Main Content

-

- ABOUT
- REFERENCES
-
APPENDICES
- A: Abbreviations
- B: International Organizations and Groups
- C: Selected International Environmental Agreements
- D: Cross-Reference List of Country Data Codes
- E: Cross-Reference List of Hydrographic Data Codes
- F: Cross-Reference List of Geographic Names
- G: Weights and Measures
- H: Strategic Materials
- T: Terrorist Organizations
- FAQs
- CONTACT
- THE WORLD FACTBOOK ARCHIVE

note: resembles the flag of Kenya; one of only two national flags to display six colors as part of its primary design, the other is South Africa's

Agency Copyright Notice
-
Jump to topic
- Introduction
- Geography
-
People and Society
- Age structure
- Birth rate
- Children under the age of 5 years underweight
- Contraceptive prevalence rate
- Current Health Expenditure
- Death rate
- Demographic profile
- Dependency ratios
- Drinking water source
- Education expenditures
- Ethnic groups
- HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
- HIV/AIDS - deaths
- HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
- Infant mortality rate
- Languages
- Life expectancy at birth
- Literacy
- Major infectious diseases
- Major urban areas - population
- Maternal mortality rate
- Median age
- Nationality
- Net migration rate
- Obesity - adult prevalence rate
- Population
- Population distribution
- Population growth rate
- Religions
- Sanitation facility access
- Sex ratio
- Total fertility rate
- Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
- Urbanization
-
Government
- Administrative divisions
- Capital
- Citizenship
- Constitution
- Country name
- Diplomatic representation from the US
- Diplomatic representation in the US
- Executive branch
- Flag description
- Government type
- Independence
- International organization participation
- Judicial branch
- Legislative branch
- National anthem
- National holiday
- National symbol(s)
- Political parties and leaders
- Suffrage
-
Economy
- Agriculture - products
- Budget
- Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)
- Current account balance
- Ease of Doing Business Index scores
- Economic overview
- Exchange rates
- Exports
- GDP - composition, by end use
- GDP - per capita (PPP)
- GDP (official exchange rate)
- GDP (purchasing power parity) - real
- GDP real growth rate
- Gross national saving
- Imports
- Inflation rate (consumer prices)
- Population below poverty line
- Public debt
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
- Taxes and other revenues
-
Energy
- Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy
- Crude oil - exports
- Crude oil - imports
- Crude oil - production
- Crude oil - proved reserves
- Electricity - consumption
- Electricity - exports
- Electricity - from fossil fuels
- Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
- Electricity - from nuclear fuels
- Electricity - from other renewable sources
- Electricity - imports
- Electricity - installed generating capacity
- Electricity - production
- Electricity access
- Natural gas - consumption
- Natural gas - exports
- Natural gas - imports
- Natural gas - production
- Natural gas - proved reserves
- Refined petroleum products - consumption
- Refined petroleum products - exports
- Refined petroleum products - imports
- Refined petroleum products - production
- Communications
- Transportation
- Military and Security
- Transnational Issues
-
Introduction :: South Sudan
-
Background: This entry usually highlights major historic events and current issues and may include a statement about one or two key future trends.

British explorer Samuel BAKER established the colony of Equatoria in 1870, in the name of the Ottoman Khedive of Egypt who claimed the territory. Headquartered in Gondokoro (near modern day Juba), Equatoria in theory composed most of what is now South Sudan. After being cut off from colonial administration during the Mahdist War from 1885-1898, Equatoria was made a state under the Anglo-Egyptian condominium in 1899. It was largely left to itself over the following decades, but Christian missionaries converted much of the population and facilitated the spread of English, rather than Arabic. Equatoria was ruled by British colonial administrators separately from what is now Sudan until the two colonies were combined at the 1947 Juba Conference, as part of British plans to prepare the region for independence. When Sudan gained its independence in 1956, it was with the understanding that the southerners would be able to participate fully in the political system. When the Arab Khartoum government reneged on its promises, a mutiny began that led to two prolonged periods of conflict (1955-1972 and 1983-2005) in which perhaps 2.5 million people died - mostly civilians - due to starvation and drought. Ongoing peace talks finally resulted in a Comprehensive Peace Agreement, signed in January 2005. As part of this agreement, the south was granted a six-year period of autonomy to be followed by a referendum on final status. The result of this referendum, held in January 2011, was a vote of 98% in favor of secession.
Since independence on 9 July 2011, South Sudan has struggled with good governance and nation building and has attempted to control opposition forces operating in its territory. Economic conditions have deteriorated since January 2012 when the government decided to shut down oil production following bilateral disagreements with Sudan. In December 2013, conflict between government and opposition forces killed tens of thousands and led to a dire humanitarian crisis with millions of South Sudanese displaced and food insecure. The warring parties signed a peace agreement in August 2015 that created a transitional government of national unity in April 2016. However, in July 2016, fighting broke out in Juba between the two principal signatories, plunging the country back into conflict. A "revitalized" peace agreement was signed in September 2018 ending the fighting. Under the agreement, the government and various rebel groups agreed that the sides would form a unified national army and create a transitional government by May 2019. The agreement was extended until November 2019 and then subsequently to February 2020. However, implementation has been stalled, in part by a failure to agree on the country's internal political boundaries. -
Geography :: South Sudan
-
Location: This entry identifies the country's regional location, neighboring countries, and adjacent bodies of water.
 East-Central Africa; south of Sudan, north of Uganda and Kenya, west of EthiopiaGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names.
East-Central Africa; south of Sudan, north of Uganda and Kenya, west of EthiopiaGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names. 8 00 N, 30 00 EMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries.
8 00 N, 30 00 EMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries. AfricaArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines.
AfricaArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres).
Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres). more than four times the size of Georgia; slightly smaller than TexasArea comparison map:
more than four times the size of Georgia; slightly smaller than TexasArea comparison map: The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: South Sudan Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: South Sudan Print Image Description
Image Descriptionmore than four times the size of Georgia; slightly smaller than Texas
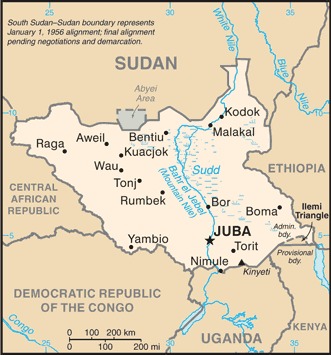
Land boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ. total: 6,018 kmborder countries (6): Central African Republic 1055 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 714 km, Ethiopia 1299 km, Kenya 317 km, Sudan 2158 km, Uganda 475 km
total: 6,018 kmborder countries (6): Central African Republic 1055 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 714 km, Ethiopia 1299 km, Kenya 317 km, Sudan 2158 km, Uganda 475 kmnote: South Sudan-Sudan boundary represents 1 January 1956 alignment; final alignment pending negotiations and demarcation; final sovereignty status of Abyei Area pending negotiations between South Sudan and Sudan
Coastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea. 0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more
0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more none (landlocked)Climate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more
none (landlocked)Climate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more hot with seasonal rainfall influenced by the annual shift of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone; rainfall heaviest in upland areas of the south and diminishes to the northTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography.
hot with seasonal rainfall influenced by the annual shift of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone; rainfall heaviest in upland areas of the south and diminishes to the northTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography. plains in the north and center rise to southern highlands along the border with Uganda and Kenya; the White Nile, flowing north out of the uplands of Central Africa, is the major geographic feature of the country; The Sudd (a name derived from floating vegetation that hinders navigation) is a large swampy area of more than 100,000 sq km fed by the waters of the White Nile that dominates the center of the countryElevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point.
plains in the north and center rise to southern highlands along the border with Uganda and Kenya; the White Nile, flowing north out of the uplands of Central Africa, is the major geographic feature of the country; The Sudd (a name derived from floating vegetation that hinders navigation) is a large swampy area of more than 100,000 sq km fed by the waters of the White Nile that dominates the center of the countryElevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point. lowest point: White Nile 381 mhighest point: Kinyeti 3,187 mNatural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future.
lowest point: White Nile 381 mhighest point: Kinyeti 3,187 mNatural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future. hydropower, fertile agricultural land, gold, diamonds, petroleum, hardwoods, limestone, iron ore, copper, chromium ore, zinc, tungsten, mica, silverLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more
hydropower, fertile agricultural land, gold, diamonds, petroleum, hardwoods, limestone, iron ore, copper, chromium ore, zinc, tungsten, mica, silverLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more agricultural land: 100%arable land: 0% / permanent crops: 0% / permanent pasture: 100%forest: 0%other: 0%Irrigated land: This entry gives the number of square kilometers of land area that is artificially supplied with water.
agricultural land: 100%arable land: 0% / permanent crops: 0% / permanent pasture: 100%forest: 0%other: 0%Irrigated land: This entry gives the number of square kilometers of land area that is artificially supplied with water. 1,000 sq km (2012)Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures.
1,000 sq km (2012)Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures. clusters found in urban areas, particularly in the western interior and around the White Nile as shown in this population distribution mapEnvironment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more
clusters found in urban areas, particularly in the western interior and around the White Nile as shown in this population distribution mapEnvironment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more water pollution; inadequate supplies of potable water; wildlife conservation and loss of biodiversity; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; periodic droughtGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere.
water pollution; inadequate supplies of potable water; wildlife conservation and loss of biodiversity; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; periodic droughtGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere. landlocked; The Sudd is a vast swamp in the north central region of South Sudan, formed by the White Nile, its size is variable but can reach some 15% of the country's total area during the rainy season; it is one of the world's largest wetlands
landlocked; The Sudd is a vast swamp in the north central region of South Sudan, formed by the White Nile, its size is variable but can reach some 15% of the country's total area during the rainy season; it is one of the world's largest wetlands -
People and Society :: South Sudan
-
Population: This entry gives an estimate from the US Bureau of the Census based on statistics from population censuses, vital statistics registration systems, or sample surveys pertaining to the recent past and on assumptions about future trends. The total population presents one overall measure of the potential impact of the country on the world and within its region. Note: Starting with the 1993 Factbook, demographic estimates for some countries (mostly African) have explicitly taken into account t . . . more
 10,561,244 (July 2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Nationality: This entry provides the identifying terms for citizens - noun and adjective.
10,561,244 (July 2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Nationality: This entry provides the identifying terms for citizens - noun and adjective. noun: South Sudanese (singular and plural)adjective: South SudaneseEthnic groups: This entry provides an ordered listing of ethnic groups starting with the largest and normally includes the percent of total population.
noun: South Sudanese (singular and plural)adjective: South SudaneseEthnic groups: This entry provides an ordered listing of ethnic groups starting with the largest and normally includes the percent of total population. Dinka (Jieng) 35.8%, Nuer (Naath) 15.6%, Shilluk (Chollo), Azande, Bari, Kakwa, Kuku, Murle, Mandari, Didinga, Ndogo, Bviri, Lndi, Anuak, Bongo, Lango, Dungotona, Acholi, Baka, Fertit (2011 est.)Languages: This entry provides a listing of languages spoken in each country and specifies any that are official national or regional languages. When data is available, the languages spoken in each country are broken down according to the percent of the total population speaking each language as a first language. For those countries without available data, languages are listed in rank order based on prevalence, starting with the most-spoken language.
Dinka (Jieng) 35.8%, Nuer (Naath) 15.6%, Shilluk (Chollo), Azande, Bari, Kakwa, Kuku, Murle, Mandari, Didinga, Ndogo, Bviri, Lndi, Anuak, Bongo, Lango, Dungotona, Acholi, Baka, Fertit (2011 est.)Languages: This entry provides a listing of languages spoken in each country and specifies any that are official national or regional languages. When data is available, the languages spoken in each country are broken down according to the percent of the total population speaking each language as a first language. For those countries without available data, languages are listed in rank order based on prevalence, starting with the most-spoken language. English (official), Arabic (includes Juba and Sudanese variants), regional languages include Dinka, Nuer, Bari, Zande, ShillukReligions: This entry is an ordered listing of religions by adherents starting with the largest group and sometimes includes the percent of total population. The core characteristics and beliefs of the world's major religions are described below. Baha'i - Founded by Mirza Husayn-Ali (known as Baha'u'llah) in Iran in 1852, Baha'i faith emphasizes monotheism and believes in one eternal transcendent God. Its guiding focus is to encourage the unity of all peoples on the earth so that justice and peace m . . . more
English (official), Arabic (includes Juba and Sudanese variants), regional languages include Dinka, Nuer, Bari, Zande, ShillukReligions: This entry is an ordered listing of religions by adherents starting with the largest group and sometimes includes the percent of total population. The core characteristics and beliefs of the world's major religions are described below. Baha'i - Founded by Mirza Husayn-Ali (known as Baha'u'llah) in Iran in 1852, Baha'i faith emphasizes monotheism and believes in one eternal transcendent God. Its guiding focus is to encourage the unity of all peoples on the earth so that justice and peace m . . . more animist, Christian, MuslimDemographic profile: This entry describes a country’s key demographic features and trends and how they vary among regional, ethnic, and socioeconomic sub-populations. Some of the topics addressed are population age structure, fertility, health, mortality, poverty, education, and migration.
animist, Christian, MuslimDemographic profile: This entry describes a country’s key demographic features and trends and how they vary among regional, ethnic, and socioeconomic sub-populations. Some of the topics addressed are population age structure, fertility, health, mortality, poverty, education, and migration.
South Sudan, independent from Sudan since July 2011 after decades of civil war, is one of the world’s poorest countries and ranks among the lowest in many socioeconomic categories. Problems are exacerbated by ongoing tensions with Sudan over oil revenues and land borders, fighting between government forces and rebel groups, and inter-communal violence. Most of the population lives off of farming, while smaller numbers rely on animal husbandry; more than 80% of the populace lives in rural areas. The maternal mortality rate is among the world’s highest for a variety of reasons, including a shortage of health care workers, facilities, and supplies; poor roads and a lack of transport; and cultural beliefs that prevent women from seeking obstetric care. Most women marry and start having children early, giving birth at home with the assistance of traditional birth attendants, who are unable to handle complications.
Educational attainment is extremely poor due to the lack of schools, qualified teachers, and materials. Less than a third of the population is literate (the rate is even lower among women), and half live below the poverty line. Teachers and students are also struggling with the switch from Arabic to English as the language of instruction. Many adults missed out on schooling because of warfare and displacement.
Almost 2 million South Sudanese have sought refuge in neighboring countries since the current conflict began in December 2013. Another 1.96 million South Sudanese are internally displaced as of August 2017. Despite South Sudan’s instability and lack of infrastructure and social services, more than 240,000 people have fled to South Sudan to escape fighting in Sudan.
Age structure: This entry provides the distribution of the population according to age. Information is included by sex and age group as follows: 0-14 years (children), 15-24 years (early working age), 25-54 years (prime working age), 55-64 years (mature working age), 65 years and over (elderly). The age structure of a population affects a nation's key socioeconomic issues. Countries with young populations (high percentage under age 15) need to invest more in schools, while countries with older population . . . more 0-14 years: 41.58% (male 2,238,534/female 2,152,685)15-24 years: 21.28% (male 1,153,108/female 1,094,568)25-54 years: 30.67% (male 1,662,409/female 1,577,062)55-64 years: 3.93% (male 228,875/female 186,571)65 years and over: 2.53% (male 153,502/female 113,930) (2020 est.)population pyramid:The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: South Sudan PrintImage DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for South Sudan. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
0-14 years: 41.58% (male 2,238,534/female 2,152,685)15-24 years: 21.28% (male 1,153,108/female 1,094,568)25-54 years: 30.67% (male 1,662,409/female 1,577,062)55-64 years: 3.93% (male 228,875/female 186,571)65 years and over: 2.53% (male 153,502/female 113,930) (2020 est.)population pyramid:The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: South Sudan PrintImage DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for South Sudan. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios: Dependency ratios are a measure of the age structure of a population. They relate the number of individuals that are likely to be economically "dependent" on the support of others. Dependency ratios contrast the ratio of youths (ages 0-14) and the elderly (ages 65+) to the number of those in the working-age group (ages 15-64). Changes in the dependency ratio provide an indication of potential social support requirements resulting from changes in population age structures. As fertility leve . . . more total dependency ratio: 80.8youth dependency ratio: 74.7elderly dependency ratio: 6.1potential support ratio: 16.5 (2020 est.)Median age: This entry is the age that divides a population into two numerically equal groups; that is, half the people are younger than this age and half are older. It is a single index that summarizes the age distribution of a population. Currently, the median age ranges from a low of about 15 in Niger and Uganda to 40 or more in several European countries and Japan. See the entry for "Age structure" for the importance of a young versus an older age structure and, by implication, a low versus a high . . . more
total dependency ratio: 80.8youth dependency ratio: 74.7elderly dependency ratio: 6.1potential support ratio: 16.5 (2020 est.)Median age: This entry is the age that divides a population into two numerically equal groups; that is, half the people are younger than this age and half are older. It is a single index that summarizes the age distribution of a population. Currently, the median age ranges from a low of about 15 in Niger and Uganda to 40 or more in several European countries and Japan. See the entry for "Age structure" for the importance of a young versus an older age structure and, by implication, a low versus a high . . . more total: 18.6 yearsmale: 18.9 yearsfemale: 18.3 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Population growth rate: The average annual percent change in the population, resulting from a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths and the balance of migrants entering and leaving a country. The rate may be positive or negative. The growth rate is a factor in determining how great a burden would be imposed on a country by the changing needs of its people for infrastructure (e.g., schools, hospitals, housing, roads), resources (e.g., food, water, electricity), and jobs. Rapid population growth can be seen as . . . more
total: 18.6 yearsmale: 18.9 yearsfemale: 18.3 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Population growth rate: The average annual percent change in the population, resulting from a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths and the balance of migrants entering and leaving a country. The rate may be positive or negative. The growth rate is a factor in determining how great a burden would be imposed on a country by the changing needs of its people for infrastructure (e.g., schools, hospitals, housing, roads), resources (e.g., food, water, electricity), and jobs. Rapid population growth can be seen as . . . more 2.7% (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 16Birth rate: This entry gives the average annual number of births during a year per 1,000 persons in the population at midyear; also known as crude birth rate. The birth rate is usually the dominant factor in determining the rate of population growth. It depends on both the level of fertility and the age structure of the population.
2.7% (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 16Birth rate: This entry gives the average annual number of births during a year per 1,000 persons in the population at midyear; also known as crude birth rate. The birth rate is usually the dominant factor in determining the rate of population growth. It depends on both the level of fertility and the age structure of the population. 38.8 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 10Death rate: This entry gives the average annual number of deaths during a year per 1,000 population at midyear; also known as crude death rate. The death rate, while only a rough indicator of the mortality situation in a country, accurately indicates the current mortality impact on population growth. This indicator is significantly affected by age distribution, and most countries will eventually show a rise in the overall death rate, in spite of continued decline in mortality at all ages, as declining . . . more
38.8 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 10Death rate: This entry gives the average annual number of deaths during a year per 1,000 population at midyear; also known as crude death rate. The death rate, while only a rough indicator of the mortality situation in a country, accurately indicates the current mortality impact on population growth. This indicator is significantly affected by age distribution, and most countries will eventually show a rise in the overall death rate, in spite of continued decline in mortality at all ages, as declining . . . more 11.4 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Net migration rate: This entry includes the figure for the difference between the number of persons entering and leaving a country during the year per 1,000 persons (based on midyear population). An excess of persons entering the country is referred to as net immigration (e.g., 3.56 migrants/1,000 population); an excess of persons leaving the country as net emigration (e.g., -9.26 migrants/1,000 population). The net migration rate indicates the contribution of migration to the overall level of population chan . . . more
11.4 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Net migration rate: This entry includes the figure for the difference between the number of persons entering and leaving a country during the year per 1,000 persons (based on midyear population). An excess of persons entering the country is referred to as net immigration (e.g., 3.56 migrants/1,000 population); an excess of persons leaving the country as net emigration (e.g., -9.26 migrants/1,000 population). The net migration rate indicates the contribution of migration to the overall level of population chan . . . more 0.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures.
0.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures. clusters found in urban areas, particularly in the western interior and around the White Nile as shown in this population distribution mapUrbanization: This entry provides two measures of the degree of urbanization of a population. The first, urban population, describes the percentage of the total population living in urban areas, as defined by the country. The second, rate of urbanization, describes the projected average rate of change of the size of the urban population over the given period of time. It is possible for a country with a 100% urban population to still display a change in the rate of urbanization (up or down). For example . . . more
clusters found in urban areas, particularly in the western interior and around the White Nile as shown in this population distribution mapUrbanization: This entry provides two measures of the degree of urbanization of a population. The first, urban population, describes the percentage of the total population living in urban areas, as defined by the country. The second, rate of urbanization, describes the projected average rate of change of the size of the urban population over the given period of time. It is possible for a country with a 100% urban population to still display a change in the rate of urbanization (up or down). For example . . . more urban population: 20.2% of total population (2020)rate of urbanization: 4.1% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population: This entry provides the population of the capital and up to six major cities defined as urban agglomerations with populations of at least 750,000 people. An urban agglomeration is defined as comprising the city or town proper and also the suburban fringe or thickly settled territory lying outside of, but adjacent to, the boundaries of the city. For smaller countries, lacking urban centers of 750,000 or more, only the population of the capital is presented.
urban population: 20.2% of total population (2020)rate of urbanization: 4.1% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population: This entry provides the population of the capital and up to six major cities defined as urban agglomerations with populations of at least 750,000 people. An urban agglomeration is defined as comprising the city or town proper and also the suburban fringe or thickly settled territory lying outside of, but adjacent to, the boundaries of the city. For smaller countries, lacking urban centers of 750,000 or more, only the population of the capital is presented. 403,000 JUBA (capital) (2020)Sex ratio: This entry includes the number of males for each female in five age groups - at birth, under 15 years, 15-64 years, 65 years and over, and for the total population. Sex ratio at birth has recently emerged as an indicator of certain kinds of sex discrimination in some countries. For instance, high sex ratios at birth in some Asian countries are now attributed to sex-selective abortion and infanticide due to a strong preference for sons. This will affect future marriage patterns and fertilit . . . more
403,000 JUBA (capital) (2020)Sex ratio: This entry includes the number of males for each female in five age groups - at birth, under 15 years, 15-64 years, 65 years and over, and for the total population. Sex ratio at birth has recently emerged as an indicator of certain kinds of sex discrimination in some countries. For instance, high sex ratios at birth in some Asian countries are now attributed to sex-selective abortion and infanticide due to a strong preference for sons. This will affect future marriage patterns and fertilit . . . more at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.05 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.23 male(s)/female65 years and over: 1.35 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2020 est.)Maternal mortality rate: The maternal mortality rate (MMR) is the annual number of female deaths per 100,000 live births from any cause related to or aggravated by pregnancy or its management (excluding accidental or incidental causes). The MMR includes deaths during pregnancy, childbirth, or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, for a specified year.
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.05 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.23 male(s)/female65 years and over: 1.35 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2020 est.)Maternal mortality rate: The maternal mortality rate (MMR) is the annual number of female deaths per 100,000 live births from any cause related to or aggravated by pregnancy or its management (excluding accidental or incidental causes). The MMR includes deaths during pregnancy, childbirth, or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, for a specified year. 1,150 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Infant mortality rate: This entry gives the number of deaths of infants under one year old in a given year per 1,000 live births in the same year. This rate is often used as an indicator of the level of health in a country.
1,150 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Infant mortality rate: This entry gives the number of deaths of infants under one year old in a given year per 1,000 live births in the same year. This rate is often used as an indicator of the level of health in a country. total: 69.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 76 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 63.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Life expectancy at birth: This entry contains the average number of years to be lived by a group of people born in the same year, if mortality at each age remains constant in the future. Life expectancy at birth is also a measure of overall quality of life in a country and summarizes the mortality at all ages. It can also be thought of as indicating the potential return on investment in human capital and is necessary for the calculation of various actuarial measures.
total: 69.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 76 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 63.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Life expectancy at birth: This entry contains the average number of years to be lived by a group of people born in the same year, if mortality at each age remains constant in the future. Life expectancy at birth is also a measure of overall quality of life in a country and summarizes the mortality at all ages. It can also be thought of as indicating the potential return on investment in human capital and is necessary for the calculation of various actuarial measures. total population: 55.5 yearsmale: 54.6 yearsfemale: 56.5 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 222Total fertility rate: This entry gives a figure for the average number of children that would be born per woman if all women lived to the end of their childbearing years and bore children according to a given fertility rate at each age. The total fertility rate (TFR) is a more direct measure of the level of fertility than the crude birth rate, since it refers to births per woman. This indicator shows the potential for population change in the country. A rate of two children per woman is considered the replaceme . . . more
total population: 55.5 yearsmale: 54.6 yearsfemale: 56.5 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 222Total fertility rate: This entry gives a figure for the average number of children that would be born per woman if all women lived to the end of their childbearing years and bore children according to a given fertility rate at each age. The total fertility rate (TFR) is a more direct measure of the level of fertility than the crude birth rate, since it refers to births per woman. This indicator shows the potential for population change in the country. A rate of two children per woman is considered the replaceme . . . more 5.54 children born/woman (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Contraceptive prevalence rate: This field gives the percent of women of reproductive age (15-49) who are married or in union and are using, or whose sexual partner is using, a method of contraception according to the date of the most recent available data. The contraceptive prevalence rate is an indicator of health services, development, and women’s empowerment. It is also useful in understanding, past, present, and future fertility trends, especially in developing countries.
5.54 children born/woman (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Contraceptive prevalence rate: This field gives the percent of women of reproductive age (15-49) who are married or in union and are using, or whose sexual partner is using, a method of contraception according to the date of the most recent available data. The contraceptive prevalence rate is an indicator of health services, development, and women’s empowerment. It is also useful in understanding, past, present, and future fertility trends, especially in developing countries. 4% (2010)Drinking water source: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved drinking water sources available to segments of the population of a country. Improved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: piped water into dwelling, yard, or plot; public tap or standpipe; tubewell or borehole; protected dug well; protected spring; or rainwater collection. Unimproved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: unprotected dug well; unprotected spring; cart with small tank or . . . more
4% (2010)Drinking water source: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved drinking water sources available to segments of the population of a country. Improved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: piped water into dwelling, yard, or plot; public tap or standpipe; tubewell or borehole; protected dug well; protected spring; or rainwater collection. Unimproved drinking water - use of any of the following sources: unprotected dug well; unprotected spring; cart with small tank or . . . more improved: urban: 85.2% of populationrural: 71.7% of populationtotal: 74.3% of populationunimproved: urban: 14.8% of populationrural: 28.3% of populationtotal: 25.7% of population (2017 est.)Current Health Expenditure: Current Health Expenditure (CHE) describes the share of spending on health in each country relative to the size of its economy. It includes expenditures corresponding to the final consumption of health care goods and services and excludes investment, exports, and intermediate consumption. CHE shows the importance of the health sector in the economy and indicates the priority given to health in monetary terms. Note: Current Health Expenditure replaces the former Health Expenditures field . . . more
improved: urban: 85.2% of populationrural: 71.7% of populationtotal: 74.3% of populationunimproved: urban: 14.8% of populationrural: 28.3% of populationtotal: 25.7% of population (2017 est.)Current Health Expenditure: Current Health Expenditure (CHE) describes the share of spending on health in each country relative to the size of its economy. It includes expenditures corresponding to the final consumption of health care goods and services and excludes investment, exports, and intermediate consumption. CHE shows the importance of the health sector in the economy and indicates the priority given to health in monetary terms. Note: Current Health Expenditure replaces the former Health Expenditures field . . . more 9.8% (2017)Sanitation facility access: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved sanitation facilities available to segments of the population of a country. Improved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush to a piped sewer system, septic tank or pit latrine; ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrine; pit latrine with slab; or a composting toilet. Unimproved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush not piped to a sewer system, septic tank . . . more
9.8% (2017)Sanitation facility access: This entry provides information about access to improved or unimproved sanitation facilities available to segments of the population of a country. Improved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush to a piped sewer system, septic tank or pit latrine; ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrine; pit latrine with slab; or a composting toilet. Unimproved sanitation - use of any of the following facilities: flush or pour-flush not piped to a sewer system, septic tank . . . more improved: urban: 54.1% of populationrural: 10.7% of populationtotal: 19.1% of populationunimproved: urban: 45.9% of populationrural: 89.3% of populationtotal: 80.9% of population (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives an estimate of the percentage of adults (aged 15-49) living with HIV/AIDS. The adult prevalence rate is calculated by dividing the estimated number of adults living with HIV/AIDS at yearend by the total adult population at yearend.
improved: urban: 54.1% of populationrural: 10.7% of populationtotal: 19.1% of populationunimproved: urban: 45.9% of populationrural: 89.3% of populationtotal: 80.9% of population (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives an estimate of the percentage of adults (aged 15-49) living with HIV/AIDS. The adult prevalence rate is calculated by dividing the estimated number of adults living with HIV/AIDS at yearend by the total adult population at yearend. 2.4% (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 21HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: This entry gives an estimate of all people (adults and children) alive at yearend with HIV infection, whether or not they have developed symptoms of AIDS.
2.4% (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 21HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: This entry gives an estimate of all people (adults and children) alive at yearend with HIV infection, whether or not they have developed symptoms of AIDS. 190,000 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 34HIV/AIDS - deaths: This entry gives an estimate of the number of adults and children who died of AIDS during a given calendar year.
190,000 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 34HIV/AIDS - deaths: This entry gives an estimate of the number of adults and children who died of AIDS during a given calendar year. 9,100 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Major infectious diseases: This entry lists major infectious diseases likely to be encountered in countries where the risk of such diseases is assessed to be very high as compared to the United States. These infectious diseases represent risks to US government personnel traveling to the specified country for a period of less than three years. The degree of risk is assessed by considering the foreign nature of these infectious diseases, their severity, and the probability of being affected by the diseases present. Th . . . more
9,100 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Major infectious diseases: This entry lists major infectious diseases likely to be encountered in countries where the risk of such diseases is assessed to be very high as compared to the United States. These infectious diseases represent risks to US government personnel traveling to the specified country for a period of less than three years. The degree of risk is assessed by considering the foreign nature of these infectious diseases, their severity, and the probability of being affected by the diseases present. Th . . . more degree of risk: very high (2020)food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, Trypanosomiasis-Gambiense (African sleeping sickness)water contact diseases: schistosomiasisanimal contact diseases: rabiesrespiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitisObesity - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives the percent of a country's population considered to be obese. Obesity is defined as an adult having a Body Mass Index (BMI) greater to or equal to 30.0. BMI is calculated by taking a person's weight in kg and dividing it by the person's squared height in meters.
degree of risk: very high (2020)food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, Trypanosomiasis-Gambiense (African sleeping sickness)water contact diseases: schistosomiasisanimal contact diseases: rabiesrespiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitisObesity - adult prevalence rate: This entry gives the percent of a country's population considered to be obese. Obesity is defined as an adult having a Body Mass Index (BMI) greater to or equal to 30.0. BMI is calculated by taking a person's weight in kg and dividing it by the person's squared height in meters. 6.6% (2014)country comparison to the world: 165Children under the age of 5 years underweight: This entry gives the percent of children under five considered to be underweight. Underweight means weight-for-age is approximately 2 kg below for standard at age one, 3 kg below standard for ages two and three, and 4 kg below standard for ages four and five. This statistic is an indicator of the nutritional status of a community. Children who suffer from growth retardation as a result of poor diets and/or recurrent infections tend to have a greater risk of suffering illness and death.
6.6% (2014)country comparison to the world: 165Children under the age of 5 years underweight: This entry gives the percent of children under five considered to be underweight. Underweight means weight-for-age is approximately 2 kg below for standard at age one, 3 kg below standard for ages two and three, and 4 kg below standard for ages four and five. This statistic is an indicator of the nutritional status of a community. Children who suffer from growth retardation as a result of poor diets and/or recurrent infections tend to have a greater risk of suffering illness and death. 27.7% (2010)country comparison to the world: 9Education expenditures: This entry provides the public expenditure on education as a percent of GDP.
27.7% (2010)country comparison to the world: 9Education expenditures: This entry provides the public expenditure on education as a percent of GDP. 1.5% of GDP (2016)country comparison to the world: 168Literacy: This entry includes a definition of literacy and UNESCO's percentage estimates for populations aged 15 years and over, including total population, males, and females. There are no universal definitions and standards of literacy. Unless otherwise specified, all rates are based on the most common definition - the ability to read and write at a specified age. Detailing the standards that individual countries use to assess the ability to read and write is beyond the scope of the Factbook. Info . . . more
1.5% of GDP (2016)country comparison to the world: 168Literacy: This entry includes a definition of literacy and UNESCO's percentage estimates for populations aged 15 years and over, including total population, males, and females. There are no universal definitions and standards of literacy. Unless otherwise specified, all rates are based on the most common definition - the ability to read and write at a specified age. Detailing the standards that individual countries use to assess the ability to read and write is beyond the scope of the Factbook. Info . . . more definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 34.5%male: 40.3%female: 28.9% (2018)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24: This entry gives the percent of the total labor force ages 15-24 unemployed during a specified year.
definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 34.5%male: 40.3%female: 28.9% (2018)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24: This entry gives the percent of the total labor force ages 15-24 unemployed during a specified year.
-
Government :: South Sudan
-
Country name: This entry includes all forms of the country's name approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (Italy is used as an example): conventional long form (Italian Republic), conventional short form (Italy), local long form (Repubblica Italiana), local short form (Italia), former (Kingdom of Italy), as well as the abbreviation. Also see the Terminology note.
 conventional long form: Republic of South Sudanconventional short form: South Sudanetymology: self-descriptive name from the country's former position within Sudan prior to independence; the name "Sudan" derives from the Arabic "bilad-as-sudan" meaning "Land of the Black [peoples]"Government type: This entry gives the basic form of government. Definitions of the major governmental terms are as follows. (Note that for some countries more than one definition applies.): Absolute monarchy - a form of government where the monarch rules unhindered, i.e., without any laws, constitution, or legally organized opposition. Anarchy - a condition of lawlessness or political disorder brought about by the absence of governmental authority. Authoritarian - a form of government in whic . . . more
conventional long form: Republic of South Sudanconventional short form: South Sudanetymology: self-descriptive name from the country's former position within Sudan prior to independence; the name "Sudan" derives from the Arabic "bilad-as-sudan" meaning "Land of the Black [peoples]"Government type: This entry gives the basic form of government. Definitions of the major governmental terms are as follows. (Note that for some countries more than one definition applies.): Absolute monarchy - a form of government where the monarch rules unhindered, i.e., without any laws, constitution, or legally organized opposition. Anarchy - a condition of lawlessness or political disorder brought about by the absence of governmental authority. Authoritarian - a form of government in whic . . . more presidential republicCapital: This entry gives the name of the seat of government, its geographic coordinates, the time difference relative to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and the time observed in Washington, DC, and, if applicable, information on daylight saving time (DST). Where appropriate, a special note has been added to highlight those countries that have multiple time zones.
presidential republicCapital: This entry gives the name of the seat of government, its geographic coordinates, the time difference relative to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and the time observed in Washington, DC, and, if applicable, information on daylight saving time (DST). Where appropriate, a special note has been added to highlight those countries that have multiple time zones. name: Jubageographic coordinates: 04 51 N, 31 37 Etime difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: the name derives from Djouba, another name for the Bari people of South SudanAdministrative divisions: This entry generally gives the numbers, designatory terms, and first-order administrative divisions as approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (BGN). Changes that have been reported but not yet acted on by the BGN are noted. Geographic names conform to spellings approved by the BGN with the exception of the omission of diacritical marks and special characters.
name: Jubageographic coordinates: 04 51 N, 31 37 Etime difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: the name derives from Djouba, another name for the Bari people of South SudanAdministrative divisions: This entry generally gives the numbers, designatory terms, and first-order administrative divisions as approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (BGN). Changes that have been reported but not yet acted on by the BGN are noted. Geographic names conform to spellings approved by the BGN with the exception of the omission of diacritical marks and special characters. 10 states; Central Equatoria, Eastern Equatoria, Jonglei, Lakes, Northern Bahr el Ghazal, Unity, Upper Nile, Warrap, Western Bahr el Ghazal, Western Equatoria; note - in 2015, the creation of 28 new states was announced and in 2017 four additional; following the February 2020 peace agreement, the country was reportedly again reorganized into the 10 original states, plus 2 administrative areas, Pibor and Ruweng, and 1 special administrative status area, Abyei; this latest administrative revision has not yet been vetted by the US Board on Geographic NamesIndependence: For most countries, this entry gives the date that sovereignty was achieved and from which nation, empire, or trusteeship. For the other countries, the date given may not represent "independence" in the strict sense, but rather some significant nationhood event such as the traditional founding date or the date of unification, federation, confederation, establishment, fundamental change in the form of government, or state succession. For a number of countries, the establishment of statehood . . . more
10 states; Central Equatoria, Eastern Equatoria, Jonglei, Lakes, Northern Bahr el Ghazal, Unity, Upper Nile, Warrap, Western Bahr el Ghazal, Western Equatoria; note - in 2015, the creation of 28 new states was announced and in 2017 four additional; following the February 2020 peace agreement, the country was reportedly again reorganized into the 10 original states, plus 2 administrative areas, Pibor and Ruweng, and 1 special administrative status area, Abyei; this latest administrative revision has not yet been vetted by the US Board on Geographic NamesIndependence: For most countries, this entry gives the date that sovereignty was achieved and from which nation, empire, or trusteeship. For the other countries, the date given may not represent "independence" in the strict sense, but rather some significant nationhood event such as the traditional founding date or the date of unification, federation, confederation, establishment, fundamental change in the form of government, or state succession. For a number of countries, the establishment of statehood . . . more 9 July 2011 (from Sudan)National holiday: This entry gives the primary national day of celebration - usually independence day.
9 July 2011 (from Sudan)National holiday: This entry gives the primary national day of celebration - usually independence day. Independence Day, 9 July (2011)Constitution: This entry provides information on a country’s constitution and includes two subfields. The history subfield includes the dates of previous constitutions and the main steps and dates in formulating and implementing the latest constitution. For countries with 1-3 previous constitutions, the years are listed; for those with 4-9 previous, the entry is listed as “several previous,” and for those with 10 or more, the entry is “many previous.” The amendments subfield summarizes the process of am . . . more
Independence Day, 9 July (2011)Constitution: This entry provides information on a country’s constitution and includes two subfields. The history subfield includes the dates of previous constitutions and the main steps and dates in formulating and implementing the latest constitution. For countries with 1-3 previous constitutions, the years are listed; for those with 4-9 previous, the entry is listed as “several previous,” and for those with 10 or more, the entry is “many previous.” The amendments subfield summarizes the process of am . . . more history: previous 2005 (preindependence); latest signed 7 July 2011, effective 9 July 2011 (Transitional Constitution of the Republic of South Sudan, 2011)amendments: proposed by the National Legislature or by the president of the republic; passage requires submission of the proposal to the Legislature at least one month prior to consideration, approval by at least two-thirds majority vote in both houses of the Legislature, and assent of the president; amended 2013, 2015, 2018Citizenship: This entry provides information related to the acquisition and exercise of citizenship; it includes four subfields: citizenship by birth describes the acquisition of citizenship based on place of birth, known as Jus soli, regardless of the citizenship of parents. citizenship by descent only describes the acquisition of citizenship based on the principle of Jus sanguinis, or by descent, where at least one parent is a citizen of the state and being born within the territorial limits of the s . . . more
history: previous 2005 (preindependence); latest signed 7 July 2011, effective 9 July 2011 (Transitional Constitution of the Republic of South Sudan, 2011)amendments: proposed by the National Legislature or by the president of the republic; passage requires submission of the proposal to the Legislature at least one month prior to consideration, approval by at least two-thirds majority vote in both houses of the Legislature, and assent of the president; amended 2013, 2015, 2018Citizenship: This entry provides information related to the acquisition and exercise of citizenship; it includes four subfields: citizenship by birth describes the acquisition of citizenship based on place of birth, known as Jus soli, regardless of the citizenship of parents. citizenship by descent only describes the acquisition of citizenship based on the principle of Jus sanguinis, or by descent, where at least one parent is a citizen of the state and being born within the territorial limits of the s . . . more citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of South Sudandual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: 10 yearsSuffrage: This entry gives the age at enfranchisement and whether the right to vote is universal or restricted.
citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of South Sudandual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: 10 yearsSuffrage: This entry gives the age at enfranchisement and whether the right to vote is universal or restricted. 18 years of age; universalExecutive branch: This entry includes five subentries: chief of state; head of government; cabinet; elections/appointments; election results. Chief of state includes the name, title, and beginning date in office of the titular leader of the country who represents the state at official and ceremonial functions but may not be involved with the day-to-day activities of the government. Head of government includes the name, title of the top executive designated to manage the executive branch of the government, a . . . more
18 years of age; universalExecutive branch: This entry includes five subentries: chief of state; head of government; cabinet; elections/appointments; election results. Chief of state includes the name, title, and beginning date in office of the titular leader of the country who represents the state at official and ceremonial functions but may not be involved with the day-to-day activities of the government. Head of government includes the name, title of the top executive designated to manage the executive branch of the government, a . . . more chief of state: President Salva KIIR Mayardit (since 9 July 2011); First Vice President Riek MACHAR Teny Dhurgon (since 22 February 2020); Vice President James Wani IGGA (since 26 April 2016); Vice President TABAN Deng Gai (since 22 February 2020); Vice President Rebecca Nyandeng Chol GARANG de Mabior (since 22 February 2020); Vice President Hussein ABDELBAGI Ayii (since 22 February 2020); note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Salva KIIR Mayardit (since 9 July 2011); First Vice President Taban Deng GAI (since 26 July 2016); Vice President James Wani IGGA (since 26 April 2016); Vice President TABAN Deng Gai (since 22 February 2020); Vice President Rebecca Nyandeng Chol GARANG de Mabior (since 22 February 2020); Vice President Hussein ABDELBAGI Ayii (since 22 February 2020); note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmentcabinet: National Council of Ministers appointed by the president, approved by the Transitional National Legislative Assemblyelections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 11-15 April 2010 (next election scheduled for 2015 postponed to 2018 and again to 2021)election results: Salva KIIR Mayardit elected president; percent of vote - Salva KIIR Mayardit (SPLM) 93%, Lam AKOL (SPLM-DC) 7%Legislative branch: This entry has three subfields. The description subfield provides the legislative structure (unicameral – single house; bicameral – an upper and a lower house); formal name(s); number of member seats; types of constituencies or voting districts (single seat, multi-seat, nationwide); electoral voting system(s); and member term of office. The elections subfield includes the dates of the last election and next election. The election results subfield lists percent of vote by party/coalition an . . . more
chief of state: President Salva KIIR Mayardit (since 9 July 2011); First Vice President Riek MACHAR Teny Dhurgon (since 22 February 2020); Vice President James Wani IGGA (since 26 April 2016); Vice President TABAN Deng Gai (since 22 February 2020); Vice President Rebecca Nyandeng Chol GARANG de Mabior (since 22 February 2020); Vice President Hussein ABDELBAGI Ayii (since 22 February 2020); note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Salva KIIR Mayardit (since 9 July 2011); First Vice President Taban Deng GAI (since 26 July 2016); Vice President James Wani IGGA (since 26 April 2016); Vice President TABAN Deng Gai (since 22 February 2020); Vice President Rebecca Nyandeng Chol GARANG de Mabior (since 22 February 2020); Vice President Hussein ABDELBAGI Ayii (since 22 February 2020); note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmentcabinet: National Council of Ministers appointed by the president, approved by the Transitional National Legislative Assemblyelections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 11-15 April 2010 (next election scheduled for 2015 postponed to 2018 and again to 2021)election results: Salva KIIR Mayardit elected president; percent of vote - Salva KIIR Mayardit (SPLM) 93%, Lam AKOL (SPLM-DC) 7%Legislative branch: This entry has three subfields. The description subfield provides the legislative structure (unicameral – single house; bicameral – an upper and a lower house); formal name(s); number of member seats; types of constituencies or voting districts (single seat, multi-seat, nationwide); electoral voting system(s); and member term of office. The elections subfield includes the dates of the last election and next election. The election results subfield lists percent of vote by party/coalition an . . . more description: bicameral National Legislature consists of:
description: bicameral National Legislature consists of:
Council of States, established by presidential decree in August 2011 (50 seats; 20 former members of the Council of States and 30 appointed representatives)
Transitional National Legislative Assembly, established on 4 August 2016, in accordance with the August 2015 Agreement on the Resolution of the Conflict in the Republic of South Sudan (400 seats; 170 members elected in April 2010, 96 members of the former National Assembly, 66 members appointed after independence, and 68 members added as a result of the 2016 Agreement); the TNLA will be expanded to 550 members after the transitional government formselections:
Council of States - established and members appointed 1 August 2011
National Legislative Assembly - last held 11-15 April 2010 but did not take office until July 2011; current parliamentary term extended until 2021)election results:
Council of States - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - SPLM 20, unknown 30; composition - men 44, women 6, percent of women 12%
National Legislative Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - SPLM 251, DCP 10, independent 6, unknown 133; composition - men 291, women 109, percent of women 27.3%; note - total National Legislature percent of women 25.6%Judicial branch: This entry includes three subfields. The highest court(s) subfield includes the name(s) of a country's highest level court(s), the number and titles of the judges, and the types of cases heard by the court, which commonly are based on civil, criminal, administrative, and constitutional law. A number of countries have separate constitutional courts. The judge selection and term of office subfield includes the organizations and associated officials responsible for nominating and appointing j . . . more highest courts: Supreme Court of South Sudan (consists of the chief and deputy chief justices, 9 other justices and normally organized into panels of 3 justices, except when sitting as a Constitutional panel of all 9 justices chaired by the chief justice)judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the president upon proposal of the Judicial Service Council, a 9-member judicial and administrative body; justice tenure set by the National Legislaturesubordinate courts: national level - Courts of Appeal; High Courts; County Courts; state level - High Courts; County Courts; customary courts; other specialized courts and tribunalsPolitical parties and leaders: This entry includes a listing of significant political parties, coalitions, and electoral lists as of each country's last legislative election, unless otherwise noted.
highest courts: Supreme Court of South Sudan (consists of the chief and deputy chief justices, 9 other justices and normally organized into panels of 3 justices, except when sitting as a Constitutional panel of all 9 justices chaired by the chief justice)judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the president upon proposal of the Judicial Service Council, a 9-member judicial and administrative body; justice tenure set by the National Legislaturesubordinate courts: national level - Courts of Appeal; High Courts; County Courts; state level - High Courts; County Courts; customary courts; other specialized courts and tribunalsPolitical parties and leaders: This entry includes a listing of significant political parties, coalitions, and electoral lists as of each country's last legislative election, unless otherwise noted. Democratic Change or DC [Onyoti Adigo NYIKWEC] (formerly Sudan People's Liberation Movement-Democratic Movement or SPLM-DC)
Democratic Change or DC [Onyoti Adigo NYIKWEC] (formerly Sudan People's Liberation Movement-Democratic Movement or SPLM-DC)
Sudan People's Liberation Movement or SPLM [Salva KIIR Mayardit]
Sudan People’s Liberation Movement-In Opposition or SPLM-IO [Riek MACHAR Teny Dhurgon]International organization participation: This entry lists in alphabetical order by abbreviation those international organizations in which the subject country is a member or participates in some other way. AU, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOM, IPU, ITU, MIGA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WMODiplomatic representation in the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, chancery address, telephone, FAX, consulate general locations, and consulate locations. The use of the annotated title Appointed Ambassador refers to a new ambassador who has presented his/her credentials to the secretary of state but not the US president. Such ambassadors fulfill all diplomatic functions except meeting with or appearing at functions attended by the president until such time as they formally present their credentials at a White Hou . . . more
AU, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOM, IPU, ITU, MIGA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WMODiplomatic representation in the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, chancery address, telephone, FAX, consulate general locations, and consulate locations. The use of the annotated title Appointed Ambassador refers to a new ambassador who has presented his/her credentials to the secretary of state but not the US president. Such ambassadors fulfill all diplomatic functions except meeting with or appearing at functions attended by the president until such time as they formally present their credentials at a White Hou . . . more chief of mission: Ambassador Philip Jada NATANA (since 17 September 2018)chancery: 1015 31st Street NW, Third Floor, Washington, DC 20007telephone: [1] (202) 293-7940FAX: [1] (202) 293-7941Diplomatic representation from the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, embassy address, mailing address, telephone number, FAX number, branch office locations, consulate general locations, and consulate locations.
chief of mission: Ambassador Philip Jada NATANA (since 17 September 2018)chancery: 1015 31st Street NW, Third Floor, Washington, DC 20007telephone: [1] (202) 293-7940FAX: [1] (202) 293-7941Diplomatic representation from the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, embassy address, mailing address, telephone number, FAX number, branch office locations, consulate general locations, and consulate locations. chief of mission: Ambassador Thomas HUSHEK (since 5 June 2018)telephone: [211] 912-105-188embassy: Kololo Road adjacent to the EU's compound, JubaFlag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags.
chief of mission: Ambassador Thomas HUSHEK (since 5 June 2018)telephone: [211] 912-105-188embassy: Kololo Road adjacent to the EU's compound, JubaFlag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags. three equal horizontal bands of black (top), red, and green; the red band is edged in white; a blue isosceles triangle based on the hoist side contains a gold, five-pointed star; black represents the people of South Sudan, red the blood shed in the struggle for freedom, green the verdant land, and blue the waters of the Nile; the gold star represents the unity of the states making up South Sudan
three equal horizontal bands of black (top), red, and green; the red band is edged in white; a blue isosceles triangle based on the hoist side contains a gold, five-pointed star; black represents the people of South Sudan, red the blood shed in the struggle for freedom, green the verdant land, and blue the waters of the Nile; the gold star represents the unity of the states making up South Sudannote: resembles the flag of Kenya; one of only two national flags to display six colors as part of its primary design, the other is South Africa's
National symbol(s): A national symbol is a faunal, floral, or other abstract representation - or some distinctive object - that over time has come to be closely identified with a country or entity. Not all countries have national symbols; a few countries have more than one. African fish eagle; national colors: red, green, blue, yellow, black, whiteNational anthem: A generally patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
African fish eagle; national colors: red, green, blue, yellow, black, whiteNational anthem: A generally patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not. name: South Sudan Oyee! (Hooray!)lyrics/music: collective of 49 poets/Juba University students and teachers
name: South Sudan Oyee! (Hooray!)lyrics/music: collective of 49 poets/Juba University students and teachersnote: adopted 2011; anthem selected in a national contest
-
Economy :: South Sudan
-
Economic overview: This section briefly describes four key economic components for a given country:* National Economy, including economic histories, domestic labor and wage markets, and the economic sector portfolios that drive fiscal and monetary policymaking;* Financial Power & Public Finance, including brief discussions of lending/exchange rates, capital stocks/flows, and foreign direct investments arising from a country's financial and capital markets;* International Trade, including chief imports an . . . more

Industry and infrastructure in landlocked South Sudan are severely underdeveloped and poverty is widespread, following several decades of civil war with Sudan. Continued fighting within the new nation is disrupting what remains of the economy. The vast majority of the population is dependent on subsistence agriculture and humanitarian assistance. Property rights are insecure and price signals are weak, because markets are not well-organized.
South Sudan has little infrastructure – about 10,000 kilometers of roads, but just 2% of them paved. Electricity is produced mostly by costly diesel generators, and indoor plumbing and potable water are scarce, so less than 2% of the population has access to electricity. About 90% of consumed goods, capital, and services are imported from neighboring countries – mainly Uganda, Kenya and Sudan. Chinese investment plays a growing role in the infrastructure and energy sectors.
Nevertheless, South Sudan does have abundant natural resources. South Sudan holds one of the richest agricultural areas in Africa, with fertile soils and abundant water supplies. Currently the region supports 10-20 million head of cattle. At independence in 2011, South Sudan produced nearly three-fourths of former Sudan's total oil output of nearly a half million barrels per day. The Government of South Sudan relies on oil for the vast majority of its budget revenues, although oil production has fallen sharply since independence. South Sudan is one of the most oil-dependent countries in the world, with 98% of the government’s annual operating budget and 80% of its gross domestic product (GDP) derived from oil. Oil is exported through a pipeline that runs to refineries and shipping facilities at Port Sudan on the Red Sea. The economy of South Sudan will remain linked to Sudan for some time, given the existing oil infrastructure. The outbreak of conflict in December 2013, combined with falling crude oil production and prices, meant that GDP fell significantly between 2014 and 2017. Since the second half of 2017 oil production has risen, and is currently about 130,000 barrels per day.
Poverty and food insecurity has risen due to displacement of people caused by the conflict. With famine spreading, 66% of the population in South Sudan is living on less than about $2 a day, up from 50.6% in 2009, according to the World Bank. About 80% of the population lives in rural areas, with agriculture, forestry and fishing providing the livelihood for a majority of the households. Much of rural sector activity is focused on low-input, low-output subsistence agriculture.
South Sudan is burdened by considerable debt because of increased military spending and high levels of government corruption. Economic mismanagement is prevalent. Civil servants, including police and the military, are not paid on time, creating incentives to engage in looting and banditry. South Sudan has received more than $11 billion in foreign aid since 2005, largely from the US, the UK, and the EU. Inflation peaked at over 800% per year in October 2016 but dropped to 118% in 2017. The government has funded its expenditures by borrowing from the central bank and foreign sources, using forward sales of oil as collateral. The central bank’s decision to adopt a managed floating exchange rate regime in December 2015 triggered a 97% depreciation of the currency and spawned a growing black market.
Long-term challenges include rooting out public sector corruption, improving agricultural productivity, alleviating poverty and unemployment, improving fiscal transparency - particularly in regard to oil revenues, taming inflation, improving government revenues, and creating a rules-based business environment.
GDP real growth rate: This entry gives GDP growth on an annual basis adjusted for inflation and expressed as a percent. The growth rates are year-over-year, and not compounded. Inflation rate (consumer prices): This entry furnishes the annual percent change in consumer prices compared with the previous year's consumer prices.
Inflation rate (consumer prices): This entry furnishes the annual percent change in consumer prices compared with the previous year's consumer prices. GDP (purchasing power parity) - real: This entry gives the gross domestic product (GDP) or value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. A nation's GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP) exchange rates is the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States in the year noted. This is the measure most economists prefer when looking at per-capita welfare and when comparing living conditions or use of resources across countries. The measur . . . more
GDP (purchasing power parity) - real: This entry gives the gross domestic product (GDP) or value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. A nation's GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP) exchange rates is the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States in the year noted. This is the measure most economists prefer when looking at per-capita welfare and when comparing living conditions or use of resources across countries. The measur . . . more $20.01 billion (2017 est.)$21.1 billion (2016 est.)$24.52 billion (2015 est.)
$20.01 billion (2017 est.)$21.1 billion (2016 est.)$24.52 billion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate): This entry gives the gross domestic product (GDP) or value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. A nation's GDP at official exchange rates (OER) is the home-currency-denominated annual GDP figure divided by the bilateral average US exchange rate with that country in that year. The measure is simple to compute and gives a precise measure of the value of output. Many economists prefer this measure when gauging the economic power an economy maintains vis- . . . more $3.06 billion (2017 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP): This entry shows GDP on a purchasing power parity basis divided by population as of 1 July for the same year.
$3.06 billion (2017 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP): This entry shows GDP on a purchasing power parity basis divided by population as of 1 July for the same year. $1,600 (2017 est.)$1,700 (2016 est.)$2,100 (2015 est.)
$1,600 (2017 est.)$1,700 (2016 est.)$2,100 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 199Gross national saving: Gross national saving is derived by deducting final consumption expenditure (household plus government) from Gross national disposable income, and consists of personal saving, plus business saving (the sum of the capital consumption allowance and retained business profits), plus government saving (the excess of tax revenues over expenditures), but excludes foreign saving (the excess of imports of goods and services over exports). The figures are presented as a percent of GDP. A negative . . . more 3.6% of GDP (2017 est.)18.7% of GDP (2016 est.)7.4% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 179GDP - composition, by end use: This entry shows who does the spending in an economy: consumers, businesses, government, and foreigners. The distribution gives the percentage contribution to total GDP of household consumption, government consumption, investment in fixed capital, investment in inventories, exports of goods and services, and imports of goods and services, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. household consumption consists of expenditures by resident households, and by nonprofit insti . . . more
3.6% of GDP (2017 est.)18.7% of GDP (2016 est.)7.4% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 179GDP - composition, by end use: This entry shows who does the spending in an economy: consumers, businesses, government, and foreigners. The distribution gives the percentage contribution to total GDP of household consumption, government consumption, investment in fixed capital, investment in inventories, exports of goods and services, and imports of goods and services, and will total 100 percent of GDP if the data are complete. household consumption consists of expenditures by resident households, and by nonprofit insti . . . more household consumption: 34.9% (2011 est.)government consumption: 17.1% (2011 est.)investment in fixed capital: 10.4% (2011 est.)exports of goods and services: 64.9% (2011 est.)imports of goods and services: -27.2% (2011 est.)Ease of Doing Business Index scores: The World Bank Group Doing Business project measures business regulations and enforcement mechanisms across economies and selected cities. The project evaluates domestic small and medium-size companies and measures the regulations applying to them through their life cycle. The project encourages economies to compete towards more efficient regulation; offers measurable benchmarks for reform; and serves as a resource for academics, journalists, private sector researchers and others intereste . . . more
household consumption: 34.9% (2011 est.)government consumption: 17.1% (2011 est.)investment in fixed capital: 10.4% (2011 est.)exports of goods and services: 64.9% (2011 est.)imports of goods and services: -27.2% (2011 est.)Ease of Doing Business Index scores: The World Bank Group Doing Business project measures business regulations and enforcement mechanisms across economies and selected cities. The project evaluates domestic small and medium-size companies and measures the regulations applying to them through their life cycle. The project encourages economies to compete towards more efficient regulation; offers measurable benchmarks for reform; and serves as a resource for academics, journalists, private sector researchers and others intereste . . . more 26.2 (2020)Agriculture - products: This entry is an ordered listing of major crops and products starting with the most important.
26.2 (2020)Agriculture - products: This entry is an ordered listing of major crops and products starting with the most important. sorghum, maize, rice, millet, wheat, gum arabic, sugarcane, mangoes, papayas, bananas, sweet potatoes, sunflower seeds, cotton, sesame seeds, cassava (manioc, tapioca), beans, peanuts; cattle, sheepPopulation below poverty line: National estimates of the percentage of the population falling below the poverty line are based on surveys of sub-groups, with the results weighted by the number of people in each group. Definitions of poverty vary considerably among nations. For example, rich nations generally employ more generous standards of poverty than poor nations.
sorghum, maize, rice, millet, wheat, gum arabic, sugarcane, mangoes, papayas, bananas, sweet potatoes, sunflower seeds, cotton, sesame seeds, cassava (manioc, tapioca), beans, peanuts; cattle, sheepPopulation below poverty line: National estimates of the percentage of the population falling below the poverty line are based on surveys of sub-groups, with the results weighted by the number of people in each group. Definitions of poverty vary considerably among nations. For example, rich nations generally employ more generous standards of poverty than poor nations. 66% (2015 est.)Budget: This entry includes revenues, expenditures, and capital expenditures. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
66% (2015 est.)Budget: This entry includes revenues, expenditures, and capital expenditures. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. revenues: 259.6 million (FY2017/18 est.)expenditures: 298.6 million (FY2017/18 est.)Taxes and other revenues: This entry records total taxes and other revenues received by the national government during the time period indicated, expressed as a percent of GDP. Taxes include personal and corporate income taxes, value added taxes, excise taxes, and tariffs. Other revenues include social contributions - such as payments for social security and hospital insurance - grants, and net revenues from public enterprises. Normalizing the data, by dividing total revenues by GDP, enables easy comparisons acr . . . more
revenues: 259.6 million (FY2017/18 est.)expenditures: 298.6 million (FY2017/18 est.)Taxes and other revenues: This entry records total taxes and other revenues received by the national government during the time period indicated, expressed as a percent of GDP. Taxes include personal and corporate income taxes, value added taxes, excise taxes, and tariffs. Other revenues include social contributions - such as payments for social security and hospital insurance - grants, and net revenues from public enterprises. Normalizing the data, by dividing total revenues by GDP, enables easy comparisons acr . . . more 8.5% (of GDP) (FY2017/18 est.)country comparison to the world: 218Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-): This entry records the difference between national government revenues and expenditures, expressed as a percent of GDP. A positive (+) number indicates that revenues exceeded expenditures (a budget surplus), while a negative (-) number indicates the reverse (a budget deficit). Normalizing the data, by dividing the budget balance by GDP, enables easy comparisons across countries and indicates whether a national government saves or borrows money. Countries with high budget deficits (relat . . . more
8.5% (of GDP) (FY2017/18 est.)country comparison to the world: 218Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-): This entry records the difference between national government revenues and expenditures, expressed as a percent of GDP. A positive (+) number indicates that revenues exceeded expenditures (a budget surplus), while a negative (-) number indicates the reverse (a budget deficit). Normalizing the data, by dividing the budget balance by GDP, enables easy comparisons across countries and indicates whether a national government saves or borrows money. Countries with high budget deficits (relat . . . more -1.3% (of GDP) (FY2017/18 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Public debt: This entry records the cumulative total of all government borrowings less repayments that are denominated in a country's home currency. Public debt should not be confused with external debt, which reflects the foreign currency liabilities of both the private and public sector and must be financed out of foreign exchange earnings.
-1.3% (of GDP) (FY2017/18 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Public debt: This entry records the cumulative total of all government borrowings less repayments that are denominated in a country's home currency. Public debt should not be confused with external debt, which reflects the foreign currency liabilities of both the private and public sector and must be financed out of foreign exchange earnings. Current account balance: This entry records a country's net trade in goods and services, plus net earnings from rents, interest, profits, and dividends, and net transfer payments (such as pension funds and worker remittances) to and from the rest of the world during the period specified. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
Current account balance: This entry records a country's net trade in goods and services, plus net earnings from rents, interest, profits, and dividends, and net transfer payments (such as pension funds and worker remittances) to and from the rest of the world during the period specified. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. Exports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise exports on an f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
Exports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise exports on an f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. $1.13 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 155Imports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise imports on a c.i.f. (cost, insurance, and freight) or f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
$1.13 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 155Imports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise imports on a c.i.f. (cost, insurance, and freight) or f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. $3.795 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Reserves of foreign exchange and gold: This entry gives the dollar value for the stock of all financial assets that are available to the central monetary authority for use in meeting a country's balance of payments needs as of the end-date of the period specified. This category includes not only foreign currency and gold, but also a country's holdings of Special Drawing Rights in the International Monetary Fund, and its reserve position in the Fund.
$3.795 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Reserves of foreign exchange and gold: This entry gives the dollar value for the stock of all financial assets that are available to the central monetary authority for use in meeting a country's balance of payments needs as of the end-date of the period specified. This category includes not only foreign currency and gold, but also a country's holdings of Special Drawing Rights in the International Monetary Fund, and its reserve position in the Fund. $73 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Exchange rates: This entry provides the average annual price of a country's monetary unit for the time period specified, expressed in units of local currency per US dollar, as determined by international market forces or by official fiat. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 4217 alphabetic currency code for the national medium of exchange is presented in parenthesis. Closing daily exchange rates are not presented in The World Factbook, but are used to convert stock values - e.g., the . . . more
$73 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Exchange rates: This entry provides the average annual price of a country's monetary unit for the time period specified, expressed in units of local currency per US dollar, as determined by international market forces or by official fiat. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 4217 alphabetic currency code for the national medium of exchange is presented in parenthesis. Closing daily exchange rates are not presented in The World Factbook, but are used to convert stock values - e.g., the . . . more South Sudanese pounds (SSP) per US dollar -0.885 (2017 est.)0.903 (2016 est.)0.9214 (2015 est.)0.885 (2014 est.)0.7634 (2013 est.)
South Sudanese pounds (SSP) per US dollar -0.885 (2017 est.)0.903 (2016 est.)0.9214 (2015 est.)0.885 (2014 est.)0.7634 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: South Sudan
-
Electricity access: This entry provides information on access to electricity. Electrification data – collected from industry reports, national surveys, and international sources – consists of four subfields. Population without electricity provides an estimate of the number of citizens that do not have access to electricity. Electrification – total population is the percent of a country’s total population with access to electricity, electrification – urban areas is the percent of a country’s urban population w . . . more
 population without electricity: 11 million (2019)electrification - total population: 28.2% (2018)electrification - urban areas: 46.8% (2018)electrification - rural areas: 23.6% (2018)Electricity - production: This entry is the annual electricity generated expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution.
population without electricity: 11 million (2019)electrification - total population: 28.2% (2018)electrification - urban areas: 46.8% (2018)electrification - rural areas: 23.6% (2018)Electricity - production: This entry is the annual electricity generated expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution. 412.8 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 169Electricity - consumption: This entry consists of total electricity generated annually plus imports and minus exports, expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution.
412.8 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 169Electricity - consumption: This entry consists of total electricity generated annually plus imports and minus exports, expressed in kilowatt-hours. The discrepancy between the amount of electricity generated and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is accounted for as loss in transmission and distribution. 391.8 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Electricity - exports: This entry is the total exported electricity in kilowatt-hours.
391.8 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Electricity - exports: This entry is the total exported electricity in kilowatt-hours. 0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 201Electricity - imports: This entry is the total imported electricity in kilowatt-hours.
0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 201Electricity - imports: This entry is the total imported electricity in kilowatt-hours. 0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Electricity - installed generating capacity: This entry is the total capacity of currently installed generators, expressed in kilowatts (kW), to produce electricity. A 10-kilowatt (kW) generator will produce 10 kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity, if it runs continuously for one hour.
0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Electricity - installed generating capacity: This entry is the total capacity of currently installed generators, expressed in kilowatts (kW), to produce electricity. A 10-kilowatt (kW) generator will produce 10 kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity, if it runs continuously for one hour. 80,400 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Electricity - from fossil fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by burning fossil fuels (such as coal, petroleum products, and natural gas), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
80,400 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Electricity - from fossil fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by burning fossil fuels (such as coal, petroleum products, and natural gas), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 100% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Electricity - from nuclear fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity through radioactive decay of nuclear fuel, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
100% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Electricity - from nuclear fuels: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity through radioactive decay of nuclear fuel, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 186Electricity - from hydroelectric plants: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by water-driven turbines, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 186Electricity - from hydroelectric plants: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by water-driven turbines, expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Electricity - from other renewable sources: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by using renewable energy sources other than hydroelectric (including, for example, wind, waves, solar, and geothermal), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity.
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Electricity - from other renewable sources: This entry measures the capacity of plants that generate electricity by using renewable energy sources other than hydroelectric (including, for example, wind, waves, solar, and geothermal), expressed as a share of the country's total generating capacity. 1% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Crude oil - production: This entry is the total amount of crude oil produced, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
1% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Crude oil - production: This entry is the total amount of crude oil produced, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 150,200 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Crude oil - exports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil exported, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
150,200 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Crude oil - exports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil exported, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 147,300 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Crude oil - imports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil imported, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
147,300 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Crude oil - imports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil imported, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Crude oil - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of crude oil, in barrels (bbl). Proved reserves are those quantities of petroleum which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions.
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Crude oil - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of crude oil, in barrels (bbl). Proved reserves are those quantities of petroleum which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions. 3.75 billion bbl (1 January 2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Refined petroleum products - production: This entry is the country's total output of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors.
3.75 billion bbl (1 January 2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Refined petroleum products - production: This entry is the country's total output of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors. 0 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 205Refined petroleum products - consumption: This entry is the country's total consumption of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors.
0 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 205Refined petroleum products - consumption: This entry is the country's total consumption of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors. 8,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 165Refined petroleum products - exports: This entry is the country's total exports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
8,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 165Refined petroleum products - exports: This entry is the country's total exports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 205Refined petroleum products - imports: This entry is the country's total imports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 205Refined petroleum products - imports: This entry is the country's total imports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 7,160 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 157Natural gas - production: This entry is the total natural gas produced in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors.
7,160 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 157Natural gas - production: This entry is the total natural gas produced in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors. 0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Natural gas - consumption: This entry is the total natural gas consumed in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors.
0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Natural gas - consumption: This entry is the total natural gas consumed in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors. 0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Natural gas - exports: This entry is the total natural gas exported in cubic meters (cu m).
0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Natural gas - exports: This entry is the total natural gas exported in cubic meters (cu m). 0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 188Natural gas - imports: This entry is the total natural gas imported in cubic meters (cu m).
0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 188Natural gas - imports: This entry is the total natural gas imported in cubic meters (cu m). 0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 191Natural gas - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of natural gas in cubic meters (cu m). Proved reserves are those quantities of natural gas, which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions.
0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 191Natural gas - proved reserves: This entry is the stock of proved reserves of natural gas in cubic meters (cu m). Proved reserves are those quantities of natural gas, which, by analysis of geological and engineering data, can be estimated with a high degree of confidence to be commercially recoverable from a given date forward, from known reservoirs and under current economic conditions. 63.71 billion cu m (1 January 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy: This entry is the total amount of carbon dioxide, measured in metric tons, released by burning fossil fuels in the process of producing and consuming energy.
63.71 billion cu m (1 January 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy: This entry is the total amount of carbon dioxide, measured in metric tons, released by burning fossil fuels in the process of producing and consuming energy. 1.224 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 163
1.224 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 163 -
Communications :: South Sudan
-
Telephones - fixed lines: This entry gives the total number of fixed telephone lines in use, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants.
 total subscriptions: 0subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 225Telephones - mobile cellular: This entry gives the total number of mobile cellular telephone subscribers, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Note that because of the ubiquity of mobile phone use in developed countries, the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants can exceed 100.
total subscriptions: 0subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 225Telephones - mobile cellular: This entry gives the total number of mobile cellular telephone subscribers, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Note that because of the ubiquity of mobile phone use in developed countries, the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants can exceed 100. total subscriptions: 3,439,784subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 33.46 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 136Telecommunication systems: This entry includes a brief general assessment of a country's telecommunications system with details on the domestic and international components. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: 2G - is short for second-generation cellular network. After 2G was launched, the previous mobile wireless network systems were retroactively dubbed 1G. While radio signals on 1G networks are analog, radio signals on 2G networks are digital. Both systems use digital signaling . . . more
total subscriptions: 3,439,784subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 33.46 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 136Telecommunication systems: This entry includes a brief general assessment of a country's telecommunications system with details on the domestic and international components. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: 2G - is short for second-generation cellular network. After 2G was launched, the previous mobile wireless network systems were retroactively dubbed 1G. While radio signals on 1G networks are analog, radio signals on 2G networks are digital. Both systems use digital signaling . . . more general assessment: one of the least developed telecommunications and Internet systems in the world; the international community has provided billions in aid to help the young country, unfortunate instability, widespread poverty and low literacy rate all contribute to a struggle for their telecom sector; the few carriers in the market have reduced the areas in which they offer service, not expanded them; recently the government shut down the largest cellphone carrier isolating 1.4 million customers over a disputed service fee arrangement (2020)domestic: fixed-line less than 1 per 100 subscriptions, mobile-cellular 33 per 100 persons (2019)international: country code - 211 (2017)note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderatedBroadcast media: This entry provides information on the approximate number of public and private TV and radio stations in a country, as well as basic information on the availability of satellite and cable TV services.
general assessment: one of the least developed telecommunications and Internet systems in the world; the international community has provided billions in aid to help the young country, unfortunate instability, widespread poverty and low literacy rate all contribute to a struggle for their telecom sector; the few carriers in the market have reduced the areas in which they offer service, not expanded them; recently the government shut down the largest cellphone carrier isolating 1.4 million customers over a disputed service fee arrangement (2020)domestic: fixed-line less than 1 per 100 subscriptions, mobile-cellular 33 per 100 persons (2019)international: country code - 211 (2017)note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderatedBroadcast media: This entry provides information on the approximate number of public and private TV and radio stations in a country, as well as basic information on the availability of satellite and cable TV services.
a single TV channel and a radio station are controlled by the government; several community and commercial FM stations are operational, mostly sponsored by outside aid donors; some foreign radio broadcasts are available
(2019)Internet country code: This entry includes the two-letter codes maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in the ISO 3166 Alpha-2 list and used by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) to establish country-coded top-level domains (ccTLDs). .ssInternet users: This entry gives the total number of individuals within a country who can access the Internet at home, via any device type (computer or mobile) and connection. The percent of population with Internet access (i.e., the penetration rate) helps gauge how widespread Internet use is within a country. Statistics vary from country to country and may include users who access the Internet at least several times a week to those who access it only once within a period of several months.
.ssInternet users: This entry gives the total number of individuals within a country who can access the Internet at home, via any device type (computer or mobile) and connection. The percent of population with Internet access (i.e., the penetration rate) helps gauge how widespread Internet use is within a country. Statistics vary from country to country and may include users who access the Internet at least several times a week to those who access it only once within a period of several months. Broadband - fixed subscriptions: This entry gives the total number of fixed-broadband subscriptions, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Fixed broadband is a physical wired connection to the Internet (e.g., coaxial cable, optical fiber) at speeds equal to or greater than 256 kilobits/second (256 kbit/s).
Broadband - fixed subscriptions: This entry gives the total number of fixed-broadband subscriptions, as well as the number of subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. Fixed broadband is a physical wired connection to the Internet (e.g., coaxial cable, optical fiber) at speeds equal to or greater than 256 kilobits/second (256 kbit/s). total: 200subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 203
total: 200subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 203 -
Transportation :: South Sudan
-
National air transport system: This entry includes four subfields describing the air transport system of a given country in terms of both structure and performance. The first subfield, number of registered air carriers, indicates the total number of air carriers registered with the country’s national aviation authority and issued an air operator certificate as required by the Convention on International Civil Aviation. The second subfield, inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers, lists the total number . . . more
 number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 2annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 0 mt-kmCivil aircraft registration country code prefix: This entry provides the one- or two-character alphanumeric code indicating the nationality of civil aircraft. Article 20 of the Convention on International Civil Aviation (Chicago Convention), signed in 1944, requires that all aircraft engaged in international air navigation bear appropriate nationality marks. The aircraft registration number consists of two parts: a prefix consisting of a one- or two-character alphanumeric code indicating nationality and a registration suffix of one to fi . . . more
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 2annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 0 mt-kmCivil aircraft registration country code prefix: This entry provides the one- or two-character alphanumeric code indicating the nationality of civil aircraft. Article 20 of the Convention on International Civil Aviation (Chicago Convention), signed in 1944, requires that all aircraft engaged in international air navigation bear appropriate nationality marks. The aircraft registration number consists of two parts: a prefix consisting of a one- or two-character alphanumeric code indicating nationality and a registration suffix of one to fi . . . more Z8 (2016)Airports: This entry gives the total number of airports or airfields recognizable from the air. The runway(s) may be paved (concrete or asphalt surfaces) or unpaved (grass, earth, sand, or gravel surfaces) and may include closed or abandoned installations. Airports or airfields that are no longer recognizable (overgrown, no facilities, etc.) are not included. Note that not all airports have accommodations for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control.
Z8 (2016)Airports: This entry gives the total number of airports or airfields recognizable from the air. The runway(s) may be paved (concrete or asphalt surfaces) or unpaved (grass, earth, sand, or gravel surfaces) and may include closed or abandoned installations. Airports or airfields that are no longer recognizable (overgrown, no facilities, etc.) are not included. Note that not all airports have accommodations for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control. 89 (2020)country comparison to the world: 63Airports - with paved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with paved runways (concrete or asphalt surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listing. Not all . . . more
89 (2020)country comparison to the world: 63Airports - with paved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with paved runways (concrete or asphalt surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listing. Not all . . . more total: 4 (2020)over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 1Airports - with unpaved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with unpaved runways (grass, dirt, sand, or gravel surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listin . . . more
total: 4 (2020)over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 1Airports - with unpaved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with unpaved runways (grass, dirt, sand, or gravel surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listin . . . more total: 84 (2020)2,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 12914 to 1,523 m: 38under 914 m: 33Heliports: This entry gives the total number of heliports with hard-surface runways, helipads, or landing areas that support routine sustained helicopter operations exclusively and have support facilities including one or more of the following facilities: lighting, fuel, passenger handling, or maintenance. It includes former airports used exclusively for helicopter operations but excludes heliports limited to day operations and natural clearings that could support helicopter landings and takeoffs.
total: 84 (2020)2,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 12914 to 1,523 m: 38under 914 m: 33Heliports: This entry gives the total number of heliports with hard-surface runways, helipads, or landing areas that support routine sustained helicopter operations exclusively and have support facilities including one or more of the following facilities: lighting, fuel, passenger handling, or maintenance. It includes former airports used exclusively for helicopter operations but excludes heliports limited to day operations and natural clearings that could support helicopter landings and takeoffs. 3 (2020)Railways: This entry states the total route length of the railway network and of its component parts by gauge, which is the measure of the distance between the inner sides of the load-bearing rails. The four typical types of gauges are: broad, standard, narrow, and dual. Other gauges are listed under note. Some 60% of the world's railways use the standard gauge of 1.4 m (4.7 ft). Gauges vary by country and sometimes within countries. The choice of gauge during initial construction was mainly in resp . . . more
3 (2020)Railways: This entry states the total route length of the railway network and of its component parts by gauge, which is the measure of the distance between the inner sides of the load-bearing rails. The four typical types of gauges are: broad, standard, narrow, and dual. Other gauges are listed under note. Some 60% of the world's railways use the standard gauge of 1.4 m (4.7 ft). Gauges vary by country and sometimes within countries. The choice of gauge during initial construction was mainly in resp . . . more total: 248 km (2018)
total: 248 km (2018)note: a narrow gauge, single-track railroad between Babonosa (Sudan) and Wau, the only existing rail system, was repaired in 2010 with $250 million in UN funds, but is not currently operational
country comparison to the world: 126Roadways: This entry gives the total length of the road network and includes the length of the paved and unpaved portions. total: 90,200 km (2019)paved: 300 km (2019)unpaved: 89,900 km (2019)
total: 90,200 km (2019)paved: 300 km (2019)unpaved: 89,900 km (2019)note: most of the road network is unpaved and much of it is in disrepair
country comparison to the world: 55Waterways: This entry gives the total length of navigable rivers, canals, and other inland bodies of water. see entry for Sudan
see entry for Sudan -
Military and Security :: South Sudan
-
Military and security forces: This entry lists the military and security forces subordinate to defense ministries or the equivalent (typically ground, naval, air, and marine forces), as well as those belonging to interior ministries or the equivalent (typically gendarmeries, border/coast guards, paramilitary police, and other internal security forces).
 South Sudan People’s Defence Force (SSPDF): Ground Force, Air Force, Air Defense Forces, Presidential Guard (2019)Military expenditures: This entry gives estimates on spending on defense programs for the most recent year available as a percent of gross domestic product (GDP); the GDP is calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). For countries with no military forces, this figure can include expenditures on public security and police.
South Sudan People’s Defence Force (SSPDF): Ground Force, Air Force, Air Defense Forces, Presidential Guard (2019)Military expenditures: This entry gives estimates on spending on defense programs for the most recent year available as a percent of gross domestic product (GDP); the GDP is calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). For countries with no military forces, this figure can include expenditures on public security and police. 3.5% of GDP (2019)3.7% of GDP (2018)2.4% of GDP (2017)4.6% of GDP (2016)10% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 19Military and security service personnel strengths: This entry provides estimates of military and security services personnel strengths. The numbers are based on a wide-range of publicly available information. Unless otherwise noted, military estimates focus on the major services (army, navy, air force, and where applicable, gendarmeries) and do not account for activated reservists or delineate military service members assigned to joint staffs or defense ministries.
3.5% of GDP (2019)3.7% of GDP (2018)2.4% of GDP (2017)4.6% of GDP (2016)10% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 19Military and security service personnel strengths: This entry provides estimates of military and security services personnel strengths. The numbers are based on a wide-range of publicly available information. Unless otherwise noted, military estimates focus on the major services (army, navy, air force, and where applicable, gendarmeries) and do not account for activated reservists or delineate military service members assigned to joint staffs or defense ministries. the South Sudan People’s Defense Force (SSPDF) has an estimated 190,000 active personnel, including ground, air, and riverine forces (2019)Military equipment inventories and acquisitions: This entry provides basic information on each country’s military equipment inventories, as well as how they acquire their equipment; it is intended to show broad trends in major military equipment holdings, such as tanks and other armored vehicles, air defense systems, artillery, naval ships, helicopters, and fixed-wing aircraft. Arms acquisition information is an overview of major arms suppliers over a specific period of time, including second-hand arms delivered as aid, with a focus on m . . . more
the South Sudan People’s Defense Force (SSPDF) has an estimated 190,000 active personnel, including ground, air, and riverine forces (2019)Military equipment inventories and acquisitions: This entry provides basic information on each country’s military equipment inventories, as well as how they acquire their equipment; it is intended to show broad trends in major military equipment holdings, such as tanks and other armored vehicles, air defense systems, artillery, naval ships, helicopters, and fixed-wing aircraft. Arms acquisition information is an overview of major arms suppliers over a specific period of time, including second-hand arms delivered as aid, with a focus on m . . . more the SSPDF inventory is primarily of Soviet origin; from 2010 to 2015, Russia and the United Arab Emirates were the leading suppliers of arms and equipment; South Sudan has been under a UN arms embargo since 2018 (2020)Military service age and obligation: This entry gives the required ages for voluntary or conscript military service and the length of service obligation.
the SSPDF inventory is primarily of Soviet origin; from 2010 to 2015, Russia and the United Arab Emirates were the leading suppliers of arms and equipment; South Sudan has been under a UN arms embargo since 2018 (2020)Military service age and obligation: This entry gives the required ages for voluntary or conscript military service and the length of service obligation. 18 is the legal minimum age for compulsory and voluntary military service; the Government of South Sudan signed agreements in March 2012 and August 2015 that included the demobilization of all child soldiers within the armed forces and opposition, but the recruitment of child soldiers by the warring parties continues; as of the end of 2018, UNICEF estimated that more than 19,000 child soldiers had been used in the country's civil war since it began in December 2013 (2018)Military - note: This entry includes miscellaneous military information of significance not included elsewhere.
18 is the legal minimum age for compulsory and voluntary military service; the Government of South Sudan signed agreements in March 2012 and August 2015 that included the demobilization of all child soldiers within the armed forces and opposition, but the recruitment of child soldiers by the warring parties continues; as of the end of 2018, UNICEF estimated that more than 19,000 child soldiers had been used in the country's civil war since it began in December 2013 (2018)Military - note: This entry includes miscellaneous military information of significance not included elsewhere. under the September 2018 peace agreement, all armed groups in South Sudan were to assemble at designated sites where fighters could be either disarmed and demobilized, or integrated into unified military and police forces; the unified forces were then to be retrained and deployed prior to the formation of a national unity government; all fighters were ordered to these sites in July 2019; some progress toward merging the various armed forces into a national army has been made; for example, in May 2020, South Sudan announced that it was graduating some unified forces at various training centers across the country, and in June the SSPDF incorporated some senior officers from the main opposition force, the Sudan People's Liberation Movement Army - in Opposition (SPLM/A-IO) into its rank structure; nevertheless, progress has been slow, and as of December 2020 armed clashes continued to occur between government forces and armed militant groups
under the September 2018 peace agreement, all armed groups in South Sudan were to assemble at designated sites where fighters could be either disarmed and demobilized, or integrated into unified military and police forces; the unified forces were then to be retrained and deployed prior to the formation of a national unity government; all fighters were ordered to these sites in July 2019; some progress toward merging the various armed forces into a national army has been made; for example, in May 2020, South Sudan announced that it was graduating some unified forces at various training centers across the country, and in June the SSPDF incorporated some senior officers from the main opposition force, the Sudan People's Liberation Movement Army - in Opposition (SPLM/A-IO) into its rank structure; nevertheless, progress has been slow, and as of December 2020 armed clashes continued to occur between government forces and armed militant groups
the United Nations Mission in South Sudan (UNMISS) has operated in the country since 2011 with the objectives of consolidating peace and security and helping establish conditions for the successful economic and political development of South Sudan; UNMISS had more than 18,000 personnel deployed in the country as of May 2020
United Nations Interim Security Force for Abyei (UNISFA) has operated in the disputed Abyei region along the border between Sudan and South Sudan since 2011; UNISFA's mission includes ensuring security, protecting civilians, strengthening the capacity of the Abyei Police Service, de-mining, monitoring/verifying the redeployment of armed forces from the area, and facilitating the flow of humanitarian aid; UNISFA had about 4,000 personnel deployed as of March 2020 (2020) -
Transnational Issues :: South Sudan
-
Disputes - international: This entry includes a wide variety of situations that range from traditional bilateral boundary disputes to unilateral claims of one sort or another. Information regarding disputes over international terrestrial and maritime boundaries has been reviewed by the US Department of State. References to other situations involving borders or frontiers may also be included, such as resource disputes, geopolitical questions, or irredentist issues; however, inclusion does not necessarily constitute . . . more

South Sudan-Sudan boundary represents 1 January 1956 alignment, final alignment pending negotiations and demarcation; final sovereignty status of Abyei Area pending negotiations between South Sudan and Sudan; periodic violent skirmishes with South Sudanese residents over water and grazing rights persist among related pastoral populations along the border with the Central African Republic; the boundary that separates Kenya and South Sudan's sovereignty is unclear in the "Ilemi Triangle," which Kenya has administered since colonial times
Refugees and internally displaced persons: This entry includes those persons residing in a country as refugees, internally displaced persons (IDPs), or stateless persons. Each country's refugee entry includes only countries of origin that are the source of refugee populations of 5,000 or more. The definition of a refugee according to a UN Convention is "a person who is outside his/her country of nationality or habitual residence; has a well-founded fear of persecution because of his/her race, religion, nationality, membership in a . . . more refugees (country of origin): 729,530 (Sudan) (refugees and asylum seekers), 16,176 (Democratic Republic of the Congo) (refugees and asylum seekers) (2020)IDPs: 1.66 million (alleged coup attempt and ethnic conflict beginning in December 2013; information is lacking on those displaced in earlier years by: fighting in Abyei between the Sudanese Armed Forces and the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA) in May 2011; clashes between the SPLA and dissident militia groups in South Sudan; inter-ethnic conflicts over resources and cattle; attacks from the Lord's Resistance Army; floods and drought) (2020)Trafficking in persons: Trafficking in persons is modern-day slavery, involving victims who are forced, defrauded, or coerced into labor or sexual exploitation. The International Labor Organization (ILO), the UN agency charged with addressing labor standards, employment, and social protection issues, estimated in 2011 that 20.9 million people worldwide were victims of forced labor, bonded labor, forced child labor, sexual servitude, and involuntary servitude. Human trafficking is a multi-dimensional threat, depri . . . more
refugees (country of origin): 729,530 (Sudan) (refugees and asylum seekers), 16,176 (Democratic Republic of the Congo) (refugees and asylum seekers) (2020)IDPs: 1.66 million (alleged coup attempt and ethnic conflict beginning in December 2013; information is lacking on those displaced in earlier years by: fighting in Abyei between the Sudanese Armed Forces and the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA) in May 2011; clashes between the SPLA and dissident militia groups in South Sudan; inter-ethnic conflicts over resources and cattle; attacks from the Lord's Resistance Army; floods and drought) (2020)Trafficking in persons: Trafficking in persons is modern-day slavery, involving victims who are forced, defrauded, or coerced into labor or sexual exploitation. The International Labor Organization (ILO), the UN agency charged with addressing labor standards, employment, and social protection issues, estimated in 2011 that 20.9 million people worldwide were victims of forced labor, bonded labor, forced child labor, sexual servitude, and involuntary servitude. Human trafficking is a multi-dimensional threat, depri . . . more current situation: South Sudan is a source and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; South Sudanese women and girls, particularly those who are internally displaced, orphaned, refugees, or from rural areas, are vulnerable to forced labor and sexual exploitation, often in urban centers; children may be victims of forced labor in construction, market vending, shoe shining, car washing, rock breaking, brick making, delivery cart pulling, and begging; girls are also forced into marriages and subsequently subjected to sexual slavery or domestic servitude; women and girls migrate willingly from Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to South Sudan with the promise of legitimate jobs and are forced into the sex trade; inter-ethnic abductions and abductions by criminal groups continue, with abductees subsequently forced into domestic servitude, herding, or sex trafficking; in 2014, the recruitment and use of child soldiers increased significantly within government security forces and was also prevalent among opposition forcestier rating: Tier 3 – South Sudan does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; despite the government’s formal recommitment to an action plan to eliminate the recruitment and use of child soldiers by 2016, the practice expanded during 2014, and the government did not hold any officers criminally responsible; government officials reportedly are complicit in trafficking offenses but these activities continue to go uninvestigated; authorities reportedly identified five trafficking victims but did not transfer them to care facilities; law enforcement continued to arrest and imprison individuals for prostitution, including trafficking victims; no known steps were taken to address the exploitation of South Sudanese nationals working abroad or foreign workers in South Sudan (2015)
current situation: South Sudan is a source and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; South Sudanese women and girls, particularly those who are internally displaced, orphaned, refugees, or from rural areas, are vulnerable to forced labor and sexual exploitation, often in urban centers; children may be victims of forced labor in construction, market vending, shoe shining, car washing, rock breaking, brick making, delivery cart pulling, and begging; girls are also forced into marriages and subsequently subjected to sexual slavery or domestic servitude; women and girls migrate willingly from Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to South Sudan with the promise of legitimate jobs and are forced into the sex trade; inter-ethnic abductions and abductions by criminal groups continue, with abductees subsequently forced into domestic servitude, herding, or sex trafficking; in 2014, the recruitment and use of child soldiers increased significantly within government security forces and was also prevalent among opposition forcestier rating: Tier 3 – South Sudan does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; despite the government’s formal recommitment to an action plan to eliminate the recruitment and use of child soldiers by 2016, the practice expanded during 2014, and the government did not hold any officers criminally responsible; government officials reportedly are complicit in trafficking offenses but these activities continue to go uninvestigated; authorities reportedly identified five trafficking victims but did not transfer them to care facilities; law enforcement continued to arrest and imprison individuals for prostitution, including trafficking victims; no known steps were taken to address the exploitation of South Sudanese nationals working abroad or foreign workers in South Sudan (2015)