-
Introduction :: Sri Lanka
-
Background:
The first Sinhalese arrived in Sri Lanka late in the 6th century B.C., probably from northern India. Buddhism was introduced circa 250 B.C., and the first kingdoms developed at the cities of Anuradhapura (from circa 200 B.C. to circa A.D. 1000) and Polonnaruwa (from about 1070 to 1200). In the 14th century, a south Indian dynasty established a Tamil kingdom in northern Sri Lanka. The Portuguese controlled the coastal areas of the island in the 16th century followed by the Dutch in the 17th century. The island was ceded to the British in 1796, became a crown colony in 1802, and was formally united under British rule by 1815. As Ceylon, it became independent in 1948; its name was changed to Sri Lanka in 1972. Prevailing tensions between the Sinhalese majority and Tamil separatists erupted into war in July 1983. Fighting between the government and Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) continued for over a quarter century. Although Norway brokered peace negotiations that led to a ceasefire in 2002, the fighting slowly resumed and was again in full force by 2006. The government defeated the LTTE in May 2009.
During the post-conflict years under President Mahinda RAJAPAKSA, the government initiated infrastructure development projects, many of which were financed by loans from China. His regime faced significant allegations of human rights violations and a shrinking democratic space for civil society. In 2015, a new coalition government headed by President Maithripala SIRISENA of the Sri Lanka Freedom Party and Prime Minister Ranil WICKREMESINGHE of the United National Party came to power with pledges to advance economic, governance, anti-corruption, reconciliation, justice, and accountability reforms. However, implementation of these reforms has been uneven. In October 2018, President SIRISENA attempted to oust Prime Minister WICKREMESINGHE, swearing in former President RAJAPAKSA as the new prime minister and issuing an order to dissolve the parliament and hold elections. This sparked a seven-week constitutional crisis that ended when the Supreme Court ruled SIRISENA’s actions unconstitutional, RAJAPAKSA resigned, and WICKREMESINGHE was reinstated. In November 2019, Gotabaya RAJAPAKSA won the presidential election and appointed his brother, Mahinda, prime minister.
-
Geography :: Sri Lanka
-
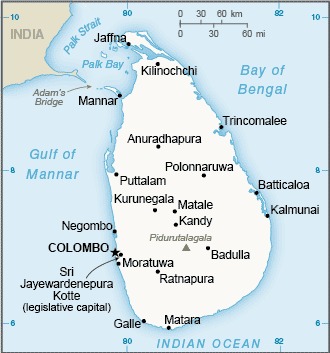
Location:Southern Asia, island in the Indian Ocean, south of IndiaGeographic coordinates:7 00 N, 81 00 EMap references:AsiaArea:total: 65,610 sq kmland: 64,630 sq kmwater: 980 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 122Area - comparative:slightly larger than West VirginiaArea comparison map:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth Asia :: Sri Lanka Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth Asia :: Sri Lanka Print Image Description
Image Descriptionslightly larger than West Virginia
Land boundaries:0 kmCoastline:1,340 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:tropical monsoon; northeast monsoon (December to March); southwest monsoon (June to October)Terrain:mostly low, flat to rolling plain; mountains in south-central interiorElevation:mean elevation: 228 mlowest point: Indian Ocean 0 mhighest point: Pidurutalagala 2,524 mNatural resources:limestone, graphite, mineral sands, gems, phosphates, clay, hydropower, arable landLand use:agricultural land: 43.5% (2011 est.)arable land: 20.7% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 15.8% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 7% (2011 est.)forest: 29.4% (2011 est.)other: 27.1% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:5,700 sq km (2012)Population distribution:the population is primarily concentrated within a broad wet zone in the southwest, urban centers along the eastern coast, and on the Jaffna Peninsula in the northNatural hazards:occasional cyclones and tornadoesEnvironment - current issues:deforestation; soil erosion; wildlife populations threatened by poaching and urbanization; coastal degradation from mining activities and increased pollution; coral reef destruction; freshwater resources being polluted by industrial wastes and sewage runoff; waste disposal; air pollution in ColomboEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:strategic location near major Indian Ocean sea lanes; Adam's Bridge is a chain of limestone shoals between the southeastern coast of India and the northwestern coast of Sri Lanka; geological evidence suggests that this 50-km long Bridge once connected India and Sri Lanka; ancient records seem to indicate that a foot passage was possible between the two land masses until the 15th century when the land bridge broke up in a cyclone -
People and Society :: Sri Lanka
-
Population:22,889,201 (July 2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Nationality:noun: Sri Lankan(s)adjective: Sri LankanEthnic groups:Sinhalese 74.9%, Sri Lankan Tamil 11.2%, Sri Lankan Moors 9.2%, Indian Tamil 4.2%, other 0.5% (2012 est.)Languages:Sinhala (official and national language) 87%, Tamil (official and national language) 28.5%, English 23.8% (2012 est.)
note: data represent main languages spoken by the population aged 10 years and older; shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census; English is commonly used in government and is referred to as the "link language" in the constitution
Religions:Buddhist (official) 70.2%, Hindu 12.6%, Muslim 9.7%, Roman Catholic 6.1%, other Christian 1.3%, other 0.05% (2012 est.)Age structure:0-14 years: 23.11% (male 2,696,379/female 2,592,450)15-24 years: 14.58% (male 1,700,442/female 1,636,401)25-54 years: 41.2% (male 4,641,842/female 4,789,101)55-64 years: 10.48% (male 1,110,481/female 1,288,056)65 years and over: 10.63% (male 1,023,315/female 1,410,734) (2020 est.)population pyramid:The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth Asia :: Sri Lanka PrintImage DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Sri Lanka. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 53.7youth dependency ratio: 36.4elderly dependency ratio: 17.3potential support ratio: 5.8 (2020 est.)Median age:total: 33.7 yearsmale: 32.3 yearsfemale: 35.1 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 97Population growth rate:0.67% (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Birth rate:14.2 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 131Death rate:6.5 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Net migration rate:-1.3 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 149Population distribution:the population is primarily concentrated within a broad wet zone in the southwest, urban centers along the eastern coast, and on the Jaffna Peninsula in the northUrbanization:urban population: 18.7% of total population (2020)rate of urbanization: 0.85% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:103,000 Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (legislative capital) (2018), 613,000 COLOMBO (capital) (2020)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.97 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.86 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.73 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2020 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:25.6 years (2016 est.)note: median age at first birth among women 30-34
Maternal mortality rate:36 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 106Infant mortality rate:total: 7.8 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 8.8 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 6.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 150Life expectancy at birth:total population: 77.5 yearsmale: 74 yearsfemale: 81.1 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Total fertility rate:2.01 children born/woman (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 111Contraceptive prevalence rate:61.7% (2016)Drinking water source:improved: urban: 98.1% of populationrural: 91.4% of populationtotal: 92.6% of populationunimproved: urban: 1.9% of populationrural: 8.6% of populationtotal: 7.4% of population (2017 est.)Current Health Expenditure:3.8% (2017)Physicians density:0.93 physicians/1,000 population (2017)Hospital bed density:4.2 beds/1,000 population (2017)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 97.1% of populationrural: 99.3% of populationtotal: 98.9% of populationunimproved: urban: 2.9% of populationrural: 0.7% of populationtotal: 1.1% of population (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:<.1% (2019 est.)HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:3,600 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 127HIV/AIDS - deaths:<200 (2019 est.)Major infectious diseases:degree of risk:intermediate
(2020)vectorborne diseases: dengue feverwater contact diseases: leptospirosisanimal contact diseases: rabiesObesity - adult prevalence rate:5.2% (2016)country comparison to the world: 182Children under the age of 5 years underweight:20.5% (2016)country comparison to the world: 23Education expenditures:2.1% of GDP (2018)country comparison to the world: 160Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 91.9%male: 93%female: 91% (2017)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 14 yearsmale: 14 yearsfemale: 15 years (2018)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 21%male: 16.8%female: 28.4% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 60 -
Government :: Sri Lanka
-
Country name:conventional long form: Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lankaconventional short form: Sri Lankalocal long form: Shri Lanka Prajatantrika Samajavadi Janarajaya/Ilankai Jananayaka Choshalichak Kutiyarachulocal short form: Shri Lanka/Ilankaiformer: Serendib, Ceylonetymology: the name means "resplendent island" in SanskritGovernment type:presidential republicCapital:name: Colombo (commercial capital); Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (legislative capital)geographic coordinates: 6 55 N, 79 50 Etime difference: UTC+5.5 (10.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: Colombo may derive from the Sinhala "kolon thota," meaning "port on the river" (referring to the Kelani River that empties into the Indian Ocean at Colombo); alternatively, the name may derive from the Sinhala "kola amba thota" meaning "harbor with mango trees"; it is also possible that the Portuguese named the city after Christopher COLUMBUS, who lived in Portugal for many years (as Cristovao COLOMBO) before discovering the Americas for the Spanish crown in 1492 - not long before the Portuguese made their way to Sri Lanka in 1505; Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte translates as "Resplendent City of Growing Victory" in SinhalaAdministrative divisions:9 provinces; Central, Eastern, North Central, Northern, North Western, Sabaragamuwa, Southern, Uva, WesternIndependence:4 February 1948 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day (National Day), 4 February (1948)Constitution:history: several previous; latest adopted 16 August 1978, certified 31 August 1978amendments: proposed by Parliament; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of its total membership, certification by the president of the republic or the Parliament speaker, and in some cases approval in a referendum by absolute majority of valid votes; amended many times, last in 2020Legal system:mixed legal system of Roman-Dutch civil law, English common law, Jaffna Tamil customary law, and Muslim personal lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Sri Lankadual citizenship recognized: no, except in cases where the government rules it is to the benefit of Sri Lankaresidency requirement for naturalization: 7 yearsSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Gotabaya RAJAPAKSA (since 18 November 2019); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government; Prime Minister Mahinda RAJAPAKSA (since 21 November 2019)head of government: President Gotabaya RAJAPAKSA (since 18 November 2019)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president in consultation with the prime ministerelections/appointments: president directly elected by preferential majority popular vote for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 16 November 2019 (next to be held in 2024); prime minister appointed by the president from among members of Parliament for a 5-year term)election results: Gotabaya RAJAPAKSA elected president; percent of vote - Gotabaya RAJAPAKSA (SLPP) 52.2%, Sajith PREMADASA (UNP) 42%, other 5.8%Legislative branch:description: unicameral Parliament (225 seats; 196 members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote using a preferential method in which voters select 3 candidates in order of preference; remaining 29 seats allocated to other political parties and groups in proportion to share of national vote; members serve 5-year terms)elections: last held on 17 August 2015 (next originally scheduled for 25 April 2020 but postponed to due to the COVID-19 pandemic)election results: percent of vote by coalition/party - SLFPA 59.1%, SJB 23.9%, JVP 3.8%, TNA 2.8%, UNP 2.2%, TNPF 0.6%, EPDP 0.5%, other 7.1%; seats by coalition/party - SLFPA 145, SJB 54, TNA 10, JVP 3, other 13; composition - NAJudicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court of the Republic (consists of the chief justice and 9 justices); note - the court has exclusive jurisdiction to review legislationjudge selection and term of office: chief justice nominated by the Constitutional Council (CC), a 9-member high-level advisory body, and appointed by the president; other justices nominated by the CC and appointed by the president on the advice of the chief justice; all justices can serve until age 65subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; High Courts; Magistrates' Courts; municipal and primary courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Crusaders for Democracy [Ganeshalingam CHANDRALINGAM]
Eelam People's Democratic Party or EPDP [Douglas DEVANANDA]
Eelam People's Revolutionary Liberation Front [Suresh PREMACHANDRAN]
Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna or JVP [Anura Kumara DISSANAYAKE]
Jathika Hela Urumaya or JHU [Karunarathna PARANAWITHANA, Ven. Hadigalle Wimalasara THERO]
National Peoples Power or JVP [Anura Kumara DISSANAYAKE]
Samagi Jana Balawegaya or SJB [Sajith PREMADASA]
Sri Lanka Freedom Party or SLFP [Maithripala SIRISENA]
Sri Lanka Muslim Congress or SLMC [Rauff HAKEEM]
Sri Lanka People's Freedom Alliance [Mahinda RAJAPAKSA]
Sri Lanka Podujana Peramuna or SLPP [G. L. PEIRIS]
Tamil National Alliance or TNA [Rajavarothiam SAMPANTHAN] (alliance includes Illankai Tamil Arasu Kachchi [Mavai SENATHIRAJAH], People's Liberation Organisation of Tamil Eelam [D. SIDDARTHAN], Tamil Eelam Liberation Organization [Selvam ADAIKALANATHAN])
Tamil National People's Front [Gajendrakumar PONNAMBALAM]
United National Front for Good Governance or UNFGG [Ranil WICKREMESINGHE] (coalition includes JHU, UNP)
United National Party or UNP [Ranil WICKREMESINGHE]
United People's Freedom Alliance or UPFA [Maithripala SIRISENA] (coalition includes SLFP)International organization participation:ABEDA, ADB, ARF, BIMSTEC, C, CD, CICA (observer), CP, FAO, G-11, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, SAARC, SACEP, SCO (dialogue member), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador E. Rodney M. PERERA (since 8 July 2019)chancery: 3025 Whitehaven Street NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 483-4025 through 4028FAX: [1] (202) 232-7181consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Alaina B. TEPLITZ (since 1 November 2018); note - also accredited to Maldivestelephone: [94] (11) 249-8500embassy: 210 Galle Road, Colombo 03mailing address: P. O. Box 106, ColomboFAX: [94] (11) 243-7345Flag description:yellow with two panels; the smaller hoist-side panel has two equal vertical bands of green (hoist side) and orange; the other larger panel depicts a yellow lion holding a sword on a maroon rectangular field that also displays a yellow bo leaf in each corner; the yellow field appears as a border around the entire flag and extends between the two panels; the lion represents Sinhalese ethnicity, the strength of the nation, and bravery; the sword demonstrates the sovereignty of the nation; the four bo leaves - symbolizing Buddhism and its influence on the country - stand for the four virtues of kindness, friendliness, happiness, and equanimity; orange signifies Sri Lankan Tamils, green Sri Lankan Moors, and maroon the Sinhalese majority; yellow denotes other ethnic groups; also referred to as the Lion FlagNational symbol(s):lion, water lily; national colors: maroon, yellowNational anthem:name: "Sri Lanka Matha" (Mother Sri Lanka)lyrics/music: Ananda SAMARKONEnote: adopted 1951
-
Economy :: Sri Lanka
-
Economic overview:
Sri Lanka is attempting to sustain economic growth while maintaining macroeconomic stability under the IMF program it began in 2016. The government's high debt payments and bloated civil service, which have contributed to historically high budget deficits, remain a concern. Government debt is about 79% of GDP and remains among the highest of the emerging markets. In the coming years, Sri Lanka will need to balance its elevated debt repayment schedule with its need to maintain adequate foreign exchange reserves.
In May 2016, Sri Lanka regained its preferential trade status under the European Union’s Generalized System of Preferences Plus, enabling many of its firms to export products, including its top export garments, tax free to the EU. In 2017, Parliament passed a new Inland Revenue Act in an effort to increase tax collection and broaden the tax base in response to recommendations made under its IMF program. In November 2017, the Financial Action Task Force on money laundering and terrorist financing listed Sri Lanka as non-compliant, but reported subsequently that Sri Lanka had made good progress in implementing an action plan to address deficiencies.
Tourism has experienced strong growth in the years since the resolution of the government's 26-year conflict with the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam. In 2017, the government promulgated plans to transform the country into a knowledge-based, export-oriented Indian Ocean hub by 2025.
GDP real growth rate:2.29% (2019 est.)3.32% (2018 est.)3.58% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Inflation rate (consumer prices):4.3% (2019 est.)4.2% (2018 est.)6.5% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Credit ratings:Fitch rating: CCC (2020)Moody's rating: Caa1 (2020)Standard & Poors rating: CCC+ (2020)GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:$256.006 billion (2019 est.)$250.29 billion (2018 est.)$242.28 billion (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):$84.016 billion (2019 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$4,103 (2019 est.)$4,030 (2018 est.)$3,919 (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
country comparison to the world: 163Gross national saving:33.8% of GDP (2017 est.)32.8% of GDP (2016 est.)28.8% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 20GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 7.8% (2017 est.)industry: 30.5% (2017 est.)services: 61.7% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 62% (2017 est.)government consumption: 8.5% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 26.3% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 10.2% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 21.9% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -29.1% (2017 est.)Ease of Doing Business Index scores:73.3 (2020)Agriculture - products:rice, sugarcane, grains, pulses, oilseed, spices, vegetables, fruit, tea, rubber, coconuts; milk, eggs, hides, beef; fishIndustries:processing of rubber, tea, coconuts, tobacco and other agricultural commodities; telecommunications, insurance, banking; tourism, shipping; clothing, textiles; cement, petroleum refining, information technology services, constructionIndustrial production growth rate:4.6% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Labor force:8 million (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 27%industry: 26%services: 47% (31 December 2016)Unemployment rate:4.83% (2019 est.)4.44% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Population below poverty line:6.7% (2012 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 3%highest 10%: 32.2% (2012 est.)Budget:revenues: 12.07 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 16.88 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:13.8% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-5.5% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Public debt:79.1% of GDP (2017 est.)79.6% of GDP (2016 est.)note: covers central government debt and excludes debt instruments directly owned by government entities other than the treasury (e.g. commercial bank borrowings of a government corporation); the data includes treasury debt held by foreign entities as well as intragovernmental debt; intragovernmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement; sub-national entities are usually not permitted to sell debt instruments
country comparison to the world: 35Fiscal year:calendar yearCurrent account balance:-$10 million (2019 est.)-$17 million (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 69Exports:$16.322 billion (2019 est.)$15.238 billion (2018 est.)$15.166 billion (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 82Exports - partners:US 24.6%, UK 9%, India 5.8%, Singapore 4.5%, Germany 4.3%, Italy 4.3% (2017)Exports - commodities:textiles and apparel, tea and spices; rubber manufactures; precious stones; coconut products, fishImports:$24.984 billion (2019 est.)$26.521 billion (2018 est.)$26.063 billion (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 74Imports - commodities:petroleum, textiles, machinery and transportation equipment, building materials, mineral products, foodstuffsImports - partners:India 22%, China 19.9%, Singapore 6.9%, UAE 5.7%, Japan 4.9% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$7.959 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$6.019 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 78Debt - external:$51.72 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$45.26 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Exchange rates:Sri Lankan rupees (LKR) per US dollar -185.8 (2020 est.)181.2 (2019 est.)178.545 (2018 est.)135.86 (2014 est.)130.57 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Sri Lanka
-
Electricity access:electrification - total population: 100% (2019)Electricity - production:13.66 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 90Electricity - consumption:12.67 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 202Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Electricity - installed generating capacity:3.998 million kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 89Electricity - from fossil fuels:52% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 187Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:42% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Electricity - from other renewable sources:6% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 103Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Crude oil - imports:33,540 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Refined petroleum products - production:34,210 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 84Refined petroleum products - consumption:116,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 74Refined petroleum products - exports:3,871 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 96Refined petroleum products - imports:66,280 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 70Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 201Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 189Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 192Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 197Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:25.19 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 80
-
Communications :: Sri Lanka
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 2,641,982subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 11.62 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 47Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 26,160,623subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 115.06 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Telecommunication systems:general assessment: telephone services have improved significantly; strong growth anticipated as Sri Lanka is lagging behind other Asian telecoms; increase in mobile broadband penetration; govt. funds telecom sector to expand fiber and LTE networks and growing investment in 5G services (2020)domestic: fixed-line 12 per 100 and mobile-cellular 115 per 100; national trunk network consists of digital microwave radio relay and fiber-optic links; fixed wireless local loops have been installed; competition is strong in mobile cellular systems and mobile cellular subscribership is increasing (2019)international: country code - 94; landing points for the SeaMeWe -3,-5, Dhiraagu-SLT Submarine Cable Network, WARF Submarine Cable, Bharat Lanka Cable System and the Bay of Bengal Gateway submarine cables providing connectivity to Asia, Africa, Southeast Asia, Australia, the Middle East, and Europe; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) (2019)note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderatedBroadcast media:government operates 5 TV channels and 19 radio channels; multi-channel satellite and cable TV subscription services available; 25 private TV stations and about 43 radio stations; 6 non-profit TV stations and 4 radio stationsInternet country code:.lkInternet users:total: 7,700,876percent of population: 34.11% (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 1,544,313subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 7 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 63
-
Transportation :: Sri Lanka
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 3 (2020)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 34annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 5,882,376 (2018)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 436.2 million mt-km (2018)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:4R (2016)Airports:18 (2020)country comparison to the world: 140Airports - with paved runways:total: 11 (2020)over 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 5914 to 1,523 m: 4Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 7 (2020)1,524 to 2,437 m: 2914 to 1,523 m: 3under 914 m: 2Heliports:1 (2020)Pipelines:7 km refined productsRailways:total: 1,562 km (2016)broad gauge: 1,562 km 1.676-m gauge (2016)country comparison to the world: 82Roadways:total: 114,093 km (2010)paved: 16,977 km (2010)unpaved: 97,116 km (2010)country comparison to the world: 43Waterways:160 km (primarily on rivers in southwest) (2012)country comparison to the world: 100Merchant marine:total: 97by type: bulk carrier 8, container ship 1, general cargo 17, oil tanker 13, other 58 (2019)country comparison to the world: 92Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Colombocontainer port(s) (TEUs): Colombo (6,209,000) (2017)
-
Military and Security :: Sri Lanka
-
Military and security forces:Sri Lanka Army (includes National Guard and the Volunteer Force), Sri Lanka Navy (includes Marine Corps), Sri Lanka Air Force, Sri Lanka Coast Guard; Civil Security Department (Home Guard); Sri Lanka National Police: Special Task Force (counter-terrorism and counter-insurgency) (2019)Military expenditures:1.9% of GDP (2019)1.9% of GDP (2018)2.1% of GDP (2017)2.1% of GDP (2016)2.6% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 56Military and security service personnel strengths:the Sri Lankan military has approximately 250,000 total personnel (180,000 Army; 40,000 Navy; 30,000 Air Force) (2019)Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:the Sri Lankan military inventory consists mostly of Chinese and Russian-origin equipment, as well as smaller amounts from Israel, the UK, and the US; since 2000, China, India, Israel, and the US have been the leading suppliers of arms to Sri Lanka (2019 est.)Military deployments:110 Central African Republic (MINUSCA); 140 Lebanon (UNIFIL); 240 Mali (MINUSMA); 170 South Sudan (UNMISS) (2020)Military service age and obligation:18-22 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2019)
-
Terrorism :: Sri Lanka
-
Terrorist group(s):Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham; Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (2019)note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
-
Transnational Issues :: Sri Lanka
-
Disputes - international:
none
Refugees and internally displaced persons:IDPs: 27,000 (civil war; more than half displaced prior to 2008; many of the more than 480,000 IDPs registered as returnees have not reached durable solutions) (2019)Trafficking in persons:current situation: Sri Lanka is primarily a source and, to a lesser extent, a destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; some Sri Lankan adults and children who migrate willingly to the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and Afghanistan to work in the construction, garment, and domestic service sectors are subsequently subjected to forced labor or debt bondage (incurred through high recruitment fees or money advances); some Sri Lankan women are forced into prostitution in Jordan, Maldives, Malaysia, Singapore, and other countries; within Sri Lanka, women and children are subjected to sex trafficking, and children are also forced to beg and work in the agriculture, fireworks, and fish-drying industries; a small number of women from Asia, Central Asia, Europe, and the Middle East have been forced into prostitution in Sri Lanka in recent yearstier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Sri Lanka does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; in 2014, Sri Lanka was granted a waiver from an otherwise required downgrade to Tier 3 because its government has a written plan that, if implemented, would constitute making significant efforts to bring itself into compliance with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; law enforcement continues to demonstrate a lack of understanding of trafficking crimes and inadequate investigations, relying on trafficking cases to be prosecuted under the procurement statute rather than the trafficking statute, which carries more stringent penalties; authorities convicted only one offender under the procurement statute, a decrease from 2013; the government approved guidelines for the identification of victims and their referral to protective services but failed to ensure that victims were not jailed and charged for crimes committed as a direct result of being trafficked; no government employees were investigated or prosecuted, despite allegations of complicity (2015)