Main Content

-

- ABOUT
- REFERENCES
-
APPENDICES
- A: Abbreviations
- B: International Organizations and Groups
- C: Selected International Environmental Agreements
- D: Cross-Reference List of Country Data Codes
- E: Cross-Reference List of Hydrographic Data Codes
- F: Cross-Reference List of Geographic Names
- G: Weights and Measures
- H: Strategic Materials
- T: Terrorist Organizations
- FAQs
- CONTACT
- THE WORLD FACTBOOK ARCHIVE



















Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice
- Jump to topic
-
Introduction :: British Indian Ocean Territory
-
Background: This entry usually highlights major historic events and current issues and may include a statement about one or two key future trends.

Formerly administered as part of the British Crown Colony of Mauritius, the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) was established as an overseas territory of the UK in 1965. A number of the islands of the territory were later transferred to the Seychelles when it attained independence in 1976. Subsequently, BIOT has consisted only of the six main island groups comprising the Chagos Archipelago. Only Diego Garcia, the largest and most southerly of the islands, is inhabited. It contains a joint UK-US naval support facility and hosts one of four dedicated ground antennas that assist in the operation of the Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation system (the others are on Kwajalein (Marshall Islands), at Cape Canaveral, Florida (US), and on Ascension Island (Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha)). The US Air Force also operates a telescope array on Diego Garcia as part of the Ground-Based Electro-Optical Deep Space Surveillance System (GEODSS) for tracking orbital debris, which can be a hazard to spacecraft and astronauts.
Between 1967 and 1973, former agricultural workers, earlier residents in the islands, were relocated primarily to Mauritius, but also to the Seychelles. Negotiations between 1971 and 1982 resulted in the establishment of a trust fund by the British Government as compensation for the displaced islanders, known as Chagossians. Beginning in 1998, the islanders pursued a series of lawsuits against the British Government seeking further compensation and the right to return to the territory. In 2006 and 2007, British court rulings invalidated the immigration policies contained in the 2004 BIOT Constitution Order that had excluded the islanders from the archipelago, but upheld the special military status of Diego Garcia. In 2008, the House of Lords, as the final court of appeal in the UK, ruled in favor of the British Government by overturning the lower court rulings and finding no right of return for the Chagossians. In March 2015, the Permanent Court of Arbitration unanimously held that the marine protected area (MPA) that the UK declared around the Chagos Archipelago in April 2010 was in violation of the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea.
In February 2019, the International Court of Justice ruled in an advisory opinion that Britain’s decolonization of Mauritius was not completed lawfully because of continued Chagossian claims. A non-binding May 2019 UN General Assembly vote demanded that Britain end its “colonial administration” of the Chagos Archipelago and that it be returned to Mauritius. UK officials defend Britain's sovereignty over the islands and argue that the issue is a bilateral dispute between Mauritius and the UK that does not warrant international intervention. -
Geography :: British Indian Ocean Territory
-
Location: This entry identifies the country's regional location, neighboring countries, and adjacent bodies of water.
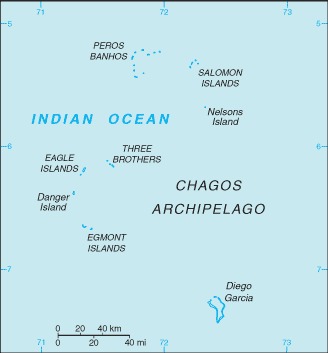
 archipelago in the Indian Ocean, south of India, about halfway between Africa and IndonesiaGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names.
archipelago in the Indian Ocean, south of India, about halfway between Africa and IndonesiaGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names. 6 00 S, 71 30 E;note - Diego Garcia 7 20 S, 72 25 EMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries.
6 00 S, 71 30 E;note - Diego Garcia 7 20 S, 72 25 EMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries. Political Map of the WorldArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines.
Political Map of the WorldArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. total: 60 sq kmland: 60 sq km (44 Diego Garcia)water: 54,340 sq kmnote: includes the entire Chagos Archipelago of 55 islandscountry comparison to the world: 229Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres).
total: 60 sq kmland: 60 sq km (44 Diego Garcia)water: 54,340 sq kmnote: includes the entire Chagos Archipelago of 55 islandscountry comparison to the world: 229Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres). land area is about one-third the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ.
land area is about one-third the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ. 0 kmCoastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea.
0 kmCoastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea. 698 kmMaritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more
698 kmMaritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more territorial sea: 12 nmEnvironment (Protection and Preservation) Zone: 200 nmClimate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more
territorial sea: 12 nmEnvironment (Protection and Preservation) Zone: 200 nmClimate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more tropical marine; hot, humid, moderated by trade windsTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography.
tropical marine; hot, humid, moderated by trade windsTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography. flat and low (most areas do not exceed two m in elevation)Elevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point.
flat and low (most areas do not exceed two m in elevation)Elevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point. lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 mhighest point: ocean-side dunes on Diego Garcia 9 mNatural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future.
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 mhighest point: ocean-side dunes on Diego Garcia 9 mNatural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future. coconuts, fish, sugarcaneLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more
coconuts, fish, sugarcaneLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more agricultural land: 0% (2011 est.)arable land: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0% (2011 est.)forest: 0% (2011 est.)other: 100% (2011 est.)Natural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes.
agricultural land: 0% (2011 est.)arable land: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0% (2011 est.)forest: 0% (2011 est.)other: 100% (2011 est.)Natural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes. none; located outside routes of Indian Ocean cyclonesEnvironment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more
none; located outside routes of Indian Ocean cyclonesEnvironment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more wastewater discharge into the lagoon on Diego GarciaGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere.
wastewater discharge into the lagoon on Diego GarciaGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere.
note 1: archipelago of 55 islands; Diego Garcia, the largest and southernmost island, occupies a strategic location in the central Indian Ocean; the island is the site of a joint US-UK military facility
note 2: Diego Garcia is the only inhabited island of the BIOT and one of only two British territories where traffic drives on the right, the other being Gibraltar
-
People and Society :: British Indian Ocean Territory
-
Population: This entry gives an estimate from the US Bureau of the Census based on statistics from population censuses, vital statistics registration systems, or sample surveys pertaining to the recent past and on assumptions about future trends. The total population presents one overall measure of the potential impact of the country on the world and within its region. Note: Starting with the 1993 Factbook, demographic estimates for some countries (mostly African) have explicitly taken into account t . . . more
 no indigenous inhabitants
no indigenous inhabitantsnote: approximately 1,200 former agricultural workers resident in the Chagos Archipelago, often referred to as Chagossians or Ilois, were relocated to Mauritius and the Seychelles in the 1960s and 1970s; approximately 3,000 UK and US military personnel and civilian contractors living on the island of Diego Garcia (2018)
-
Government :: British Indian Ocean Territory
-
Country name: This entry includes all forms of the country's name approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (Italy is used as an example): conventional long form (Italian Republic), conventional short form (Italy), local long form (Repubblica Italiana), local short form (Italia), former (Kingdom of Italy), as well as the abbreviation. Also see the Terminology note.
 conventional long form: British Indian Ocean Territoryconventional short form: noneabbreviation: BIOTetymology: self-descriptive name specifying the territory's affiliation and locationDependency status: This entry describes the formal relationship between a particular nonindependent entity and an independent state.
conventional long form: British Indian Ocean Territoryconventional short form: noneabbreviation: BIOTetymology: self-descriptive name specifying the territory's affiliation and locationDependency status: This entry describes the formal relationship between a particular nonindependent entity and an independent state. overseas territory of the UK; administered by a commissioner, resident in the Foreign and Commonwealth Office in LondonLegal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more
overseas territory of the UK; administered by a commissioner, resident in the Foreign and Commonwealth Office in LondonLegal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more the laws of the UK apply where applicableExecutive branch: This entry includes five subentries: chief of state; head of government; cabinet; elections/appointments; election results. Chief of state includes the name, title, and beginning date in office of the titular leader of the country who represents the state at official and ceremonial functions but may not be involved with the day-to-day activities of the government. Head of government includes the name, title of the top executive designated to manage the executive branch of the government, a . . . more
the laws of the UK apply where applicableExecutive branch: This entry includes five subentries: chief of state; head of government; cabinet; elections/appointments; election results. Chief of state includes the name, title, and beginning date in office of the titular leader of the country who represents the state at official and ceremonial functions but may not be involved with the day-to-day activities of the government. Head of government includes the name, title of the top executive designated to manage the executive branch of the government, a . . . more chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952)head of government: Commissioner Dr. Peter HAYES (since 17 October 2012); Administrator John MCMANUS (since April 2011); note - both reside in the UK and are represented by the officer commanding British Forces on Diego Garciacabinet: NAelections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; commissioner and administrator appointed by the monarchInternational organization participation: This entry lists in alphabetical order by abbreviation those international organizations in which the subject country is a member or participates in some other way.
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952)head of government: Commissioner Dr. Peter HAYES (since 17 October 2012); Administrator John MCMANUS (since April 2011); note - both reside in the UK and are represented by the officer commanding British Forces on Diego Garciacabinet: NAelections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; commissioner and administrator appointed by the monarchInternational organization participation: This entry lists in alphabetical order by abbreviation those international organizations in which the subject country is a member or participates in some other way. UPUDiplomatic representation in the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, chancery address, telephone, FAX, consulate general locations, and consulate locations. The use of the annotated title Appointed Ambassador refers to a new ambassador who has presented his/her credentials to the secretary of state but not the US president. Such ambassadors fulfill all diplomatic functions except meeting with or appearing at functions attended by the president until such time as they formally present their credentials at a White Hou . . . more
UPUDiplomatic representation in the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, chancery address, telephone, FAX, consulate general locations, and consulate locations. The use of the annotated title Appointed Ambassador refers to a new ambassador who has presented his/her credentials to the secretary of state but not the US president. Such ambassadors fulfill all diplomatic functions except meeting with or appearing at functions attended by the president until such time as they formally present their credentials at a White Hou . . . more none (overseas territory of the UK)Diplomatic representation from the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, embassy address, mailing address, telephone number, FAX number, branch office locations, consulate general locations, and consulate locations.
none (overseas territory of the UK)Diplomatic representation from the US: This entry includes the chief of mission, embassy address, mailing address, telephone number, FAX number, branch office locations, consulate general locations, and consulate locations. none (overseas territory of the UK)Flag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags.
none (overseas territory of the UK)Flag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags. white with six blue wavy horizontal stripes; the flag of the UK is in the upper hoist-side quadrant; the striped section bears a palm tree and yellow crown (the symbols of the territory) centered on the outer half of the flag; the wavy stripes represent the Indian Ocean; although not officially described, the six blue stripes may stand for the six main atolls of the archipelago
white with six blue wavy horizontal stripes; the flag of the UK is in the upper hoist-side quadrant; the striped section bears a palm tree and yellow crown (the symbols of the territory) centered on the outer half of the flag; the wavy stripes represent the Indian Ocean; although not officially described, the six blue stripes may stand for the six main atolls of the archipelago -
Economy :: British Indian Ocean Territory
-
Economic overview: This section briefly describes four key economic components for a given country:* National Economy, including economic histories, domestic labor and wage markets, and the economic sector portfolios that drive fiscal and monetary policymaking;* Financial Power & Public Finance, including brief discussions of lending/exchange rates, capital stocks/flows, and foreign direct investments arising from a country's financial and capital markets;* International Trade, including chief imports an . . . more
 All economic activity is concentrated on the largest island of Diego Garcia, where a joint UK-US military facility is located. Construction projects and various services needed to support the military installation are performed by military and contract employees from the UK, Mauritius, the Philippines, and the US. Some of the natural resources found in this territory include coconuts, fish, and sugarcane.Ease of Doing Business Index scores: The World Bank Group Doing Business project measures business regulations and enforcement mechanisms across economies and selected cities. The project evaluates domestic small and medium-size companies and measures the regulations applying to them through their life cycle. The project encourages economies to compete towards more efficient regulation; offers measurable benchmarks for reform; and serves as a resource for academics, journalists, private sector researchers and others intereste . . . more
All economic activity is concentrated on the largest island of Diego Garcia, where a joint UK-US military facility is located. Construction projects and various services needed to support the military installation are performed by military and contract employees from the UK, Mauritius, the Philippines, and the US. Some of the natural resources found in this territory include coconuts, fish, and sugarcane.Ease of Doing Business Index scores: The World Bank Group Doing Business project measures business regulations and enforcement mechanisms across economies and selected cities. The project evaluates domestic small and medium-size companies and measures the regulations applying to them through their life cycle. The project encourages economies to compete towards more efficient regulation; offers measurable benchmarks for reform; and serves as a resource for academics, journalists, private sector researchers and others intereste . . . more Exchange rates: This entry provides the average annual price of a country's monetary unit for the time period specified, expressed in units of local currency per US dollar, as determined by international market forces or by official fiat. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 4217 alphabetic currency code for the national medium of exchange is presented in parenthesis. Closing daily exchange rates are not presented in The World Factbook, but are used to convert stock values - e.g., the . . . more
Exchange rates: This entry provides the average annual price of a country's monetary unit for the time period specified, expressed in units of local currency per US dollar, as determined by international market forces or by official fiat. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 4217 alphabetic currency code for the national medium of exchange is presented in parenthesis. Closing daily exchange rates are not presented in The World Factbook, but are used to convert stock values - e.g., the . . . more
the US dollar is used
-
Communications :: British Indian Ocean Territory
-
Telecommunication systems: This entry includes a brief general assessment of a country's telecommunications system with details on the domestic and international components. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: 2G - is short for second-generation cellular network. After 2G was launched, the previous mobile wireless network systems were retroactively dubbed 1G. While radio signals on 1G networks are analog, radio signals on 2G networks are digital. Both systems use digital signaling . . . more
 general assessment: separate facilities for military and public needs are available (2018)domestic: all commercial telephone services are available, including connection to the Internet (2018)international: country code (Diego Garcia) - 246; landing point for the SAFE submarine cable that provides direct connectivity to Africa, Asia and near-by Indian Ocean island countries; international telephone service is carried by satellite (2019)Broadcast media: This entry provides information on the approximate number of public and private TV and radio stations in a country, as well as basic information on the availability of satellite and cable TV services.
general assessment: separate facilities for military and public needs are available (2018)domestic: all commercial telephone services are available, including connection to the Internet (2018)international: country code (Diego Garcia) - 246; landing point for the SAFE submarine cable that provides direct connectivity to Africa, Asia and near-by Indian Ocean island countries; international telephone service is carried by satellite (2019)Broadcast media: This entry provides information on the approximate number of public and private TV and radio stations in a country, as well as basic information on the availability of satellite and cable TV services. Armed Forces Radio and Television Service (AFRTS) broadcasts over 3 separate frequencies for US and UK military personnel stationed on the islandsInternet country code: This entry includes the two-letter codes maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in the ISO 3166 Alpha-2 list and used by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) to establish country-coded top-level domains (ccTLDs).
Armed Forces Radio and Television Service (AFRTS) broadcasts over 3 separate frequencies for US and UK military personnel stationed on the islandsInternet country code: This entry includes the two-letter codes maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in the ISO 3166 Alpha-2 list and used by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) to establish country-coded top-level domains (ccTLDs). .ioCommunications - note: This entry includes miscellaneous communications information of significance not included elsewhere.
.ioCommunications - note: This entry includes miscellaneous communications information of significance not included elsewhere. Diego Garcia hosts one of four dedicated ground antennas that assist in the operation of the Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation system (the others are on Kwajalein (Marshall Islands), at Cape Canaveral, Florida (US), and on Ascension Island (Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha))
Diego Garcia hosts one of four dedicated ground antennas that assist in the operation of the Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation system (the others are on Kwajalein (Marshall Islands), at Cape Canaveral, Florida (US), and on Ascension Island (Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha)) -
Transportation :: British Indian Ocean Territory
-
Airports: This entry gives the total number of airports or airfields recognizable from the air. The runway(s) may be paved (concrete or asphalt surfaces) or unpaved (grass, earth, sand, or gravel surfaces) and may include closed or abandoned installations. Airports or airfields that are no longer recognizable (overgrown, no facilities, etc.) are not included. Note that not all airports have accommodations for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control.
 1 (2020)country comparison to the world: 214Airports - with paved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with paved runways (concrete or asphalt surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listing. Not all . . . more
1 (2020)country comparison to the world: 214Airports - with paved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with paved runways (concrete or asphalt surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listing. Not all . . . more total: 1 (2019)over 3,047 m: 1Roadways: This entry gives the total length of the road network and includes the length of the paved and unpaved portions.
total: 1 (2019)over 3,047 m: 1Roadways: This entry gives the total length of the road network and includes the length of the paved and unpaved portions.
note: short section of paved road between port and airfield on Diego Garcia
Ports and terminals: This entry lists major ports and terminals primarily on the basis of the amount of cargo tonnage shipped through the facilities on an annual basis. In some instances, the number of containers handled or ship visits were also considered. Most ports service multiple classes of vessels including bulk carriers (dry and liquid), break bulk cargoes (goods loaded individually in bags, boxes, crates, or drums; sometimes palletized), containers, roll-on/roll-off, and passenger ships. The listing le . . . more major seaport(s): Diego Garcia
major seaport(s): Diego Garcia -
Military and Security :: British Indian Ocean Territory
-
Military and security forces: This entry lists the military and security forces subordinate to defense ministries or the equivalent (typically ground, naval, air, and marine forces), as well as those belonging to interior ministries or the equivalent (typically gendarmeries, border/coast guards, paramilitary police, and other internal security forces).
 no regular military forces (2014)Military - note: This entry includes miscellaneous military information of significance not included elsewhere.
no regular military forces (2014)Military - note: This entry includes miscellaneous military information of significance not included elsewhere. defense is the responsibility of the UK; in November 2016, the UK extended the US lease on Diego Garcia for 20 years; the lease now expires in December 2036 (2016)
defense is the responsibility of the UK; in November 2016, the UK extended the US lease on Diego Garcia for 20 years; the lease now expires in December 2036 (2016) -
Transnational Issues :: British Indian Ocean Territory
-
Disputes - international: This entry includes a wide variety of situations that range from traditional bilateral boundary disputes to unilateral claims of one sort or another. Information regarding disputes over international terrestrial and maritime boundaries has been reviewed by the US Department of State. References to other situations involving borders or frontiers may also be included, such as resource disputes, geopolitical questions, or irredentist issues; however, inclusion does not necessarily constitute . . . more

Mauritius and Seychelles claim the Chagos Islands; negotiations between 1971 and 1982 resulted in the establishment of a trust fund by the British Government as compensation for the displaced islanders, known as Chagossians, who were evicted between 1967-73; in 2001, the former inhabitants of the archipelago were granted UK citizenship and the right of return; in 2006 and 2007, British court rulings invalidated the immigration policies contained in the 2004 BIOT Constitution Order that had excluded the islanders from the archipelago; in 2008 a House of Lords' decision overturned lower court rulings, once again denying the right of return to Chagossians; in addition, the UK created the world's largest marine protection area around the Chagos islands prohibiting the extraction of any natural resources therein