-
Introduction :: Lithuania
-
Background:Lithuanian lands were united under MINDAUGAS in 1236; over the next century, through alliances and conquest, Lithuania extended its territory to include most of present-day Belarus and Ukraine. By the end of the 14th century Lithuania was the largest state in Europe. An alliance with Poland in 1386 led the two countries into a union through the person of a common ruler. In 1569, Lithuania and Poland formally united into a single dual state, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. This entity survived until 1795 when its remnants were partitioned by surrounding countries. Lithuania regained its independence following World War I but was annexed by the USSR in 1940 - an action never recognized by the US and many other countries. On 11 March 1990, Lithuania became the first of the Soviet republics to declare its independence, but Moscow did not recognize this proclamation until September of 1991 (following the abortive coup in Moscow). The last Russian troops withdrew in 1993. Lithuania subsequently restructured its economy for integration into Western European institutions; it joined both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004. In 2015, Lithuania joined the euro zone, and it joined the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development in 2018.
-
Geography :: Lithuania
-
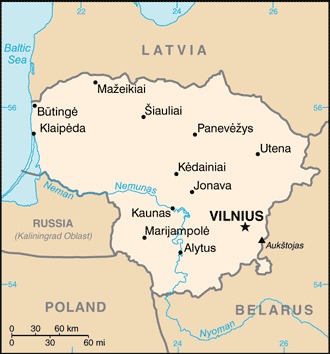
Location:Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, between Latvia and Russia, west of BelarusGeographic coordinates:56 00 N, 24 00 EMap references:EuropeArea:total: 65,300 sq kmland: 62,680 sq kmwater: 2,620 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 123Area - comparative:slightly larger than West VirginiaArea comparison map:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalEurope :: Lithuania Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalEurope :: Lithuania Print Image Description
Image Descriptionslightly larger than West Virginia
Land boundaries:total: 1,549 kmborder countries (4): Belarus 640 km, Latvia 544 km, Poland 104 km, Russia (Kaliningrad) 261 kmCoastline:90 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmClimate:transitional, between maritime and continental; wet, moderate winters and summersTerrain:lowland, many scattered small lakes, fertile soilElevation:mean elevation: 110 mlowest point: Baltic Sea 0 mhighest point: Aukstojas 294 mNatural resources:peat, arable land, amberLand use:agricultural land: 44.8% (2011 est.)arable land: 34.9% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0.5% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 9.4% (2011 est.)forest: 34.6% (2011 est.)other: 20.6% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:44 sq km (2012)Population distribution:fairly even population distribution throughout the country, but somewhat greater concentrations in the southern cities of Vilnius and Kaunas, and the western port of KlaipedaNatural hazards:occasional floods, droughtsEnvironment - current issues:water pollution; air pollution; deforestation; threatened animal and plant species; chemicals and waste materials released into the environment contaminate soil and groundwater; soil degradation and erosionEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:fertile central plains are separated by hilly uplands that are ancient glacial deposits -
People and Society :: Lithuania
-
Population:2,731,464 (July 2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 141Nationality:noun: Lithuanian(s)adjective: LithuanianEthnic groups:Lithuanian 84.1%, Polish 6.6%, Russian 5.8%, Belarusian 1.2%, other 1.1%, unspecified 1.2% (2011 est.)Languages:Lithuanian (official) 82%, Russian 8%, Polish 5.6%, other 0.9%, unspecified 3.5% (2011 est.)Religions:Roman Catholic 77.2%, Russian Orthodox 4.1%, Old Believer 0.8%, Evangelical Lutheran 0.6%, Evangelical Reformist 0.2%, other (including Sunni Muslim, Jewish, Greek Catholic, and Karaite) 0.8%, none 6.1%, unspecified 10.1% (2011 est.)Age structure:0-14 years: 15.26% (male 213,802/female 202,948)15-24 years: 10.23% (male 144,679/female 134,822)25-54 years: 38.96% (male 528,706/female 535,485)55-64 years: 15.1% (male 183,854/female 228,585)65 years and over: 20.45% (male 190,025/female 368,558) (2020 est.)population pyramid:The World Factbook Field Image ModalEurope :: Lithuania PrintImage DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Lithuania. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 56.5youth dependency ratio: 24.2elderly dependency ratio: 32.3potential support ratio: 3.1 (2020 est.)Median age:total: 44.5 yearsmale: 40.2 yearsfemale: 48.2 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 15Population growth rate:-1.13% (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 231Birth rate:9.5 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 196Death rate:15 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Net migration rate:-5.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 202Population distribution:fairly even population distribution throughout the country, but somewhat greater concentrations in the southern cities of Vilnius and Kaunas, and the western port of KlaipedaUrbanization:urban population: 68% of total population (2020)rate of urbanization: -0.31% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:539,000 VILNIUS (capital) (2020)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.99 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.8 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.52 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.86 male(s)/female (2020 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:27.5 years (2017 est.)Maternal mortality rate:5 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 167Infant mortality rate:total: 3.8 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 4.2 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 3.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 191Life expectancy at birth:total population: 75.5 yearsmale: 70.3 yearsfemale: 81.1 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 115Total fertility rate:1.6 children born/woman (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Drinking water source:improved: urban: 100% of populationrural: 92.8% of populationtotal: 97.5% of populationunimproved: urban: 0% of populationrural: 7.2% of populationtotal: 2.5% of population (2017 est.)Current Health Expenditure:6.5% (2017)Physicians density:4.83 physicians/1,000 population (2017)Hospital bed density:6.6 beds/1,000 population (2017)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 99.3% of population (2015 est.)rural: 87.5% of populationtotal: 95.5% of populationunimproved: urban: 0.7% of populationrural: 12.5% of populationtotal: 4.5% of population (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.1% (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 125HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:3,400 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 130HIV/AIDS - deaths:<100 (2019 est.)Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: intermediate (2020)vectorborne diseases: tickborne encephalitisObesity - adult prevalence rate:26.3% (2016)country comparison to the world: 43Education expenditures:3.8% of GDP (2017)country comparison to the world: 105Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99.8%male: 99.8%female: 99.8% (2015)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 17 yearsmale: 16 yearsfemale: 17 years (2018)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 11.1%male: 12%female: 10.1% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 117 -
Government :: Lithuania
-
Country name:conventional long form: Republic of Lithuaniaconventional short form: Lithuanialocal long form: Lietuvos Respublikalocal short form: Lietuvaformer: Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republicetymology: meaning of the name "Lietuva" remains unclear; it may derive from the Lietava, a stream in east central LithuaniaGovernment type:semi-presidential republicCapital:name: Vilniusgeographic coordinates: 54 41 N, 25 19 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in Octoberetymology: named after the Vilnia River, which flows into the Neris River at Vilnius; the river name derives from the Lithuanian word "vilnis" meaning "a surge"Administrative divisions:60 municipalities (savivaldybe, singular - savivaldybe); Akmene, Alytaus Miestas, Alytus, Anksciai, Birstono, Birzai, Druskininkai, Elektrenai, Ignalina, Jonava, Joniskis, Jurbarkas, Kaisiadorys, Kalvarijos, Kauno Miestas, Kaunas, Kazlu Rudos, Kedainiai, Kelme, Klaipedos Miestas, Klaipeda, Kretinga, Kupiskis, Lazdijai, Marijampole, Mazeikiai, Moletai, Neringa, Pagegiai, Pakruojis, Palangos Miestas, Panevezio Miestas, Panevezys, Pasvalys, Plunge, Prienai, Radviliskis, Raseiniai, Rietavo, Rokiskis, Sakiai, Salcininkai, Siauliu Miestas, Siauliai, Silale, Silute, Sirvintos, Skuodas, Svencionys, Taurage, Telsiai, Trakai, Ukmerge, Utena, Varena, Vilkaviskis, Vilniaus Miestas, Vilnius, Visaginas, ZarasaiIndependence:16 February 1918 (from Soviet Russia and Germany); 11 March 1990 (declared from the Soviet Union); 6 September 1991 (recognized by the Soviet Union); notable earlier dates: 6 July 1253 (coronation of MINDAUGAS, traditional founding date); 1 July 1569 (Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth created)National holiday:Independence Day (or National Day), 16 February (1918); note - 16 February 1918 was the date Lithuania established its statehood and its concomitant independence from Soviet Russia and Germany; 11 March 1990 was the date it declared the restoration of Lithuanian statehood and its concomitant independence from the Soviet UnionConstitution:history: several previous; latest adopted by referendum 25 October 1992, entered into force 2 November 1992amendments: proposed by at least one fourth of all Parliament members or by petition of at least 300,000 voters; passage requires two-thirds majority vote of Parliament in each of two readings three months apart and a presidential signature; amendments to constitutional articles on national sovereignty and constitutional amendment procedure also require three-fourths voter approval in a referendum; amended 1996, 2003, 2006Legal system:civil law system; legislative acts can be appealed to the Constitutional CourtInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Lithuaniadual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 10 yearsSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Gitanas NAUSEDA (since 12 July 2019)head of government: Prime Minister Ingrida SIMONYTE (since 24 November 2020)cabinet: Council of Ministers nominated by the prime minister, appointed by the president, and approved by Parliamentelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 12 and 26 May 2019 (next to be held in May 2024); prime minister appointed by the president, approved by Parliamentelection results: Gitanas NAUSEDA elected president in second round; percent of vote - Gitanas NAUSEDA (independent) 66.7%, Ingrida SIMONYTE (independent) 33.3%; Saulius SKVERNELIS (LVZS) approved as prime minister by Parliament vote - 90 to 4Legislative branch:description: unicameral Parliament or Seimas (141 seats; 71 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by absolute majority vote and 70 directly elected in a single nationwide constituency by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)elections: last held on 11 and 25 October 2020 (next to be held in October 2024)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - TS-LKD 50, LVZS 32, LSDP 13, LRLS 13, Freedom 11, DP 10, AWPL 3, LSDDP 3, LT 1, Greens 1, independent 4; composition - men 103, women 38, percent of women 27%Judicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of 37 judges); Constitutional Court (consists of 9 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by the president and appointed by the Seimas; judges serve 5-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the Seimas from nominations - 3 each by the president of the republic, the Seimas chairperson, and the Supreme Court president; judges serve 9-year, nonrenewable terms; one-third of membership reconstituted every 3 yearssubordinate courts: Court of Appeals; district and local courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Electoral Action of Lithuanian Poles or LLRA [Valdemar TOMASEVSKI]
Farmers and Greens Union or LVZS [Ramunas KARBAUSKIS]
Freedom Party or LP [Ausrine ARMONAITE]
Homeland Union-Lithuanian Christian Democrats or TS-LKD [Gabrielius LANDSBERGIS]
Labor Party or DP [Viktor USPASKICH]
Lithuanian Center Party or LCP [Naglis PUTEIKIS]
Lithuanian Green Party or LZP [Remigijus LAPINSKAS]]
Lithuanian Liberal Movement or LS or LRLS [Viktorija CMILYTE]
Lithuanian List or LL [Darius KUOLYS]
Lithuanian Social Democratic Party or LSDP [Gintautas PALUCKAS]
Lithuanian Social Democratic Labor Party or LSDDP [Gediminas KIRKILAS]
Freedom and Justice Party or LT [Remigijus ZEMAITAITIS]International organization participation:Australia Group, BA, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Rolandas KRISCIUNAS (since 17 September 2015)chancery: 2622 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 234-5860FAX: [1] (202) 328-0466consulate(s) general: Chicago, Los Angeles, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Robert S. GILCHRIST (since 4 February 2010)telephone: [370] (5) 266-5500embassy: Akmenu gatve 6, Vilnius, LT-03106mailing address: American Embassy, Akmenu Gatve 6, Vilnius LT-03106FAX: [370] (5) 266-5510Flag description:three equal horizontal bands of yellow (top), green, and red; yellow symbolizes golden fields, as well as the sun, light, and goodness; green represents the forests of the countryside, in addition to nature, freedom, and hope; red stands for courage and the blood spilled in defense of the homelandNational symbol(s):mounted knight known as Vytis (the Chaser), white stork; national colors: yellow, green, redNational anthem:name: "Tautiska giesme" (The National Song)lyrics/music: Vincas KUDIRKAnote: adopted 1918, restored 1990; written in 1898 while Lithuania was a part of Russia; banned during the Soviet occupation from 1940 to 1990
-
Economy :: Lithuania
-
Economic overview:
After the country declared independence from the Soviet Union in 1990, Lithuania faced an initial dislocation that is typical during transitions from a planned economy to a free-market economy. Macroeconomic stabilization policies, including privatization of most state-owned enterprises, and a strong commitment to a currency board arrangement led to an open and rapidly growing economy and rising consumer demand. Foreign investment and EU funding aided in the transition. Lithuania joined the WTO in May 2001, the EU in May 2004, and the euro zone in January 2015, and is now working to complete the OECD accession roadmap it received in July 2015. In 2017, joined the OECD Working Group on Bribery, an important step in the OECD accession process.
The Lithuanian economy was severely hit by the 2008-09 global financial crisis, but it has rebounded and become one of the fastest growing in the EU. Increases in exports, investment, and wage growth that supported consumption helped the economy grow by 3.6% in 2017. In 2015, Russia was Lithuania’s largest trading partner, followed by Poland, Germany, and Latvia; goods and services trade between the US and Lithuania totaled $2.2 billion. Lithuania opened a self-financed liquefied natural gas terminal in January 2015, providing the first non-Russian supply of natural gas to the Baltic States and reducing Lithuania’s dependence on Russian gas from 100% to approximately 30% in 2016.
Lithuania’s ongoing recovery hinges on improving the business environment, especially by liberalizing labor laws, and improving competitiveness and export growth, the latter hampered by economic slowdowns in the EU and Russia. In addition, a steady outflow of young and highly educated people is causing a shortage of skilled labor, which, combined with a rapidly aging population, could stress public finances and constrain long-term growth.
GDP real growth rate:4.33% (2019 est.)3.99% (2018 est.)4.37% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Inflation rate (consumer prices):2.3% (2019 est.)2.7% (2018 est.)3.7% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 122Credit ratings:Fitch rating: A (2020)Moody's rating: A3 (2015)Standard & Poors rating: A+ (2020)GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:$96.258 billion (2019 est.)$92.269 billion (2018 est.)$88.726 billion (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):$54.597 billion (2019 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$18,844 (2019 est.)$17,794 (2018 est.)$16,846 (2017 est.)note: data are in 2010 dollars
country comparison to the world: 76Gross national saving:18% of GDP (2017 est.)16.2% of GDP (2016 est.)17.8% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 111GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 3.5% (2017 est.)industry: 29.4% (2017 est.)services: 67.2% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 63.9% (2017 est.)government consumption: 16.6% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 18.8% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: -1.3% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 81.6% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -79.3% (2017 est.)Ease of Doing Business Index scores:93.3 (2020)Agriculture - products:grain, potatoes, sugar beets, flax, vegetables; beef, milk, eggs, pork, cheese; fishIndustries:metal-cutting machine tools, electric motors, televisions, refrigerators and freezers, petroleum refining, shipbuilding (small ships), furniture, textiles, food processing, fertilizer, agricultural machinery, optical equipment, lasers, electronic components, computers, amber jewelry, information technology, video game development, app/software development, biotechnologyIndustrial production growth rate:5.9% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 43Labor force:1.333 million (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 9.1%industry: 25.2%services: 65.8% (2015 est.)Unemployment rate:8.4% (2019 est.)8.5% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Population below poverty line:22.2% (2015 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.2%highest 10%: 28.8% (2015)Budget:revenues: 15.92 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 15.7 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:33.7% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):0.5% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Public debt:39.7% of GDP (2017 est.)40.1% of GDP (2016 est.)note: official data; data cover general government debt and include debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities, debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intragovernmental debt; intragovernmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are sold at public auctions
country comparison to the world: 129Fiscal year:calendar yearCurrent account balance:$1.817 billion (2019 est.)$131 million (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Exports:$45.358 billion (2019 est.)$41.433 billion (2018 est.)$38.763 billion (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Exports - partners:Russia 15%, Latvia 9.9%, Poland 8.1%, Germany 7.3%, US 5.2%, Estonia 5%, Sweden 4.8% (2017)Exports - commodities:refined fuel, machinery and equipment, chemicals, textiles, foodstuffs, plasticsImports:$43.733 billion (2019 est.)$41.131 billion (2018 est.)$38.745 billion (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Imports - commodities:oil, natural gas, machinery and equipment, transport equipment, chemicals, textiles and clothing, metalsImports - partners:Russia 13%, Germany 12.3%, Poland 10.6%, Latvia 7.1%, Italy 5.2%, Netherlands 5.1%, Sweden 4% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$4.45 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$1.697 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 98Debt - external:$34.48 billion (31 March 2016 est.)$31.6 billion (31 March 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 78Exchange rates:litai (LTL) per US dollar -0.82771 (2020 est.)0.90338 (2019 est.)0.87789 (2018 est.)0.9012 (2014 est.)0.7525 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Lithuania
-
Electricity access:electrification - total population: 100% (2020)Electricity - production:3.131 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 131Electricity - consumption:10.5 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Electricity - exports:730 million kWh (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - imports:11.11 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Electricity - installed generating capacity:3.71 million kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 93Electricity - from fossil fuels:73% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 99Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:4% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 132Electricity - from other renewable sources:23% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Crude oil - production:2,000 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Crude oil - exports:1,002 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Crude oil - imports:182,900 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Crude oil - proved reserves:12 million bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 88Refined petroleum products - production:196,500 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Refined petroleum products - consumption:58,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 98Refined petroleum products - exports:174,800 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Refined petroleum products - imports:42,490 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 159Natural gas - consumption:2.492 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 79Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 140Natural gas - imports:2.492 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 47Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:13.49 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 97
-
Communications :: Lithuania
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 368,515subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 13.34 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 4,663,627subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 168.82 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Telecommunication systems:general assessment: adequate; improved international capability and better residential access; SIM card penetration is high for the region; prepaid sector accounts for most subscribers; postpaid subscribers is increasing; LTE networks available to more than 99% of the population; Lithuanian FttP (fiber to the home cable connections for Internet) penetration ranked third highest in Europe; govt. and telecoms invest in fiber, fiber accounts for most new broadband connections; effective competition with 3 network operators in mobile sector and all investing in LTE and mobile data services (2020)domestic: 13 per 100 for fixed-line subscriptions; rapid expansion of mobile-cellular services has resulted in a steady decline in the number of fixed-line connections; mobile-cellular teledensity stands at about 169 per 100 persons (2019)international: country code - 370; landing points for the BCS East, BCS East-West Interlink and NordBalt connecting Lithuania to Sweden, and Latvia ; further transmission by satellite; landline connections to Latvia and Poland (2019)note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderatedBroadcast media:public broadcaster operates 3 channels with the third channel - a satellite channel - introduced in 2007; various privately owned commercial TV broadcasters operate national and multiple regional channels; many privately owned local TV stations; multi-channel cable and satellite TV services available; publicly owned broadcaster operates 3 radio networks; many privately owned commercial broadcasters, with repeater stations in various regions throughout the countryInternet country code:.ltInternet users:total: 2,226,806percent of population: 79.72% (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 116Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 788,743subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 28 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 76
-
Transportation :: Lithuania
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 3 (2020)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 50annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 26,031 (2018)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:LY (2016)Airports:61 (2013)country comparison to the world: 79Airports - with paved runways:total: 22 (2017)over 3,047 m: 3 (2017)2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 7 (2017)914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2017)under 914 m: 9 (2017)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 39 (2013)over 3,047 m: 1 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2013)under 914 m: 36 (2013)Pipelines:1921 km gas, 121 km refined products (2013)Railways:total: 1,768 km (2014)standard gauge: 22 km 1.435-m gauge (2014)broad gauge: 1,746 km 1.520-m gauge (122 km electrified) (2014)country comparison to the world: 79Roadways:total: 84,166 km (2012)paved: 72,297 km (includes 312 km of expressways) (2012)unpaved: 11,869 km (2012)country comparison to the world: 60Waterways:441 km (navigable year-round) (2007)country comparison to the world: 86Merchant marine:total: 58by type: bulk carrier 3, general cargo 21, oil tanker 2, other 32 (2019)country comparison to the world: 111Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Klaipedaoil terminal(s): Butinge oil terminalLNG terminal(s) (import): Klaipeda
-
Military and Security :: Lithuania
-
Military and security forces:Lithuanian Armed Forces (Lietuvos Ginkluotosios Pajegos): Land Forces (Sausumos Pajegos), Naval Forces (Karines Juru Pajegos), Air Forces (Karines Oro Pajegos), Special Operations Forces (Specialiuju Operaciju Pajegos); National Defense Volunteer Forces (Savanoriu Pajegos); National Riflemen's Union (paramilitary force that acts as an additional reserve force) (2020)Military expenditures:2.03% of GDP (2019 est.)1.98% of GDP (2018)1.72% of GDP (2017)1.48% of GDP (2016)1.14% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 48Military and security service personnel strengths:estimates for the Lithuanian Armed Forces vary; approximately 17,000 active duty personnel (12,500 Army, including about 5,000 National Defense Voluntary Forces; 700 Navy; 1,000 Air Force; 3,000 other, including special operations forces, logistics support, training, etc); est. 11,000 Riflemen Union (2020)Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:the Lithuanian Armed Forces' inventory is mostly a mix of Western weapons systems and Soviet-era equipment (primarily aircraft and helicopters); Germany and the UK are the leading suppliers of armaments to Lithuania since 2010 (2019 est.)Military deployments:contributes about 350 troops to the Lithuania, Poland, and Ukraine joint military brigade (LITPOLUKRBRIG), which was established in 2014; the brigade is headquartered in Warsaw and is comprised of an international staff, three battalions, and specialized units (2019)Military service age and obligation:19-26 years of age for conscripted military service (males); 9-month service obligation; in 2015, Lithuania reinstated conscription after having converted to a professional military in 2008; 18-38 for voluntary service (male and female) (2019)
-
Transnational Issues :: Lithuania
-
Disputes - international:
Lithuania and Russia committed to demarcating their boundary in 2006 in accordance with the land and maritime treaty ratified by Russia in May 2003 and by Lithuania in 1999; Lithuania operates a simplified transit regime for Russian nationals traveling from the Kaliningrad coastal exclave into Russia, while still conforming, as a EU member state having an external border with a non-EU member, to strict Schengen border rules; boundary demarcated with Latvia and Lithuania; as of January 2007, ground demarcation of the boundary with Belarus was complete and mapped with final ratification documents in preparation
Refugees and internally displaced persons:stateless persons: 2,904 (2019)Illicit drugs:transshipment and destination point for cannabis, cocaine, ecstasy, and opiates from Southwest Asia, Latin America, Western Europe, and neighboring Baltic countries; growing production of high-quality amphetamines, but limited production of cannabis, methamphetamines; susceptible to money laundering despite changes to banking legislation