-
Introduction :: Japan
-
Background:
In 1603, after decades of civil warfare, the Tokugawa shogunate (a military-led, dynastic government) ushered in a long period of relative political stability and isolation from foreign influence. For more than two centuries this policy enabled Japan to enjoy a flowering of its indigenous culture. Japan opened its ports after signing the Treaty of Kanagawa with the US in 1854 and began to intensively modernize and industrialize. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Japan became a regional power that was able to defeat the forces of both China and Russia. It occupied Korea, Formosa (Taiwan), and southern Sakhalin Island. In 1931-32 Japan occupied Manchuria, and in 1937 it launched a full-scale invasion of China. Japan attacked US forces in 1941 - triggering America's entry into World War II - and soon occupied much of East and Southeast Asia. After its defeat in World War II, Japan recovered to become an economic power and an ally of the US. While the emperor retains his throne as a symbol of national unity, elected politicians hold actual decision-making power. Following three decades of unprecedented growth, Japan's economy experienced a major slowdown starting in the 1990s, but the country remains an economic power. In March 2011, Japan's strongest-ever earthquake, and an accompanying tsunami, devastated the northeast part of Honshu island, killed thousands, and damaged several nuclear power plants. Prime Minister Shinzo ABE was reelected to office in December 2012, and has since embarked on ambitious economic and security reforms to improve Japan's economy and bolster the country's international standing. In November 2019, ABE became Japan's longest-serving post-war prime minister.
-
Geography :: Japan
-
Location:Eastern Asia, island chain between the North Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Japan, east of the Korean PeninsulaGeographic coordinates:36 00 N, 138 00 EMap references:AsiaArea:total: 377,915 sq kmland: 364,485 sq kmwater: 13,430 sq km
note: includes Bonin Islands (Ogasawara-gunto), Daito-shoto, Minami-jima, Okino-tori-shima, Ryukyu Islands (Nansei-shoto), and Volcano Islands (Kazan-retto)
country comparison to the world: 63Area - comparative:slightly smaller than CaliforniaArea comparison map: The World Factbook Field Image ModalEast Asia/Southeast Asia :: Japan Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalEast Asia/Southeast Asia :: Japan Print Image Description
Image Descriptionslightly smaller than California
Land boundaries:0 kmCoastline:29,751 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nm; between 3 nm and 12 nm in the international straits - La Perouse or Soya, Tsugaru, Osumi, and Eastern and Western Channels of the Korea or Tsushima Straitexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmClimate:varies from tropical in south to cool temperate in northTerrain:mostly rugged and mountainousElevation:mean elevation: 438 mlowest point: Hachiro-gata -4 mhighest point: Mount Fuji 3,776 mNatural resources:negligible mineral resources, fish, note, with virtually no natural energy resources, Japan is the world's largest importer of coal and liquefied natural gas, as well as the second largest importer of oilLand use:agricultural land: 12.5% (2011 est.)arable land: 11.7% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0.8% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0% (2011 est.)forest: 68.5% (2011 est.)other: 19% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:24,690 sq km (2012)Population distribution:all primary and secondary regions of high population density lie on the coast; one-third of the population resides in and around Tokyo on the central plain (Kanto Plain)Natural hazards:many dormant and some active volcanoes; about 1,500 seismic occurrences (mostly tremors but occasional severe earthquakes) every year; tsunamis; typhoons
volcanism: both Unzen (1,500 m) and Sakura-jima (1,117 m), which lies near the densely populated city of Kagoshima, have been deemed Decade Volcanoes by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to their explosive history and close proximity to human populations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Asama, Honshu Island's most active volcano, Aso, Bandai, Fuji, Iwo-Jima, Kikai, Kirishima, Komaga-take, Oshima, Suwanosejima, Tokachi, Yake-dake, and Usu; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Environment - current issues:air pollution from power plant emissions results in acid rain; acidification of lakes and reservoirs degrading water quality and threatening aquatic life; Japan is one of the largest consumers of fish and tropical timber, contributing to the depletion of these resources in Asia and elsewhere; following the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, Japan originally planned to phase out nuclear power, but it has now implemented a new policy of seeking to restart nuclear power plants that meet strict new safety standards; waste management is an ongoing issue; Japanese municipal facilities used to burn high volumes of trash, but air pollution issues forced the government to adopt an aggressive recycling policyEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:note 1: strategic location in northeast Asia; composed of four main islands - from north: Hokkaido, Honshu (the largest and most populous), Shikoku, and Kyushu (the "Home Islands") - and 6,848 smaller islands and islets
note 2: Japan annually records the most earthquakes in the world; it is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, a belt of active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters bordering the Pacific Ocean; up to 90% of the world's earthquakes and some 75% of the world's volcanoes occur within the Ring of Fire
-
People and Society :: Japan
-
Population:125,507,472 (July 2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Nationality:noun: Japanese (singular and plural)adjective: JapaneseEthnic groups:Japanese 98.1%, Chinese 0.5%, Korean 0.4%, other 1% (includes Filipino, Vietnamese, and Brazilian) (2016 est.)
note: data represent population by nationality; up to 230,000 Brazilians of Japanese origin migrated to Japan in the 1990s to work in industries; some have returned to Brazil
Languages:JapaneseReligions:Shintoism 70.4%, Buddhism 69.8%, Christianity 1.5%, other 6.9% (2015 est.)note: total adherents exceeds 100% because many people practice both Shintoism and Buddhism
Age structure:0-14 years: 12.49% (male 8,047,183/female 7,623,767)15-24 years: 9.47% (male 6,254,352/female 5,635,377)25-54 years: 36.8% (male 22,867,385/female 23,317,140)55-64 years: 12.06% (male 7,564,067/female 7,570,732)65 years and over: 29.18% (male 16,034,973/female 20,592,496) (2020 est.)population pyramid:The World Factbook Field Image ModalEast Asia/Southeast Asia :: Japan PrintImage DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Japan. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 69youth dependency ratio: 21elderly dependency ratio: 48potential support ratio: 2.1 (2020 est.)Median age:total: 48.6 yearsmale: 47.2 yearsfemale: 50 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Population growth rate:-0.27% (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 215Birth rate:7.3 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 225Death rate:10.2 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 34Net migration rate:0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 85Population distribution:all primary and secondary regions of high population density lie on the coast; one-third of the population resides in and around Tokyo on the central plain (Kanto Plain)Urbanization:urban population: 91.8% of total population (2020)rate of urbanization: -0.14% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:37.393 million TOKYO (capital), 19.165 million Osaka, 9.552 million Nagoya, 5.29 million Kitakyushu-Fukuoka, 2.922 million Shizuoka-Hamamatsu, 2.670 million Sapporo (2020)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.11 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.98 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.78 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2020 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:30.7 years (2015 est.)Maternal mortality rate:5 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 166Infant mortality rate:total: 1.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 2.1 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 1.7 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 225Life expectancy at birth:total population: 86 yearsmale: 82.7 yearsfemale: 89.5 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Total fertility rate:1.43 children born/woman (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 213Contraceptive prevalence rate:39.8% (2015)note: percent of women aged 20-49
Drinking water source:improved: total: 100% of populationunimproved: total: 0% of population (2017 est.)Current Health Expenditure:10.9% (2017)Physicians density:2.41 physicians/1,000 population (2016)Hospital bed density:13.1 beds/1,000 population (2017)Sanitation facility access:improved: total: 100% of populationunimproved: total: 0% of population (2017 est. est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:<.1% (2018 est.)HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:30,000 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 74HIV/AIDS - deaths:<200 (2017 est.)Major infectious diseases:Covid-19 (see note) (2020)note: clusters of cases of respiratory illness caused by a new coronavirus (COVID-19) in Japan; illness with this virus has ranged from mild to severe with fatalities reported; as of 8 December 2020, Japan has reported 160,098 confirmed cases of COVID19 with 2,315 deaths; the US Department of State has issued a Travel Advisory recommending increased caution in Japan due to the recent outbreak of COVID-19; the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended postponing nonessential international travel at this time and published additional guidance at https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/notices/alert/ ; on 25 May 2020, Japan ended its state of emergencyObesity - adult prevalence rate:4.3% (2016)country comparison to the world: 186Children under the age of 5 years underweight:3.4% (2010)country comparison to the world: 96Education expenditures:3.2% of GDP (2017)country comparison to the world: 127School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 15 yearsmale: 15 yearsfemale: 15 years (2016)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 3.6%male: 4.1%female: 3.1% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 171 -
Government :: Japan
-
Country name:conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Japanlocal long form: Nihon-koku/Nippon-kokulocal short form: Nihon/Nipponetymology: the English word for Japan comes via the Chinese name for the country "Cipangu"; both Nihon and Nippon mean "where the sun originates" and are frequently translated as "Land of the Rising Sun"Government type:parliamentary constitutional monarchyCapital:name: Tokyogeographic coordinates: 35 41 N, 139 45 Etime difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: originally known as Edo, meaning "estuary" in Japanese, the name was changed to Tokyo, meaning "eastern capital," in 1868Administrative divisions:47 prefectures; Aichi, Akita, Aomori, Chiba, Ehime, Fukui, Fukuoka, Fukushima, Gifu, Gunma, Hiroshima, Hokkaido, Hyogo, Ibaraki, Ishikawa, Iwate, Kagawa, Kagoshima, Kanagawa, Kochi, Kumamoto, Kyoto, Mie, Miyagi, Miyazaki, Nagano, Nagasaki, Nara, Niigata, Oita, Okayama, Okinawa, Osaka, Saga, Saitama, Shiga, Shimane, Shizuoka, Tochigi, Tokushima, Tokyo, Tottori, Toyama, Wakayama, Yamagata, Yamaguchi, YamanashiIndependence:3 May 1947 (current constitution adopted as amendment to Meiji Constitution); notable earlier dates: 11 February 660 B.C. (mythological date of the founding of the nation by Emperor JIMMU); 29 November 1890 (Meiji Constitution provides for constitutional monarchy)National holiday:Birthday of Emperor NARUHITO, 23 February (1960); note - celebrates the birthday of the current emperorConstitution:history: previous 1890; latest approved 6 October 1946, adopted 3 November 1946, effective 3 May 1947amendments: proposed by the Diet; passage requires approval by at least two-thirds majority of both houses of the Diet and approval by majority in a referendum; note - the constitution has not been amended since its enactment in 1947Legal system:civil law system based on German model; system also reflects Anglo-American influence and Japanese traditions; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme CourtInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Japandual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 yearsSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: Emperor NARUHITO (since 1 May 2019); note - succeeds his father who abdicated on 30 April 2019head of government: Prime Minister Yoshihide SUGA (since 16 September 2020 ); Deputy Prime Minister Taro ASO (since 26 December 2012)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the prime ministerelections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; the leader of the majority party or majority coalition in the House of Representatives usually becomes prime ministerLegislative branch:description: bicameral Diet or Kokkai consists of:
House of Councillors or Sangi-in (242 seats; 146 members directly elected in multi-seat districts by simple majority vote and 96 directly elected in a single national constituency by proportional representation vote; members serve 6-year terms with half the membership renewed every 3 years)
House of Representatives or Shugi-in (465 seats; 289 members directly elected in single-seat districts by simple majority vote and 176 directly elected in multi-seat districts by party-list proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)elections:
House of Councillors - last held on 10 July 2016 (next to be held in July 2019)
House of Representatives - last held on 22 October 2017 (next to be held by 21 October 2021)election results:
House of Councillors - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - LDP 55, DP 32, Komeito 14, JCP 6, Osaka Ishin no Kai (Initiatives from Osaka) 7, PLPTYF 1, SDP 1, independent 5
House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - LDP 284, CDP 55, Party of Hope 50, Komeito 29, JCP 12, JIP 11, SDP 2, independent 22note: the Diet in June 2017 redrew Japan's electoral district boundaries and reduced from 475 to 465 seats in the House of Representatives; the amended electoral law, which cuts 6 seats in single-seat districts and 4 in multi-seat districts, was reportedly intended to reduce voting disparities between densely and sparsely populated voting districtsJudicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court or Saiko saibansho (consists of the chief justice and 14 associate justices); note - the Supreme Court has jurisdiction in constitutional issuesjudge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice designated by the Cabinet and appointed by the monarch; associate justices appointed by the Cabinet and confirmed by the monarch; all justices are reviewed in a popular referendum at the first general election of the House of Representatives following each judge's appointment and every 10 years afterwardsubordinate courts: 8 High Courts (Koto-saiban-sho), each with a Family Court (Katei-saiban-sho); 50 District Courts (Chiho saibansho), with 203 additional branches; 438 Summary Courts (Kani saibansho)Political parties and leaders:Constitutional Democratic Party of Japan or CDP [Yukio EDANO]
Democratic Party of Japan or DPJ [Kohei OTSUKA]
Group of Reformists [Sakihito OZAWA]
Initiatives from Osaka (Osaka Ishin no kai) [Ichiro MATSUI]
Japan Communist Party or JCP [Kazuo SHII]
Japan Innovation Party or JIP [Ichiro MATSUI]
Party of Hope or Kibo no To [Yuichiro TAMAKI]
Komeito [Natsuo YAMAGUCHI]
Liberal Democratic Party or LDP [Yoshihide SUGA]
Liberal Party [Ichiro OZAWA] (formerly People's Life Party & Taro Yamamoto and Friends or PLPTYF)New Renaissance Party [Hiroyuki ARAI]
Party for Japanese Kokoro or PJK [Masashi NAKANO]Social Democratic Party or SDP [Tadatomo YOSHIDA]The Assembly to Energize Japan and the Independents [Kota MATSUDA]International organization participation:ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, Arctic Council (observer), ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE (observer), CERN (observer), CICA (observer), CP, CPLP (associate), EAS, EBRD, EITI (implementing country), FAO, FATF, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, G-20, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE (partner), Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SELEC (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Shinsuke SUGIYAMA (since 28 March 2018) (2018)chancery: 2520 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 238-6700FAX: [1] (202) 328-2187consulate(s) general: Anchorage (AK), Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Denver (CO), Detroit (MI), Honolulu, Houston, Las Vegas (NV), Los Angeles, Miami, Nashville (TN), New Orleans, New York, Oklahoma City (OK), Orlando (FL), Philadelphia, Phoenix (AZ), Portland (OR), San Francisco, Seattle, Saipan (Northern Mariana Islands), Tamuning (Guam)Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Joseph M. YOUNG (since 22 July 2019)telephone: [81] (03) 3224-5000embassy: 1-10-5 Akasaka, Minato-ku, Tokyo 107-8420mailing address: Unit 9800, Box 300, APO AP 96303-0300FAX: [81] (03) 3505-1862consulate(s) general: Naha (Okinawa), Osaka-Kobe, Sapporoconsulate(s): Fukuoka, NagoyaFlag description:white with a large red disk (representing the sun without rays) in the centerNational symbol(s):red sun disc, chrysanthemum; national colors: red, whiteNational anthem:name: "Kimigayo" (The Emperor"s Reign)lyrics/music: unknown/Hiromori HAYASHInote: adopted 1999; unofficial national anthem since 1883; oldest anthem lyrics in the world, dating to the 10th century or earlier; there is some opposition to the anthem because of its association with militarism and worship of the emperor
-
Economy :: Japan
-
Economic overview:
Over the past 70 years, government-industry cooperation, a strong work ethic, mastery of high technology, and a comparatively small defense allocation (slightly less than 1% of GDP) have helped Japan develop an advanced economy. Two notable characteristics of the post-World War II economy were the close interlocking structures of manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors, known as keiretsu, and the guarantee of lifetime employment for a substantial portion of the urban labor force. Both features have significantly eroded under the dual pressures of global competition and domestic demographic change.
Measured on a purchasing power parity basis that adjusts for price differences, Japan in 2017 stood as the fourth-largest economy in the world after first-place China, which surpassed Japan in 2001, and third-place India, which edged out Japan in 2012. For three postwar decades, overall real economic growth was impressive - averaging 10% in the 1960s, 5% in the 1970s, and 4% in the 1980s. Growth slowed markedly in the 1990s, averaging just 1.7%, largely because of the aftereffects of inefficient investment and the collapse of an asset price bubble in the late 1980s, which resulted in several years of economic stagnation as firms sought to reduce excess debt, capital, and labor. Modest economic growth continued after 2000, but the economy has fallen into recession four times since 2008.
Japan enjoyed an uptick in growth since 2013, supported by Prime Minister Shinzo ABE’s "Three Arrows" economic revitalization agenda - dubbed "Abenomics" - of monetary easing, "flexible" fiscal policy, and structural reform. Led by the Bank of Japan’s aggressive monetary easing, Japan is making modest progress in ending deflation, but demographic decline – a low birthrate and an aging, shrinking population – poses a major long-term challenge for the economy. The government currently faces the quandary of balancing its efforts to stimulate growth and institute economic reforms with the need to address its sizable public debt, which stands at 235% of GDP. To help raise government revenue, Japan adopted legislation in 2012 to gradually raise the consumption tax rate. However, the first such increase, in April 2014, led to a sharp contraction, so Prime Minister ABE has twice postponed the next increase, which is now scheduled for October 2019. Structural reforms to unlock productivity are seen as central to strengthening the economy in the long-run.
Scarce in critical natural resources, Japan has long been dependent on imported energy and raw materials. After the complete shutdown of Japan’s nuclear reactors following the earthquake and tsunami disaster in 2011, Japan's industrial sector has become even more dependent than before on imported fossil fuels. However, ABE’s government is seeking to restart nuclear power plants that meet strict new safety standards and is emphasizing nuclear energy’s importance as a base-load electricity source. In August 2015, Japan successfully restarted one nuclear reactor at the Sendai Nuclear Power Plant in Kagoshima prefecture, and several other reactors around the country have since resumed operations; however, opposition from local governments has delayed several more restarts that remain pending. Reforms of the electricity and gas sectors, including full liberalization of Japan’s energy market in April 2016 and gas market in April 2017, constitute an important part of Prime Minister Abe’s economic program.
Under the Abe Administration, Japan’s government sought to open the country’s economy to greater foreign competition and create new export opportunities for Japanese businesses, including by joining 11 trading partners in the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP). Japan became the first country to ratify the TPP in December 2016, but the United States signaled its withdrawal from the agreement in January 2017. In November 2017 the remaining 11 countries agreed on the core elements of a modified agreement, which they renamed the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). Japan also reached agreement with the European Union on an Economic Partnership Agreement in July 2017, and is likely seek to ratify both agreements in the Diet this year.
GDP real growth rate:0.7% (2019 est.)0.29% (2018 est.)2.19% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Inflation rate (consumer prices):0.4% (2019 est.)0.9% (2018 est.)0.4% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Credit ratings:Fitch rating: A (2015)Moody's rating: A1 (2014)Standard & Poors rating: A+ (2015)GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:$4,883,791,000,000 (2019 est.)$4,850,155,000,000 (2018 est.)$4,836,098,000,000 (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):$5,078,679,000,000 (2019 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$48,979 (2019 est.)$48,511 (2018 est.)$48,256 (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
country comparison to the world: 32Gross national saving:28% of GDP (2017 est.)27.5% of GDP (2016 est.)27.1% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 41GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 1.1% (2017 est.)industry: 30.1% (2017 est.)services: 68.7% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 55.5% (2017 est.)government consumption: 19.6% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 24% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 0% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 17.7% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -16.8% (2017 est.)Ease of Doing Business Index scores:86.1 (2020)Agriculture - products:vegetables, rice, fish, poultry, fruit, dairy products, pork, beef, flowers, potatoes/taros/yams, sugarcane, tea, legumes, wheat and barleyIndustries:among world's largest and most technologically advanced producers of motor vehicles, electronic equipment, machine tools, steel and nonferrous metals, ships, chemicals, textiles, processed foodsIndustrial production growth rate:1.4% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Labor force:66.54 million (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 2.9%industry: 26.2%services: 70.9% (February 2015 est.)Unemployment rate:2.36% (2019 est.)2.44% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Population below poverty line:16.1% (2013 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.7%highest 10%: 24.8% (2008)Budget:revenues: 1.714 trillion (2017 est.)expenditures: 1.885 trillion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:35.2% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-3.5% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Public debt:237.6% of GDP (2017 est.)235.6% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Fiscal year:1 April - 31 MarchCurrent account balance:$185.644 billion (2019 est.)$177.08 billion (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Exports:$1,084,146,000,000 (2019 est.)$1,099,855,000,000 (2018 est.)$1,059,991,000,000 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Exports - partners:US 19.4%, China 19%, South Korea 7.6%, Hong Kong 5.1%, Thailand 4.2% (2017)Exports - commodities:14.9 motor vehicles5.4 iron and steel products5 semiconductors4.8 auto parts3.5 power generating machinery3.3 plastic materials (2014 est.)Imports:$1,032,112,000,000 (2019 est.)$1,035,557,000,000 (2018 est.)$998.014 billion (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Imports - commodities:16.1 petroleum9.1 liquid natural gas3.8 clothing3.3 semiconductors2.4 coal1.4 audio and visual apparatus (2014 est.)Imports - partners:China 24.5%, US 11%, Australia 5.8%, South Korea 4.2%, Saudi Arabia 4.1% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$1.264 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)$1.233 trillion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Debt - external:$3.24 trillion (31 March 2016 est.)$2.83 trillion (31 March 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Exchange rates:yen (JPY) per US dollar -104.205 (2020 est.)108.605 (2019 est.)112.7 (2018 est.)121.02 (2014 est.)97.44 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Japan
-
Electricity access:electrification - total population: 100% (2020)Electricity - production:989.3 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Electricity - consumption:943.7 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 152Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 163Electricity - installed generating capacity:295.9 million kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Electricity - from fossil fuels:71% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 104Electricity - from nuclear fuels:1% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:8% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 121Electricity - from other renewable sources:20% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Crude oil - production:3,200 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 82Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 143Crude oil - imports:3.208 million bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Crude oil - proved reserves:44.12 million bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 77Refined petroleum products - production:3.467 million bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Refined petroleum products - consumption:3.894 million bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Refined petroleum products - exports:370,900 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 24Refined petroleum products - imports:1.1 million bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Natural gas - production:3.058 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Natural gas - consumption:127.2 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Natural gas - exports:169.9 million cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 47Natural gas - imports:116.6 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Natural gas - proved reserves:20.9 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 74Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:1.268 billion Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 5
-
Communications :: Japan
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 62,775,494subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 49.88 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 3Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 175,187,425subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 139.2 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Telecommunication systems:general assessment: excellent domestic and international service; exceedingly high mobile, mobile broadband and fixed broadband penetration; strong govt. policies for over a decade see over 90% of households with FttX; one of Japan's largest e-commerce companies planning to build its own nationwide stand-alone 5G mobile network; govt. to implement a telecom tax to pay for rural 5G network; FttH will continue to increase its share of total fixed broadband subscriptions as DSL is phased out; mature telecom system will show slow growth in the next few years to 2024 (2020)domestic: high level of modern technology and excellent service of every kind; 50 per 100 for fixed-line and 140 per 100 for mobile-cellular subscriptions (2019)international: country code - 81; numerous submarine cables with landing points for HSCS, JIH, RJCN, APCN-2, JUS, EAC-C2C, PC-1, Tata TGN-Pacific, FLAG North Asia Loop/REACH North Asia Loop, APCN-2, FASTER, SJC, SJC2, Unity/EAC-Pacific, JGA-N, APG, ASE, AJC, JUPITER, MOC, Okinawa Cellular Cable, KJCN, GOKI, KJCN, and SeaMeWE-3, submarine cables provide links throughout Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, Southeast Asia, Africa and US; satellite earth stations - 7 Intelsat (Pacific and Indian Oceans), 1 Intersputnik (Indian Ocean region), 2 Inmarsat (Pacific and Indian Ocean regions), and 8 SkyPerfect JSAT (2019)note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderatedBroadcast media:a mixture of public and commercial broadcast TV and radio stations; 6 national terrestrial TV networks including 1 public broadcaster; the large number of radio and TV stations available provide a wide range of choices; satellite and cable services provide access to international channels (2019)Internet country code:.jpInternet users:total: 106,725,643percent of population: 84.59% (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 41,496,293subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 33 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 3
-
Transportation :: Japan
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 22 (2020)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 673annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 126,387,527 (2018)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 9,420,660,000 mt-km (2018)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:JA (2016)Airports:175 (2013)country comparison to the world: 32Airports - with paved runways:total: 142 (2017)over 3,047 m: 6 (2017)2,438 to 3,047 m: 45 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 38 (2017)914 to 1,523 m: 28 (2017)under 914 m: 25 (2017)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 33 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 5 (2013)under 914 m: 28 (2013)Heliports:16 (2013)Pipelines:4456 km gas, 174 km oil, 104 km oil/gas/water (2013)Railways:total: 27,311 km (2015)standard gauge: 4,800 km 1.435-m gauge (4,800 km electrified) (2015)narrow gauge: 124 km 1.372-m gauge (124 km electrified) (2015)dual gauge: 132 km 1.435-1.067-m gauge (132 km electrified) (2015)22,207 km 1.067-m gauge (15,430 km electrified)
48 km 0.762-m gauge (48 km electrified)country comparison to the world: 11Roadways:total: 1,218,772 km (2015)paved: 992,835 km (includes 8,428 km of expressways) (2015)unpaved: 225,937 km (2015)country comparison to the world: 6Waterways:1,770 km (seagoing vessels use inland seas) (2010)country comparison to the world: 44Merchant marine:total: 5,017by type: bulk carrier 158, container ship 37, general cargo 1,767, oil tanker 661, other 2,394 (2019)country comparison to the world: 4Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Chiba, Kawasaki, Kobe, Mizushima, Moji, Nagoya, Osaka, Tokyo, Tomakomai, Yokohamacontainer port(s) (TEUs): Kobe (2,924,179), Nagoya (2,784,109), Osaka (2,326,852), Tokyo (4,500,156), Yokohama (2,926,698) (2017)LNG terminal(s) (import): Chita, Fukwoke, Futtsu, Hachinone, Hakodate, Hatsukaichi, Higashi Ohgishima, Higashi Niigata, Himeiji, Joetsu, Kagoshima, Kawagoe, Kita Kyushu, Mizushima, Nagasaki, Naoetsu, Negishi, Ohgishima, Oita, Sakai, Sakaide, Senboku, Shimizu, Shin Minato, Sodegaura, Tobata, Yanai, YokkaichiOkinawa - Nakagusuku -
Military and Security :: Japan
-
Military and security forces:Japan Self-Defense Force (JSDF): Ground Self-Defense Force (Rikujou Jieitai, GSDF; includes aviation), Maritime Self-Defense Force (Kaijou Jieitai, MSDF; includes naval aviation), Air Self-Defense Force (Koukuu Jieitai, ASDF); Japan Coast Guard (Ministry of Land, Transport, Infrastructure and Tourism) (2019)Military expenditures:0.93% of GDP (2019)0.93% of GDP (2018)0.93% of GDP (2017)0.94% of GDP (2016)0.94% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 124Military and security service personnel strengths:
the Japanese Self Defense Force (JSDF) is comprised of approximately 240,000 active personnel (145,000 Ground; 45,000 Maritime; 45,000 Air; 4,000 Joint Forces); 14,000 Coast Guard; 56,000 reserves
(2019 est.)Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:the JSDF is equipped with a mix of imported and domestically-produced equipment; Japan is capable of producing a wide range of air, ground, and naval weapons systems; the majority of its weapons imports are from the US and some domestically-produced weapons are US-origin and manufactured under license (2019)Military deployments:approximately 170 Djibouti (2020 )Military service age and obligation:18 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; mandatory retirement at age 53 for senior enlisted personnel and at 62 years for senior service officers (2012) -
Terrorism :: Japan
-
Terrorist group(s):Aum Shinrikyo (AUM/Aleph) (2019)note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
-
Transnational Issues :: Japan
-
Disputes - international:
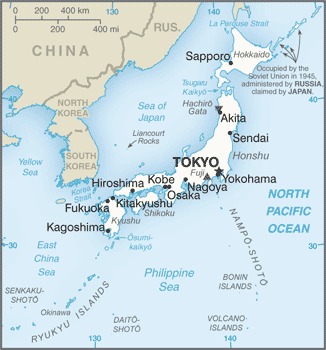
the sovereignty dispute over the islands of Etorofu, Kunashiri, and Shikotan, and the Habomai group, known in Japan as the "Northern Territories" and in Russia as the "Southern Kuril Islands," occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945, now administered by Russia and claimed by Japan, remains the primary sticking point to signing a peace treaty formally ending World War II hostilities; Japan and South Korea claim Liancourt Rocks (Take-shima/Tok-do) occupied by South Korea since 1954; the Japanese-administered Senkaku Islands are also claimed by China and Taiwan
Refugees and internally displaced persons:stateless persons: 687 (2019)