbl). Proved reserves are those quantities of petroleum which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions. 0 bbl (1 January 2018)country comparison to the world: 191Refined petroleum products - production: This entry is the country's total output of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors.
0 bbl (1 January 2018)country comparison to the world: 191Refined petroleum products - production: This entry is the country's total output of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors. 0 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 198Refined petroleum products - consumption: This entry is the country's total consumption of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors.
0 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 198Refined petroleum products - consumption: This entry is the country's total consumption of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors. 1,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 205Refined petroleum products - exports: This entry is the country's total exports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
1,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 205Refined petroleum products - exports: This entry is the country's total exports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Refined petroleum products - imports: This entry is the country's total imports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Refined petroleum products - imports: This entry is the country's total imports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 1,027 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 201Natural gas - production: This entry is the total natural gas produced in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors.
1,027 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 201Natural gas - production: This entry is the total natural gas produced in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors. 0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 193Natural gas - consumption: This entry is the total natural gas consumed in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors.
0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 193Natural gas - consumption: This entry is the total natural gas consumed in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors. 0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 195Natural gas - exports: This entry is the total natural gas exported in cubic meters (cu m).
0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 195Natural gas - exports: This entry is the total natural gas exported in cubic meters (cu m). 0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 178Natural gas - imports: This entry is the total natural gas imported in cubic meters (cu m).
0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 178Natural gas - imports: This entry is the total natural gas imported in cubic meters (cu m). 0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Natural gas - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of natural gas in cubic meters (cu m). Proved reserves are those quantities of natural gas, which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions.
0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Natural gas - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of natural gas in cubic meters (cu m). Proved reserves are those quantities of natural gas, which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions. 0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 190Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy: This entry is the total amount of carbon dioxide, measured in metric tons, released by burning fossil fuels in the process of producing and consuming energy.
0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 190Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy: This entry is the total amount of carbon dioxide, measured in metric tons, released by burning fossil fuels in the process of producing and consuming energy. 148,100 Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 203
148,100 Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 203 -
Communications :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
Telephones - fixed lines: This entry gives the total number of fixed telephone lines in use, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants.
 total subscriptions: 4,614subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2.22 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 205Telephones - mobile cellular: This entry gives the total number of mobile cellular telephone subscribers, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Note that because of the ubiquity of mobile phone use in developed countries, the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants can exceed 100.
total subscriptions: 4,614subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2.22 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 205Telephones - mobile cellular: This entry gives the total number of mobile cellular telephone subscribers, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Note that because of the ubiquity of mobile phone use in developed countries, the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants can exceed 100. total subscriptions: 160,189subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 77.08 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 188Telecommunication systems: This entry includes a brief general assessment of a country's telecommunications system with details on the domestic and international components. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: 2G - is short for second-generation cellular network. After 2G was launched, the previous mobile wireless network systems were retroactively dubbed 1G. While radio signals on 1G networks are analog, radio signals on 2G networks are digital. Both systems use digital signaling . . . more
total subscriptions: 160,189subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 77.08 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 188Telecommunication systems: This entry includes a brief general assessment of a country's telecommunications system with details on the domestic and international components. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: 2G - is short for second-generation cellular network. After 2G was launched, the previous mobile wireless network systems were retroactively dubbed 1G. While radio signals on 1G networks are analog, radio signals on 2G networks are digital. Both systems use digital signaling . . . more general assessment: local telephone network of adequate quality with most lines connected to digital switches; mobile cellular superior choice to landland; dial-up quality low; broadband expensive (2018)domestic: fixed-line 2 per 100 and mobile-cellular teledensity 77 telephones per 100 persons (2019)international: country code - 239; landing points for the Ultramar GE and ACE submarine cables from South Africa to over 20 West African countries and Europe; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderatedBroadcast media: This entry provides information on the approximate number of public and private TV and radio stations in a country, as well as basic information on the availability of satellite and cable TV services.
general assessment: local telephone network of adequate quality with most lines connected to digital switches; mobile cellular superior choice to landland; dial-up quality low; broadband expensive (2018)domestic: fixed-line 2 per 100 and mobile-cellular teledensity 77 telephones per 100 persons (2019)international: country code - 239; landing points for the Ultramar GE and ACE submarine cables from South Africa to over 20 West African countries and Europe; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderatedBroadcast media: This entry provides information on the approximate number of public and private TV and radio stations in a country, as well as basic information on the availability of satellite and cable TV services. 1 government-owned TV station; 1 government-owned radio station; 3 independent local radio stations authorized in 2005 with 2 operating at the end of 2006; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are availableInternet country code: This entry includes the two-letter codes maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in the ISO 3166 Alpha-2 list and used by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) to establish country-coded top-level domains (ccTLDs).
1 government-owned TV station; 1 government-owned radio station; 3 independent local radio stations authorized in 2005 with 2 operating at the end of 2006; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are availableInternet country code: This entry includes the two-letter codes maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in the ISO 3166 Alpha-2 list and used by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) to establish country-coded top-level domains (ccTLDs). .stInternet users: This entry gives the total number of individuals within a country who can access the Internet at home, via any device type (computer or mobile) and connection. The percent of population with Internet access (i.e., the penetration rate) helps gauge how widespread Internet use is within a country. Statistics vary from country to country and may include users who access the Internet at least several times a week to those who access it only once within a period of several months.
.stInternet users: This entry gives the total number of individuals within a country who can access the Internet at home, via any device type (computer or mobile) and connection. The percent of population with Internet access (i.e., the penetration rate) helps gauge how widespread Internet use is within a country. Statistics vary from country to country and may include users who access the Internet at least several times a week to those who access it only once within a period of several months. Broadband - fixed subscriptions: This entry gives the total number of fixed-broadband subscriptions, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Fixed broadband is a physical wired connection to the Internet (e.g., coaxial cable, optical fiber) at speeds equal to or greater than 256 kilobits/second (256 kbit/s).
Broadband - fixed subscriptions: This entry gives the total number of fixed-broadband subscriptions, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Fixed broadband is a physical wired connection to the Internet (e.g., coaxial cable, optical fiber) at speeds equal to or greater than 256 kilobits/second (256 kbit/s).
-
Transportation :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
National air transport system: This entry includes four subfields describing the air transport system of a given country in terms of both structure and performance. The first subfield, number of registered air carriers, indicates the total number of air carriers registered with the country’s national aviation authority and issued an air operator certificate as required by the Convention on International Civil Aviation. The second subfield, inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers, lists the total number . . . more
 number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 1Civil aircraft registration country code prefix: This entry provides the one- or two-character alphanumeric code indicating the nationality of civil aircraft. Article 20 of the Convention on International Civil Aviation (Chicago Convention), signed in 1944, requires that all aircraft engaged in international air navigation bear appropriate nationality marks. The aircraft registration number consists of two parts: a prefix consisting of a one- or two-character alphanumeric code indicating nationality and a registration suffix of one to fi . . . more
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 1Civil aircraft registration country code prefix: This entry provides the one- or two-character alphanumeric code indicating the nationality of civil aircraft. Article 20 of the Convention on International Civil Aviation (Chicago Convention), signed in 1944, requires that all aircraft engaged in international air navigation bear appropriate nationality marks. The aircraft registration number consists of two parts: a prefix consisting of a one- or two-character alphanumeric code indicating nationality and a registration suffix of one to fi . . . more S9 (2016)Airports: This entry gives the total number of airports or airfields recognizable from the air. The runway(s) may be paved (concrete or asphalt surfaces) or unpaved (grass, earth, sand, or gravel surfaces) and may include closed or abandoned installations. Airports or airfields that are no longer recognizable (overgrown, no facilities, etc.) are not included. Note that not all airports have accommodations for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control.
S9 (2016)Airports: This entry gives the total number of airports or airfields recognizable from the air. The runway(s) may be paved (concrete or asphalt surfaces) or unpaved (grass, earth, sand, or gravel surfaces) and may include closed or abandoned installations. Airports or airfields that are no longer recognizable (overgrown, no facilities, etc.) are not included. Note that not all airports have accommodations for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control. 2 (2013)country comparison to the world: 205Airports - with paved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with paved runways (concrete or asphalt surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listing. Not all . . . more
2 (2013)country comparison to the world: 205Airports - with paved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with paved runways (concrete or asphalt surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listing. Not all . . . more total: 2 (2019)1,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 1Roadways: This entry gives the total length of the road network and includes the length of the paved and unpaved portions.
total: 2 (2019)1,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 1Roadways: This entry gives the total length of the road network and includes the length of the paved and unpaved portions. total: 1,300 km (2018)paved: 230 km (2018)unpaved: 1,070 km (2018)country comparison to the world: 177Merchant marine: This entry provides the total and the number of each type of privately or publicly owned commercial ship for each country; military ships are not included; the five ships by type include: bulk carrier - for cargo such as coal, grain, cement, ores, and gravel; container ship - for loads in truck-size containers, a transportation system called containerization; general cargo - also referred to as break-bulk containers - for a wide variety of packaged merchandise, such as textiles, furniture . . . more
total: 1,300 km (2018)paved: 230 km (2018)unpaved: 1,070 km (2018)country comparison to the world: 177Merchant marine: This entry provides the total and the number of each type of privately or publicly owned commercial ship for each country; military ships are not included; the five ships by type include: bulk carrier - for cargo such as coal, grain, cement, ores, and gravel; container ship - for loads in truck-size containers, a transportation system called containerization; general cargo - also referred to as break-bulk containers - for a wide variety of packaged merchandise, such as textiles, furniture . . . more Ports and terminals: This entry lists major ports and terminals primarily on the basis of the amount of cargo tonnage shipped through the facilities on an annual basis. In some instances, the number of containers handled or ship visits were also considered. Most ports service multiple classes of vessels including bulk carriers (dry and liquid), break bulk cargoes (goods loaded individually in bags, boxes, crates, or drums; sometimes palletized), containers, roll-on/roll-off, and passenger ships. The listing le . . . more
Ports and terminals: This entry lists major ports and terminals primarily on the basis of the amount of cargo tonnage shipped through the facilities on an annual basis. In some instances, the number of containers handled or ship visits were also considered. Most ports service multiple classes of vessels including bulk carriers (dry and liquid), break bulk cargoes (goods loaded individually in bags, boxes, crates, or drums; sometimes palletized), containers, roll-on/roll-off, and passenger ships. The listing le . . . more major seaport(s): Sao Tome
major seaport(s): Sao Tome -
Military and Security :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
Military and security forces: This entry lists the military and security forces subordinate to defense ministries or the equivalent (typically ground, naval, air, and marine forces), as well as those belonging to interior ministries or the equivalent (typically gendarmeries, border/coast guards, paramilitary police, and other internal security forces).
 Armed Forces of Sao Tome and Principe (Forcas Armadas de Sao Tome e Principe, FASTP): Army, Coast Guard of Sao Tome e Principe (Guarda Costeira de Sao Tome e Principe, GCSTP; also called "Navy"), Presidential Guard, National Guard (2019)Military service age and obligation: This entry gives the required ages for voluntary or conscript military service and the length of service obligation.
Armed Forces of Sao Tome and Principe (Forcas Armadas de Sao Tome e Principe, FASTP): Army, Coast Guard of Sao Tome e Principe (Guarda Costeira de Sao Tome e Principe, GCSTP; also called "Navy"), Presidential Guard, National Guard (2019)Military service age and obligation: This entry gives the required ages for voluntary or conscript military service and the length of service obligation. 18 is the legal minimum age for compulsory military service; 17 is the legal minimum age for voluntary service (2012)
18 is the legal minimum age for compulsory military service; 17 is the legal minimum age for voluntary service (2012) -
Transnational Issues :: Sao Tome and Principe
-
Disputes - international: This entry includes a wide variety of situations that range from traditional bilateral boundary disputes to unilateral claims of one sort or another. Information regarding disputes over international terrestrial and maritime boundaries has been reviewed by the US Department of State. References to other situations involving borders or frontiers may also be included, such as resource disputes, geopolitical questions, or irredentist issues; however, inclusion does not necessarily constitute . . . more

none