-
Introduction :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
Background:The Siboney were the first people to inhabit the islands of Antigua and Barbuda in 2400 B.C., but Arawak Indians populated the islands when COLUMBUS landed on his second voyage in 1493. Early Spanish and French settlements were succeeded by an English colony in 1667. Slavery, established to run the sugar plantations on Antigua, was abolished in 1834. The islands became an independent state within the British Commonwealth of Nations in 1981. On 6 September 2017, Hurricane Irma passed over the island of Barbuda devastating the island and forcing the evacuation of the population to Antigua. Almost all the structures on Barbuda were destroyed and the vegetation stripped, but Antigua was spared the worst.
-
Geography :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
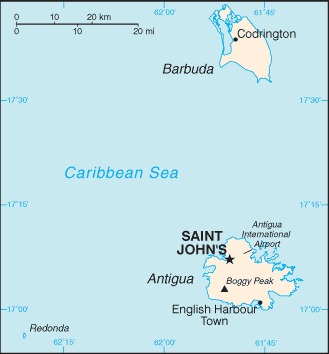
Location:Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east-southeast of Puerto RicoGeographic coordinates:17 03 N, 61 48 WMap references:Central America and the CaribbeanArea:total: 443 sq km (Antigua 280 sq km; Barbuda 161 sq km)land: 442.6 sq kmwater: 0 sq km
note: includes Redonda, 1.6 sq km
country comparison to the world: 200Area - comparative:2.5 times the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:153 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:tropical maritime; little seasonal temperature variationTerrain:mostly low-lying limestone and coral islands, with some higher volcanic areasElevation:lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 mhighest point: Mount Obama 402 mNatural resources:NEGL; pleasant climate fosters tourismLand use:agricultural land: 20.5% (2016 est.)arable land: 9.1% (2016 est.) / permanent crops: 2.3% (2016 est.) / permanent pasture: 9.1% (2016 est.)forest: 22.3% (2016 est.)other: 57.3% (2016 est.)Irrigated land:1.3 sq km (2012)Population distribution:the island of Antigua is home to approximately 97% of the population; nearly the entire population of Barbuda lives in CodringtonNatural hazards:hurricanes and tropical storms (July to October); periodic droughtsEnvironment - current issues:water management - a major concern because of limited natural freshwater resources - is further hampered by the clearing of trees to increase crop production, causing rainfall to run off quicklyEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:Antigua has a deeply indented shoreline with many natural harbors and beaches; Barbuda has a large western harbor -
People and Society :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
Population:98,179 (July 2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 196Nationality:noun: Antiguan(s), Barbudan(s)adjective: Antiguan, BarbudanEthnic groups:African descent 87.3%, mixed 4.7%, Hispanic 2.7%, White 1.6%, other 2.7%, unspecified 0.9% (2011 est.)note: data represent population by ethnic groupLanguages:English (official), Antiguan creoleReligions:Protestant 68.3% (Anglican 17.6%, Seventh Day Adventist 12.4%, Pentecostal 12.2%, Moravian 8.3%, Methodist 5.6%, Wesleyan Holiness 4.5%, Church of God 4.1%, Baptist 3.6%), Roman Catholic 8.2%, other 12.2%, unspecified 5.5%, none 5.9% (2011 est.)Age structure:0-14 years: 22.52% (male 11,243/female 10,871)15-24 years: 16.15% (male 7,891/female 7,961)25-54 years: 41.68% (male 18,757/female 22,167)55-64 years: 10.74% (male 4,693/female 5,848)65 years and over: 8.91% (male 3,736/female 5,012) (2020 est.)population pyramid:The World Factbook Field Image ModalCentral America :: Antigua and Barbuda PrintImage DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Antigua and Barbuda. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 45.3youth dependency ratio: 31.8elderly dependency ratio: 13.6potential support ratio: 7.4 (2020 est.)Median age:total: 32.7 yearsmale: 30.7 yearsfemale: 34.4 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 106Population growth rate:1.18% (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Birth rate:15.4 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Death rate:5.8 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 173Net migration rate:2.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 46Population distribution:the island of Antigua is home to approximately 97% of the population; nearly the entire population of Barbuda lives in CodringtonUrbanization:urban population: 24.4% of total population (2020)rate of urbanization: 0.55% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:21,000 SAINT JOHN'S (capital) (2018)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.99 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.85 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.8 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.89 male(s)/female (2020 est.)Infant mortality rate:total: 11.1 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 12.7 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 9.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 118Life expectancy at birth:total population: 77.3 yearsmale: 75.1 yearsfemale: 79.6 years (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Total fertility rate:1.97 children born/woman (2020 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Drinking water source:improved: total: 96.7% of populationunimproved: total: 3.2% of population (2017 est.)Current Health Expenditure:4.5% (2017)Physicians density:2.96 physicians/1,000 population (2017)Hospital bed density:2.9 beds/1,000 population (2017)Sanitation facility access:improved: total: 91.7% of populationunimproved: total: 8.1% of population (2017 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:1.1% (2018)country comparison to the world: 41HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:<1000 (2018)HIV/AIDS - deaths:<100 (2018)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:18.9% (2016)country comparison to the world: 113Education expenditures:NALiteracy:definition: age 15 and over has completed five or more years of schoolingtotal population: 99%male: 98.4%female: 99.4% (2015)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 15 yearsmale: 14 yearsfemale: 16 years (2012) -
Government :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
Country name:conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Antigua and Barbudaetymology: "antiguo" is Spanish for "ancient" or "old"; the island was discovered by Christopher COLUMBUS in 1493 and, according to tradition, named by him after the church of Santa Maria la Antigua (Old Saint Mary's) in Seville; "barbuda" is Spanish for "bearded" and the adjective may refer to the alleged beards of the indigenous people or to the island's bearded fig treesGovernment type:parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realmCapital:name: Saint John'sgeographic coordinates: 17 07 N, 61 51 Wtime difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: named after Saint John the ApostleAdministrative divisions:6 parishes and 2 dependencies*; Barbuda*, Redonda*, Saint George, Saint John, Saint Mary, Saint Paul, Saint Peter, Saint PhilipIndependence:1 November 1981 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day, 1 November (1981)Constitution:history: several previous; latest presented 31 July 1981, effective 31 October 1981 (The Antigua and Barbuda Constitution Order 1981)amendments: proposed by either house of Parliament; passage of amendments to constitutional sections such as citizenship, fundamental rights and freedoms, the establishment, power, and authority of the executive and legislative branches, the Supreme Court Order, and the procedure for amending the constitution requires approval by at least two-thirds majority vote of the membership of both houses, approval by at least two-thirds majority in a referendum, and assent to by the governor general; passage of other amendments requires only two-thirds majority vote by both houses; amended 2009, 2011Legal system:common law based on the English modelInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionCitizenship:citizenship by birth: yescitizenship by descent only: yesdual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: 7 yearsSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General Rodney WILLIAMS (since 14 August 2014)head of government: Prime Minister Gaston BROWNE (since 13 June 2014)cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime ministerelections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the governor generalLegislative branch:description: bicameral Parliament consists of:
Senate (17 seats; members appointed by the governor general)
House of Representatives (18 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 5-year terms)elections:
Senate - last appointed on 26 March 2018 (next NA)
House of Representatives - last held on 21 March 2018 (next to be held in March 2023)election results:
Senate - composition - men 8, women 9, percent of women 52.9%
House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - ABLP 59.4%, UPP 37.2%, BPM 1.4%, other 1.9% ; seats by party - ABLP 15, UPP 1, BPM 1; composition - men 16, women 2, percent of women 11.1%; note - total Parliament percent of women 31.4%Judicial branch:highest courts: the Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court (ECSC) is the superior court of the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States; the ECSC - headquartered on St. Lucia - consists of the Court of Appeal - headed by the chief justice and 4 judges - and the High Court with 18 judges; the Court of Appeal is itinerant, travelling to member states on a schedule to hear appeals from the High Court and subordinate courts; High Court judges reside in the member states, with 2 assigned to Antigua and Barbudajudge selection and term of office: chief justice of Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court appointed by the Her Majesty, Queen ELIZABETH II; other justices and judges appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission; Court of Appeal justices appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 65; High Court judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 62subordinate courts: Industrial Court; Magistrates' CourtsPolitical parties and leaders:Antigua Caribbean Liberation Movement or ACLM
Antigua Labor Party or ABLP [Gaston BROWNE]
Antigua Barbuda True Labor Party or ABTLP [Sharlene SAMUEL]
Barbuda People's Movement or BPM [Trevor WALKER]
Barbuda People's Movement for Change [Arthur NIBBS]
Barbudans for a Better Barbuda [Ordrick SAMUEL]
Democratic National Alliance or DNA [Joanne MASSIAH]
Go Green for Life [Owen GEORGE]
Progressive Labor Movement or PLM
United National Democratic Party or UNDP
United Progressive Party or UPP [Harold LOVELL] (a coalition of ACLM, PLM, UNDP)International organization participation:ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO (subscriber), ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM (observer), OAS, OECS, OPANAL, OPCW, Petrocaribe, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Sir Ronald SANDERS (since 17 September 2015)chancery: 3234 Prospect Street NW, Washington, DC 20007telephone: [1] (202) 362-5122FAX: [1] (202) 362-5525consulate(s) general: Miami, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:the US does not have an embassy in Antigua and Barbuda; the US Ambassador to Barbados is accredited to Antigua and BarbudaFlag description:red, with an inverted isosceles triangle based on the top edge of the flag; the triangle contains three horizontal bands of black (top), light blue, and white, with a yellow rising sun in the black band; the sun symbolizes the dawn of a new era, black represents the African heritage of most of the population, blue is for hope, and red is for the dynamism of the people; the "V" stands for victory; the successive yellow, blue, and white coloring is also meant to evoke the country's tourist attractions of sun, sea, and sandNational symbol(s):fallow deer; national colors: red, white, blue, black, yellowNational anthem:name: Fair Antigua, We Salute Theelyrics/music: Novelle Hamilton RICHARDS/Walter Garnet Picart CHAMBERSnote: adopted 1967; as a Commonwealth country, in addition to the national anthem, "God Save the Queen" serves as the royal anthem (see United Kingdom)
-
Economy :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
Economic overview:
Tourism continues to dominate Antigua and Barbuda's economy, accounting for nearly 60% of GDP and 40% of investment. The dual-island nation's agricultural production is focused on the domestic market and constrained by a limited water supply and a labor shortage stemming from the lure of higher wages in tourism and construction. Manufacturing comprises enclave-type assembly for export with major products being bedding, handicrafts, and electronic components.
Like other countries in the region, Antigua's economy was severely hit by effects of the global economic recession in 2009. The country suffered from the collapse of its largest private sector employer, a steep decline in tourism, a rise in debt, and a sharp economic contraction between 2009 and 2011. Antigua has not yet returned to its pre-crisis growth levels. Barbuda suffered significant damages after hurricanes Irma and Maria passed through the Caribbean in 2017.
Prospects for economic growth in the medium term will continue to depend on tourist arrivals from the US, Canada, and Europe and could be disrupted by potential damage from natural disasters. The new government, elected in 2014 and led by Prime Minister Gaston Browne, continues to face significant fiscal challenges. The government places some hope in a new Citizenship by Investment Program, to both reduce public debt levels and spur growth, and a resolution of a WTO dispute with the US.
GDP real growth rate:2.8% (2017 est.)5.3% (2016 est.)4.1% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 103Inflation rate (consumer prices):2.5% (2017 est.)-0.5% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 127GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:$2.397 billion (2017 est.)$2.334 billion (2016 est.)$2.215 billion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):$1.524 billion (2017 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$26,400 (2017 est.)$25,900 (2016 est.)$24,900 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 60Gross national saving:17.3% of GDP (2017 est.)24.5% of GDP (2016 est.)30.7% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 115GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 1.8% (2017 est.)industry: 20.8% (2017 est.)services: 77.3% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 53.5% (2017 est.)government consumption: 15.2% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 23.9% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 0.1% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 73.9% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -66.5% (2017 est.)Ease of Doing Business Index scores:68.1 (2020)Agriculture - products:cotton, fruits, vegetables, bananas, coconuts, cucumbers, mangoes, sugarcane; livestockIndustries:tourism, construction, light manufacturing (clothing, alcohol, household appliances)Industrial production growth rate:6.8% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Labor force:30,000 (1991)country comparison to the world: 203Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 7%industry: 11%services: 82% (1983 est.)Unemployment rate:11% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 155Population below poverty line:NAHousehold income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: NAhighest 10%: NABudget:revenues: 298.2 million (2017 est.)expenditures: 334 million (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:19.6% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 154Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-2.4% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 112Public debt:86.8% of GDP (2017 est.)86.2% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Fiscal year:1 April - 31 MarchCurrent account balance:-$112 million (2017 est.)$2 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 89Exports:$86.7 million (2017 est.)$56.5 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Exports - partners:Poland 62.2%, Cameroon 9.5%, US 5.1%, UK 4.5% (2017)Exports - commodities:petroleum products, bedding, handicrafts, electronic components, transport equipment, food and live animalsImports:$560 million (2017 est.)$503.4 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 198Imports - commodities:food and live animals, machinery and transport equipment, manufactures, chemicals, oilImports - partners:US 48%, Spain 4.2% (2017)Debt - external:$441.2 million (31 December 2012)$458 million (June 2010)country comparison to the world: 180Exchange rates:East Caribbean dollars (XCD) per US dollar -2.7 (2017 est.)2.7 (2016 est.)2.7 (2015 est.)2.7 (2014 est.)2.7 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
Electricity access:electrification - total population: 100% (2020)Electricity - production:331 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 179Electricity - consumption:307.8 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 99Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Electricity - installed generating capacity:124,000 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 177Electricity - from fossil fuels:97% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 153Electricity - from other renewable sources:3% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 119Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 85Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 89Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Refined petroleum products - consumption:5,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 177Refined petroleum products - exports:91 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 119Refined petroleum products - imports:5,065 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 172Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 99Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 119Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:740,300 Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 175
-
Communications :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 24,403subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 25.15 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 172Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 187,095subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 192.82 (2019 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Telecommunication systems:general assessment: good automatic telephone system with fiber-optic lines; telecom sector contributes heavily to GDP; numerous mobile network competitors licensed, but small and local; govt. to spend EC80 million in 2019 to improve state-owned telecom market competitiveness; legislative amendments extend jurisdiction of its telecom regulator in Barbuda to include mobile services (2020)domestic: fixed-line teledensity roughly 25 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular teledensity is about 193 per 100 persons (2019)international: country code - 1-268; landing points for the ECFS and Southern Caribbean Fiber submarine cable systems with links to other islands in the eastern Caribbean; satellite earth stations - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderatedBroadcast media:state-controlled Antigua and Barbuda Broadcasting Service (ABS) operates 1 TV station; multi-channel cable TV subscription services are available; ABS operates 1 radio station; roughly 15 radio stations, some broadcasting on multiple frequenciesInternet country code:.agInternet users:total: 72,870percent of population: 76% (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 9,261subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 10 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 172
-
Transportation :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 10annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 580,174 (2018)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 290,000 mt-km (2018)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:V2 (2016)Airports:3 (2020)country comparison to the world: 192Airports - with paved runways:total: 2 (2019)2,438 to 3,047 m: 1under 914 m: 1Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 1 (2013)under 914 m: 1 (2013)Roadways:total: 1,170 km (2011)paved: 386 km (2011)unpaved: 784 km (2011)country comparison to the world: 180Merchant marine:total: 780by type: bulk carrier 32, container ship 151, general cargo 534, oil tanker 2, other 61 (2019)country comparison to the world: 31Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Saint John's
-
Military and Security :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
Military and security forces:Antigua and Barbuda Defense Force (ABDF): Coast Guard and the Antigua and Barbuda Regiment (2020)Military and security service personnel strengths:the Antigua and Barbuda Defense Force (ABDF) has approximately 200 active personnel (2019 est.)Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:the ABDF's equipment inventory is limited to small arms, light weapons, and soft-skin vehicles; the Coast Guard maintains ex-US patrol vessels and some smaller boats (2019 est.)Military service age and obligation:18 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; Governor-General has powers to call up men for national service and set the age at which they could be called up (2012)
-
Transnational Issues :: Antigua and Barbuda
-
Disputes - international:
none
Trafficking in persons:current situation: Antigua and Barbuda is a destination and transit country for adults and children subjected to sex trafficking and forced labor; forced prostitution has been reported in bars, taverns, and brothels, while forced labor occurs in domestic service and the retail sectortier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Antigua and Barbuda does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government made no discernible progress in convicting traffickers in 2014 but charged two individuals in separate cases; efforts to convict traffickers have been impeded by a 2014 ruling that found the 2010 anti-trafficking act was unconstitutional because jurisdiction rests with the Magistrate’s Court rather than the High Court; no new prosecutions, convictions, or punishments were recorded in 2014; credible sources have raised concerns about trafficking-related complicity among some off-duty police officers, which could hinder investigations or victims willingness to report offenses; prevention efforts were sustained, but progress in protecting victims was uneven; seven victims were assisted, which was an increase over 2013 (2015)Illicit drugs:considered a minor transshipment point for narcotics bound for the US and Europe; more significant as an offshore financial center