-
Introduction :: New Zealand
-
Background:The Polynesian Maori reached New Zealand sometime between A.D. 1250 and 1300. In 1840, their chieftains entered into a compact with Great Britain, the Treaty of Waitangi, in which they ceded sovereignty to Queen Victoria while retaining territorial rights. That same year, the British began the first organized colonial settlement. A series of land wars between 1843 and 1872 ended with the defeat of the native peoples. The British colony of New Zealand became an independent dominion in 1907 and supported the UK militarily in both world wars. New Zealand's full participation in a number of defense alliances lapsed by the 1980s. In recent years, the government has sought to address longstanding Maori grievances.
-
Geography :: New Zealand
-
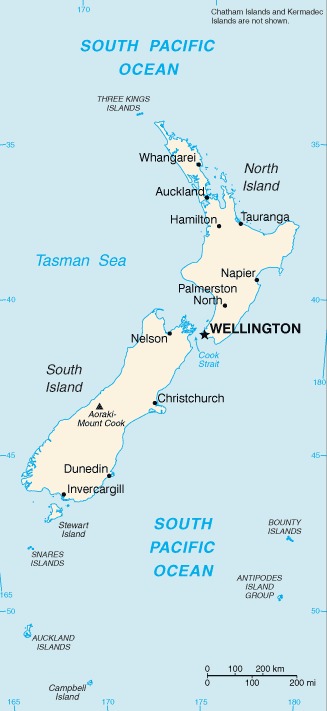
Location:Oceania, islands in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of AustraliaGeographic coordinates:41 00 S, 174 00 EMap references:OceaniaArea:total: 268,838 sq kmland: 264,537 sq kmwater: 4,301 sq km
note: includes Antipodes Islands, Auckland Islands, Bounty Islands, Campbell Island, Chatham Islands, and Kermadec Islands
country comparison to the world: 77Area - comparative:almost twice the size of North Carolina; about the size of ColoradoArea comparison map: The World Factbook Field Image ModalAustralia - Oceania :: New Zealand Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalAustralia - Oceania :: New Zealand Print Image Description
Image Descriptionalmost twice the size of North Carolina; about the size of Colorado
Land boundaries:0 kmCoastline:15,134 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:temperate with sharp regional contrastsTerrain:predominately mountainous with large coastal plainsElevation:mean elevation: 388 mlowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 mhighest point: Aoraki/Mount Cook 3,724 m; note - the mountain's height was 3,764 m until 14 December 1991 when it lost about 10 m in an avalanche of rock and ice; erosion of the ice cap since then has brought the height down another 30 mNatural resources:natural gas, iron ore, sand, coal, timber, hydropower, gold, limestoneLand use:agricultural land: 43.2% (2011 est.)arable land: 1.8% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0.3% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 41.1% (2011 est.)forest: 31.4% (2011 est.)other: 25.4% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:7,210 sq km (2012)Population distribution:over three-quarters of New Zealanders, including the indigenous Maori, live on the North Island, primarily in urban areasNatural hazards:earthquakes are common, though usually not severe; volcanic activity
volcanism: significant volcanism on North Island; Ruapehu (2,797 m), which last erupted in 2007, has a history of large eruptions in the past century; Taranaki has the potential to produce dangerous avalanches and lahars; other historically active volcanoes include Okataina, Raoul Island, Tongariro, and White Island; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Environment - current issues:water quality and availability; rapid urbanisation; deforestation; soil erosion and degradation; native flora and fauna hard-hit by invasive species; negative effects of climate changeEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: Antarctic Seals, Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:note 1: consists of two main islands and a number of smaller islands; South Island, the larger main island, is the 12th largest island in the world and is divided along its length by the Southern Alps; North Island is the 14th largest island in the world and is not as mountainous, but it is marked by volcanism
note 2: New Zealand lies along the Ring of Fire, a belt of active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters bordering the Pacific Ocean; up to 90% of the world's earthquakes and some 75% of the world's volcanoes occur within the Ring of Fire
note 3: almost 90% of the population lives in cities and over three-quarters on North Island; Wellington is the southernmost national capital in the world
-
People and Society :: New Zealand
-
Population:4,925,477 (July 2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 125Nationality:noun: New Zealander(s)adjective: New ZealandEthnic groups:European 64.1%, Maori 16.5%, Chinese 4.9%, Indian 4.7%, Samoan 3.9%, Tongan 1.8%, Cook Islands Maori 1.7%, English 1.5%, Filipino 1.5%, New Zealander 1%, other 13.7% (2018 est.)
note: based on the 2018 census of the usually resident population; percentages add up to more than 100% because respondents were able to identify more than one ethnic group
Languages:English (de facto official) 95.4%, Maori (de jure official) 4%, Samoan 2.2%, Northern Chinese 2%, Hindi 1.5%, French 1.2%, Yue 1.1%, New Zealand Sign Language (de jure official) .5%, other or not stated 17.2% (2018 est.)note: shares sum to 124.1% due to multiple responses on the 2018 census
Religions:Christian 37.3% (Catholic 10.1%, Anglican 6.8%, Presbyterian and Congregational 5.2%, Pentecostal 1.8%, Methodist 1.6%, Mormon 1.2%, other 10.7%), Hindu 2.7%, Maori 1.3%, Muslim, 1.3%, Buddhist 1.1%, other religion 1.6% (includes Judaism, Spiritualism and New Age religions, Baha'i, Asian religions other than Buddhism), no religion 48.6%, objected to answering 6.7% (2018 est.)note: based on the 2018 census of the usually resident population; percentages add up to more than 100% because respondents were able to identify more than one religion
Age structure:0-14 years: 19.63% (male 496,802/female 469,853)15-24 years: 12.92% (male 328,327/female 308,132)25-54 years: 39.98% (male 996,857/female 972,566)55-64 years: 11.93% (male 285,989/female 301,692)65 years and over: 15.54% (male 358,228/female 407,031) (2020 est.)population pyramid:The World Factbook Field Image ModalAustralia - Oceania :: New Zealand PrintImage DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for New Zealand. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 55.8youth dependency ratio: 30.3elderly dependency ratio: 25.5potential support ratio: 3.9 (2020 est.)Median age:total: 37.2 yearsmale: 36.4 yearsfemale: 37.9 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 73Population growth rate:1.44% (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Birth rate:12.8 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Death rate:6.9 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 132Net migration rate:8 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Population distribution:over three-quarters of New Zealanders, including the indigenous Maori, live on the North Island, primarily in urban areasUrbanization:urban population: 86.7% of total population (2020)rate of urbanization: 1.01% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:1.607 million Auckland, 415,000 WELLINGTON (capital) (2020)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.88 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:27.8 years (2009 est.)note: median age at first birth
Maternal mortality rate:9 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 148Infant mortality rate:total: 3.5 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 3.7 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 3.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Life expectancy at birth:total population: 82.1 yearsmale: 80.4 yearsfemale: 84 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Total fertility rate:1.87 children born/woman (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 136Contraceptive prevalence rate:79.9% (2014/15)note: percent of women aged 18-45Drinking water source:improved: urban: 100% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved: urban: 0% of populationrural: 0% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2017 est.)Current Health Expenditure:9.2% (2017)Physicians density:3.47 physicians/1,000 population (2017)Hospital bed density:2.7 beds/1,000 population (2017)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 100% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved: urban: 0% of populationrural: 0% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2017)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:<.1% (2019 est.)HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:3,500 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 129HIV/AIDS - deaths:<100 (2019 est.)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:30.8% (2016)country comparison to the world: 22Education expenditures:6.3% of GDP (2017)country comparison to the world: 23School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 19 yearsmale: 18 yearsfemale: 20 years (2018)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 11.5%male: 12.3%female: 10.7% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 114 -
Government :: New Zealand
-
Country name:conventional long form: noneconventional short form: New Zealandabbreviation: NZetymology: Dutch explorer Abel TASMAN was the first European to reach New Zealand in 1642; he named it Staten Landt, but Dutch cartographers renamed it Nova Zeelandia in 1645 after the Dutch province of Zeeland; British explorer Captain James COOK subsequently anglicized the name to New Zealand when he mapped the islands in 1769Government type:parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realmCapital:name: Wellingtongeographic coordinates: 41 18 S, 174 47 Etime difference: UTC+12 (17 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in September; ends first Sunday in April
note: New Zealand has two time zones: New Zealand standard time (UTC+12) and Chatham Islands time (45 minutes in advance of New Zealand standard time; UTC+12:45)
etymology: named in 1840 after Arthur Wellesley, the first Duke of Wellington and victorious general at the Battle of WaterlooAdministrative divisions:16 regions and 1 territory*; Auckland, Bay of Plenty, Canterbury, Chatham Islands*, Gisborne, Hawke's Bay, Manawatu-Wanganui, Marlborough, Nelson, Northland, Otago, Southland, Taranaki, Tasman, Waikato, Wellington, West CoastDependent areas:Cook Islands, Niue, TokelauIndependence:26 September 1907 (from the UK)National holiday:Waitangi Day (Treaty of Waitangi established British sovereignty over New Zealand), 6 February (1840); Anzac Day (commemorated as the anniversary of the landing of troops of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps during World War I at Gallipoli, Turkey), 25 April (1915)Constitution:history: New Zealand has no single constitution document; the Constitution Act 1986, effective 1 January 1987, includes only part of the uncodified constitution; others include a collection of statutes or "acts of Parliament," the Treaty of Waitangi, Orders in Council, letters patent, court decisions, and unwritten conventionsamendments: proposed as bill by Parliament or by referendum called either by the government or by citizens; passage of a bill as an act normally requires two separate readings with committee reviews in between to make changes and corrections, a third reading approved by the House of Representatives membership or by the majority of votes in a referendum, and assent of the governor-general; passage of amendments to reserved constitutional provisions affecting the term of Parliament, electoral districts, and voting restrictions requires approval by 75% of the House membership or the majority of votes in a referendum; amended many times, last in 2014Legal system:common law system, based on English model, with special legislation and land courts for the MaoriInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of New Zealanddual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: 3 yearsSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor-General Dame Patricia Lee REDDY (since 28 September 2016)head of government: Prime Minister Jacinda ARDERN (since 26 October 2017); Deputy Prime Minister Grant ROBERTSON (since 2 November 2020)cabinet: Executive Council appointed by the governor-general on the recommendation of the prime ministerelections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor-general appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the governor-general; deputy prime minister appointed by the governor-general; note - Prime Minister ARDERN heads up a minority coalition government consisting of the Labor and New Zealand First parties with confidence and supply support from the Green PartyLegislative branch:description: unicameral House of Representatives - commonly called Parliament (120 seats for 2020-23 term); 72 members directly elected in 65 single-seat constituencies and 7 Maori constituencies by simple majority vote and 48 directly elected by closed party-list proportional representation vote; members serve 3-year terms)elections: last held on 17 October 2020 (next scheduled for 2023)election results: percent of vote by party - Labor Party 49.1%, National Party 26.8%, ACT Party 8%, Green Party 6.3%, Maori Party 1%; seats by party - Labor Party 64, National Party 35, Green Party 10, ACT Party 10, Maori Party 1; composition - men 63, women 57, percent of women 47.5%Judicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of 5 justices, including the chief justice); note - the Supreme Court in 2004 replaced the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London) as the final appeals courtjudge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the governor-general upon the recommendation of the attorney- general; justices appointed until compulsory retirement at age 70subordinate courts: Court of Appeal; High Court; tribunals and authorities; district courts; specialized courts for issues related to employment, environment, family, Maori lands, youth, military; tribunalsPolitical parties and leaders:ACT New Zealand [David SEYMOUR]
Green Party [James SHAW]
Mana Movement [Hone HARAWIRA] (formerly Mana Party)
Maori Party [Che WILSON and Kaapua SMITH]
New Zealand First Party or NZ First [Winston PETERS]
New Zealand Labor Party [Jacinda ARDERN]
New Zealand National Party [Judith COLLINS]
United Future New Zealand [Damian LIGHT]International organization participation:ADB, ANZUS, APEC, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, C, CD, CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NSG, OECD, OPCW, Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club (associate), PCA, PIF, SICA (observer), Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Rosemary BANKS (since 11 January 2019)chancery: 37 Observatory Circle NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 328-4800FAX: [1] (202) 667-5227consulate(s) general: Honolulu (HI), Los Angeles, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Scott P. BROWN (since 27 June 2017) note - also accredited to Samoatelephone: [64] (4) 462-6000embassy: 29 Fitzherbert Terrace, Thorndon, Wellingtonmailing address: P. O. Box 1190, Wellington; PSC 467, Box 1, APO AP 96531-1034FAX: [64] (4) 499-0490consulate(s) general: AucklandFlag description:blue with the flag of the UK in the upper hoist-side quadrant with four red five-pointed stars edged in white centered in the outer half of the flag; the stars represent the Southern Cross constellationNational symbol(s):Southern Cross constellation (four, five-pointed stars), kiwi (bird), silver fern; national colors: black, white, red (ochre)National anthem:name: God Defend New Zealandlyrics/music: Thomas BRACKEN [English], Thomas Henry SMITH [Maori]/John Joseph WOODSnote: adopted 1940 as national song, adopted 1977 as co-national anthem; New Zealand has two national anthems with equal status; as a commonwealth realm, in addition to "God Defend New Zealand," "God Save the Queen" serves as a national anthem (see United Kingdom); "God Save the Queen" normally played only when a member of the royal family or the governor-general is present; in all other cases, "God Defend New Zealand" is played
-
Economy :: New Zealand
-
Economic overview:
Over the past 40 years, the government has transformed New Zealand from an agrarian economy, dependent on concessionary British market access, to a more industrialized, free market economy that can compete globally. This dynamic growth has boosted real incomes, but left behind some at the bottom of the ladder and broadened and deepened the technological capabilities of the industrial sector.
Per capita income rose for 10 consecutive years until 2007 in purchasing power parity terms, but fell in 2008-09. Debt-driven consumer spending drove robust growth in the first half of the decade, fueling a large balance of payments deficit that posed a challenge for policymakers. Inflationary pressures caused the central bank to raise its key rate steadily from January 2004 until it was among the highest in the OECD in 2007 and 2008. The higher rate attracted international capital inflows, which strengthened the currency and housing market while aggravating the current account deficit. Rising house prices, especially in Auckland, have become a political issue in recent years, as well as a policy challenge in 2016 and 2017, as the ability to afford housing has declined for many.
Expanding New Zealand’s network of free trade agreements remains a top foreign policy priority. New Zealand was an early promoter of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) and was the second country to ratify the agreement in May 2017. Following the United States’ withdrawal from the TPP in January 2017, on 10 November 2017 the remaining 11 countries agreed on the core elements of a modified agreement, which they renamed the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). In November 2016, New Zealand opened negotiations to upgrade its FTA with China; China is one of New Zealand’s most important trading partners.
GDP real growth rate:2.22% (2019 est.)3.22% (2018 est.)3.8% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Inflation rate (consumer prices):1.6% (2019 est.)1.5% (2018 est.)1.8% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Credit ratings:Fitch rating: AA (2011)Moody's rating: Aaa (2002)Standard & Poors rating: AA (2011)GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:$176.341 billion (2019 est.)$172.509 billion (2018 est.)$167.14 billion (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):$205.202 billion (2019 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$39,815 (2019 est.)$39,277 (2018 est.)$38,388 (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
country comparison to the world: 41Gross national saving:21% of GDP (2017 est.)21.5% of GDP (2016 est.)20.2% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 89GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 5.7% (2017 est.)industry: 21.5% (2017 est.)services: 72.8% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 57.2% (2017 est.)government consumption: 18.2% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 23.4% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 0.3% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 27% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -26.1% (2017 est.)Ease of Doing Business Index scores:100.0 (2020)Agriculture - products:dairy products, sheep, beef, poultry, fruit, vegetables, wine, seafood, wheat and barleyIndustries:agriculture, forestry, fishing, logs and wood articles, manufacturing, mining, construction, financial services, real estate services, tourismIndustrial production growth rate:1.8% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 137Labor force:2.709 million (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 109Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 6.6%industry: 20.7%services: 72.7% (2017 est.)Unemployment rate:4.13% (2019 est.)4.32% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Population below poverty line:NAHousehold income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: NAhighest 10%: NABudget:revenues: 74.11 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 70.97 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:36.8% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 56Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):1.6% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 21Public debt:31.7% of GDP (2017 est.)33.5% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 162Fiscal year:1 April - 31 Marchnote: this is the fiscal year for tax purposes
Current account balance:-$6.962 billion (2019 est.)-$8.742 billion (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 187Exports:$56.219 billion (2019 est.)$54.977 billion (2018 est.)$53.457 billion (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Exports - partners:China 22.4%, Australia 16.4%, US 9.9%, Japan 6.1% (2017)Exports - commodities:dairy products, meat and edible offal, logs and wood articles, fruit, crude oil, wineImports:$63.622 billion (2019 est.)$62.276 billion (2018 est.)$58.494 billion (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Imports - commodities:petroleum and products, mechanical machinery, vehicles and parts, electrical machinery, textilesImports - partners:China 19%, Australia 12.1%, US 10.5%, Japan 7.3%, Germany 5.3%, Thailand 4.6% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$20.68 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$17.81 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 58Debt - external:$91.62 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$84.03 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Exchange rates:New Zealand dollars (NZD) per US dollar -1.41794 (2020 est.)1.52334 (2019 est.)1.45709 (2018 est.)1.4279 (2014 est.)1.2039 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: New Zealand
-
Electricity access:electrification - total population: 100% (2020)Electricity - production:42.53 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 56Electricity - consumption:39.5 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 55Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 176Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 179Electricity - installed generating capacity:9.301 million kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Electricity - from fossil fuels:23% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 192Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 154Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:58% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Electricity - from other renewable sources:20% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 40Crude oil - production:24,000 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Crude oil - exports:26,440 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 48Crude oil - imports:108,900 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 43Crude oil - proved reserves:51.8 million bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Refined petroleum products - production:115,100 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Refined petroleum products - consumption:169,100 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Refined petroleum products - exports:1,782 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 106Refined petroleum products - imports:56,000 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Natural gas - production:5.097 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Natural gas - consumption:5.182 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 161Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 166Natural gas - proved reserves:33.7 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 67Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:37.75 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 68
-
Communications :: New Zealand
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 1,801,645subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 37.11 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 6,550,687subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 134.93 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 108Telecommunication systems:general assessment: excellent domestic and international systems; mobile and P2P services soar; LTE rates some of the fastest in the world; growth in mobile broadband and fiber sectors; roll out of 5G; investment and development of infrastructure enable network capabilities to propel the digital economy, digital media sector along with e-government, e-commerce across the country; newest and most powerful commercial satellite, Kacific-1 satellite, launched in 2019 to improve telecommunications in the Asia Pacific region (2020)domestic: fixed-line 37 per 100 and mobile-cellular telephone subscribership 135 per 100 persons (2019)international: country code - 64; landing points for the Southern Cross NEXT, Aqualink, Nelson-Levin, SCCN and Hawaiki submarine cable system providing links to Australia, Fiji, American Samoa, Kiribati, Samo, Tokelau, US and around New Zealand; satellite earth stations - 8 (1 Inmarsat - Pacific Ocean, 7 other) (2019)note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderatedBroadcast media:state-owned Television New Zealand operates multiple TV networks and state-owned Radio New Zealand operates 3 radio networks and an external shortwave radio service to the South Pacific region; a small number of national commercial TV and radio stations and many regional commercial television and radio stations are available; cable and satellite TV systems are available, as are a range of streaming services (2019)Internet country code:.nzInternet users:total: 4,340,672percent of population: 90.81% (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 1.647 millionsubscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 34 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 59
-
Transportation :: New Zealand
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 15 (2020)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 199annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 17,249,049 (2018)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 1,349,300,000 mt-km (2018)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:ZK (2016)Airports:123 (2013)country comparison to the world: 47Airports - with paved runways:total: 39 (2017)over 3,047 m: 2 (2017)2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 12 (2017)914 to 1,523 m: 23 (2017)under 914 m: 1 (2017)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 84 (2013)1,524 to 2,437 m: 3 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 33 (2013)under 914 m: 48 (2013)Pipelines:331 km condensate, 2500 km gas, 172 km liquid petroleum gas, 288 km oil, 198 km refined products (2018)Railways:total: 4,128 km (2018)narrow gauge: 4,128 km 1.067-m gauge (506 km electrified) (2018)country comparison to the world: 46Roadways:total: 94,000 km (2017)paved: 61,600 km (includes 199 km of expressways) (2017)unpaved: 32,400 km (2017)country comparison to the world: 53Merchant marine:total: 113by type: general cargo 12, oil tanker 4, other 97 (2019)country comparison to the world: 84Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Auckland, Lyttelton, Manukau Harbor, Marsden Point, Tauranga, Wellington
-
Military and Security :: New Zealand
-
Military and security forces:New Zealand Defence Force (NZDF): New Zealand Army, Royal New Zealand Navy, Royal New Zealand Air Force (2020)Military expenditures:1.5% of GDP (2019)1.3% of GDP (2018)1.2% of GDP (2017)1.2% of GDP (2016)1.2% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 83Military and security service personnel strengths:the New Zealand Defense Force (NZDF) has about 9,600 active duty troops (4,700 Army; 2,300 Navy; 2,600 Air Force) (2020)Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:NZDF is equipped mostly with imported weapons and equipment from Western suppliers; Australia, France, and the US are the leading suppliers since 2010 (2019 est.)Military deployments:up to 220 Antarctica (summer season only) (2020)Military service age and obligation:17 years of age for voluntary military service; soldiers cannot be deployed until the age of 18; no conscription (2019)
-
Transnational Issues :: New Zealand
-
Disputes - international:
asserts a territorial claim in Antarctica (Ross Dependency)
Illicit drugs:significant consumer of amphetamines